Abstract
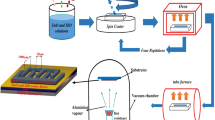
The paper discusses the fabrication of amorphous zinc oxide (a:ZnO)-top gate top contact (the gate is situated on the top and the contacts are taken from the top) thin-film transistor (TFT) using spin-spray pyrolysis (SSP) unit. The solutions of ZnO and poly-vinyl-alcohol (PVA) are synthesized separately by the sol–gel method. The ZnO and PVA solution are coated over glass substrate using the SSP unit and drop-cast technique, respectively. These films are characterized using an optical profilometer, X-ray diffractometer, energy dispersive X-ray analysis, ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometry and Keithley measurement system. The XRD and EDAX measurement confirm the amorphous nature and composition respectively. The thickness of the ZnO and PVA film are 460 nm and 600 nm, respectively. The resistance of ZnO film is 100 KΩ. Using the absorption spectrum, we calculate the bandgap of ZnO and PVA thin film samples which are 3.05 eV and 3.9 eV respectively. The metal–insulator–metal (MIM) structure is fabricated using fluorine-doped tin oxide, PVA and silver paste. The MIM structure is characterized for the electrical parameters such as capacitance and dielectric constant \((\upvarepsilon r)\) which is found to be 0.4 μF and 8 respectively at 40 Hz frequency. The TFT is fabricated by depositing the aluminium as electrode, ZnO as channel layer and and PVA as insulator layer of TFT with different W/L ratios. The TFT parameters such as threshold voltage (Vth), on/off current ratio (Ion/off) and mobility are studied and presented. The results confirm that Vth decreases with the shrinking of channel length. Current ratio Ion/off increases with the reduction of the channel length due to the increase in on-current value.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Bhat, N.K. Naveen, P. Nagaraju, Fabrication of ultrasensitive hexagonal disc structured ZnO thin film sensor to trace nitric oxide. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 00, 1–10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/21870764.2020.1848036
P. Bhat, K NKS, Nagaraju P, , Synthesis and characterization of ZnO-MWCNT nanocomposites for 1-butanol sensing application at room temperature. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 570, 139–147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.06.008
A. Nechibvute, A. Chawanda, P. Luhanga, Piezoelectric energy harvesting devices: an alternative energy source for wireless sensors. Smart Mater. Res. 2012, 1–13 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/853481
I.G. Dimitrov, A.O. Dikovska, P.A. Atanasov et al., Al doped ZnO thin films for gas sensor application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/113/1/012044
R. Kumar, G. Kumar, A. Umar, Zinc oxide nanostructures for NO2 gas—sensor applications: a review. Nano Micro Lett. 23, 97 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-014-0023-3
H.E.A. Huitema, G.H. Gelinck, J.B.P.H. Van Der Putten et al., Active-matrix displays driven by solution processed polymeric transistors. Adv. Mater. 14, 1201–1204 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095(20020903)14:17%3c1201::AID-ADMA1201%3e3.0.CO;2-5
K. Nomura, H. Ohta, A. Takagi et al., Room-temperature fabrication of transparent flexible thin-film transistors using amorphous oxide semiconductors. Nature 432, 488–492 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03090
J. Socratous, K.K. Banger, Y. Vaynzof et al., Electronic structure of low-temperature solution-processed amorphous metal oxide semiconductors for thin-film transistor applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 1873–1885 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201404375
S.T. Meyers, J.T. Anderson, C.M. Hung et al., Aqueous inorganic inks for low-temperature fabrication of ZnO TFTs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 17603–17609 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja808243k
L. Petti, H. Faber, N. Münzenrieder et al., Low-temperature spray-deposited indium oxide for flexible thin-film transistors and integrated circuits. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4914085
D. Fikri, A.H. Yuwono, N. Sofyan et al., The effect of substrate heating temperature upon spray pyrolysis process on the morphological and functional properties of fluorine tin oxide conducting glass. AIP Conf. Proc. 1826, 020003–020011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4979219
J. Liu, D.B. Buchholz, R.P.H. Chang et al., High-performance flexible transparent thin-film transistors using a hybrid gate dielectric and an amorphous zinc indium tin oxide channel. Adv. Mater. 22, 2333–2337 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200903761
G. Adamopoulos, S. Thomas, P.H. Wöbkenberg et al., High-mobility low-voltage ZnO and Li-doped ZnO transistors based on ZrO2 high-k dielectric grown by spray pyrolysis in ambient air. Adv. Mater. 23, 1894–1898 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201003935
V. Chaitra, K.S. Shamala, V. Uma, Construction of versatile advanced micro processor based controller for spray pyrolysis unit and study of characterization of nano crystalline tin oxide (SnO2) thin films. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 3, 77–80 (2011)
G. Adamopoulos, S. Thomas, D.D. Bradley et al., Low-voltage ZnO thin-film transistors based on Y2O3 and Al2O3 high-k dielectrics deposited by spray pyrolysis in air. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3568893͔
A. Dimoulas, G. Vellianitis, A. Travlos et al., Structural and electrical quality of the high-k dielectric Y2O3 on Si (001): dependence on growth parameters. J. Appl. Phys. 92, 426–431 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1483379
E.O. Filatova, A.S. Konashuk, Interpretation of the changing the band gap of Al2O3 depending on its crystalline form: connection with different local symmetries. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 20755–20761 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b06843
D. Afouxenidis, R. Mazzocco, G. Vourlias et al., ZnO-based thin film transistors employing aluminumtitanate gate dielectrics deposited by spray pyrolysis at ambient air. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 7334–7341 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b00561
Omprakash SS, Naveen Kumar SK, Holla R, Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide as a dielectric material for application in TFT’s, in Materials Today: Proceedings (Elsevier Ltd, 2018), pp. 10833–10838
S. Park, C.H. Kim, W.J. Lee et al., Sol-gel metal oxide dielectrics for all-solution-processed electronics. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 114, 1–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2017.01.003
S.S. Omprakash, S.K. Naveen Kumar, PANI/ZnO hybrid nanocomposites TFT for NAND gate application. Mater. Today Proc. 5, 10827–10832 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.12.369
S.S. Omprakash, S.K. Naveenkumar, Fabrication of custom-designed and cost-effective spin-spray pyrolysis unit. Int J EngAdvTechnol 9, 152–158 (2019). https://doi.org/10.35940/ijeat.A1097.109119
S.S. Omprakash, S.K. Naveen Kumar, Fabrication of flexible metal oxide thin film transistor by indigenously developed spray pyrolysis unit, in ECS Transactions (Electrochemical Society Inc., 2019), pp. 129–138
K. Kim, E. Lee, J. Kim et al., Interface engineering for suppression of flat-band voltage shift in a solution-processed ZnO/polymer dielectric thin film transistor. J. Mater. Chem. C 1, 7742–7747 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tc31376j
Y. Jeong, C. Pearson, Y.U. Lee et al., Zinc oxide thin-film transistors fabricated at low temperature by chemical spray pyrolysis. J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4241–4245 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-014-3342-8
M. Esro, G. Vourlias, C. Somerton et al., High-mobility ZnO thin film transistors based on solution-processed hafnium oxide gate dielectrics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 134–141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201402684
J.R. Holt, A. Madan, E.C.T. Harley et al., Observation of semiconductor device channel strain using in-line high resolution X-ray diffraction. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 154502 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4824819
S.Y. Cho, Y.H. Kang, J.Y. Jung et al., Novel zinc oxide inks with zinc oxide nanoparticles for low-temperature, solution-processed thin-film transistors. Chem. Mater. 24, 3517–3524 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm2036234
M. Alrubaiee, M. Xu, S.K. Gayen, R.R. Alfano, Localization and cross section reconstruction of fluorescent targets in ex vivo breast tissue using independent component analysis. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 87–90 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2356024
Acknowledgements
Authors Omprakash S S and Naveen Kumar S K are grateful to the CENSE Department IISc., Bangalore, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal, DST-PURSE laboratory Mangalore University, Mangalore for their Support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omprakash, S.S., Naveen Kumar, S.K. Fabrication of Amorphous ZnO TFT with Tunable Channel Length. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 23, 88–95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-021-00325-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-021-00325-0