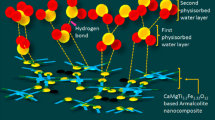
Abstract
The nanocomposites are really promising for industrial, environmental and medical applications. In this work, new types of nanocomposites have been prepared from (PVA–TiO2) nanocomposites doped by SiC nanoparticles for humidity sensor with high sensitivity, flexible, high corrosion resistance and low cost. The experimental and theoretical studies on structural and optical properties of (PVA–TiO2–SiC) nanocomposites have been investigated. The optical microscope and FTIR studies were examined. The optical properties of nanocomposites were examined in wavelength range (220–800) nm. The results showed that the optical absorbance of (PVA–TiO2) nanocomposites increases with increasing of the SiC nanoparticles concentrations. The energy band gap of (PVA–TiO2) nanocomposites decreases while the optical constants increase with the increase in SiC nanoparticles concentrations. The (PVA–TiO2–SiC) nanocomposites tested for humidity sensors at relative humidity range (40–80) RH.%. The experimental results showed that the electrical resistance for (PVA–TiO2–SiC) nanocomposites decreases with increase in relative humidity. The (PVA–TiO2–SiC) nanocomposites have highly sensitivity for relative humidity.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. Yadav, S. Sikarwar, A. Bhaduri, P. Kumar, Characterization and development of opto-electronic humidity sensor using copper oxide thin film. Int. Adv. Res. J. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2, 105–109 (2015)
H. Farahani, R. Wagiran, M.N. Hamidon, Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: a comprehensive review. Sensors 14(5), 7881–7939 (2014)
Y. Wang, Fabrication of relative humidity sensors based on polyimide nanoparticles, Doctoral dissertation, Applied Sciences: School of Engineering Science (2013)
S. Karthick, H.S. Lee, S.J. Kwon, R. Natarajan, V. Saraswathy, Standardization, calibration, and evaluation of tantalum-nano rGO–SnO2 composite as a possible candidate material in humidity sensors. Sensors 16(12), 2079 (2016)
A. Zainelabdin, G. Amin, S. Zaman, O. Nur, J. Lu, L. Hultman, M. Willander, CuO/ZnO nanocorals synthesis via hydrothermal technique: growth mechanism and their application as humidity sensor. J. Mater. Chem. 22(23), 11583–11590 (2012)
T. Fei, K. Jiang, S. Liu, T. Zhang, Humidity sensor based on a cross-linked porous polymer with unexpectedly good properties. RSC Adv. 4(41), 21429–21434 (2014)
M. Hdidar, S. Chouikhi, A. Fattoum, M. Arous, A. Kallel, Influence of TiO2 rutile doping on the thermal and dielectric properties of nanocomposite films based PVA. J. Alloys Compd. 750, 375–383 (2018)
J.H. Jang, J.I. Han, Cylindrical relative humidity sensor based on poly-vinyl alcohol (PVA) for wearable computing devices with enhanced sensitivity. Sens. Actuators A 261, 268–273 (2017)
S.G. Rathod, R.F. Bhajantri, V. Ravindrachary, T. Sheela, P.K. Pujari, J. Naik, B. Poojary, Pressure sensitive dielectric properties of TiO2 doped PVA/CN-Li nanocomposite. J. Polym. Res. 22(2), 6 (2015)
S.B. Aziz, M.A. Rasheed, S.R. Saeed, O.G. Abdullah, Synthesis and characterization of CdS nanoparticles grown in a polymer solution using in situ chemical reduction technique. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 12, 3263–3274 (2017)
T.S. Gaaz, A.B. Sulong, M.N. Akhtar, A.A.H. Kadhum, Properties and applications of polyvinyl alcohol, halloysite nanotubes and their nanocomposites. Molecules 20, 22833–22847 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201219884
D.C. Young, Computational Chemistry: A Practical Guide for Applying Techniques to Real-World Problems (Wiley, New York, 2001)
M. Joshi, R.P. Singh, Cross linking polymers (PVA & PEG) with TiO2 nanoparticles for humidity sensing. Sens. Transducers 110(11), 105 (2009)
M.M. El-Desoky, I.M. Morad, M.H. Wasfy, A.F. Mansour, Structural and optical properties of TiO2/PVA nanocomposites. IOSR J. Appl. Phys. (IOSR-JAP) 9(5), 33–43 (2017)
Z.J. Zhong, Optical Properties and Spectroscopy of Nanomaterials (World Scientific, Singapore, 2009)
S. Ilican, M. Caglar, Y. Caglar, The effect of deposition parameters on the physical properties of CdxZn1-xS films deposited by spray pyrolysis method. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 9(5), 1414–1417 (2007)
T.K. Hamad, R.M. Yusop, B. Abdullah, E. Yousif, Laser induced modification of the optical properties of nano-ZnO doped PVC films. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 787595 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/787595
A.A. Nathan, A. Onoja, A. Amah, Influence of PVA, PVP on crystal and optical properties of europium doped strontium aluminate nanoparticles. Am. J. Eng. Res. 4(4), 85–91 (2015)
S. Suresh, Investigation of the optical and dielectric properties of the urea L-malic acid NLO single crystal. Am. Chem. Sci. J. 3(3), 325–337 (2013)
K.C. Lalithambika, K. Shanthakumari, S. Sriram, Optical properties of CdO thin films deposited by chemical bath method. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 6(5), 3071–3077 (2014)
F.E. Ghodsi, H. Absalan, Comparative study of ZnO thin films prepared by different sol–gel route. Acta Phys. Pol. Ser. A Gen. Phys. 118(4), 659 (2010)
M.A. Gaffar, A.A. El-Fadl, S.B. Anooz, Influence of strontium doping on the indirect band gap and optical constants of ammonium zinc chloride crystals. Physica B 327(1), 43–54 (2003)
N.G. Imam, M.B. Mohamed, Environmentally friendly Zn0.75Cd0.25S/PVA hetero system nanocomposite: UV-stimulated emission and absorption spectra. J. Mol. Struct. 1105, 80–86 (2016)
P. Atkins, J. De Paula, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2011)
E. Kavitha, N. Sundaraganesan, S. Sebastian, Molecular structure, vibrational spectroscopic and HOMO, LUMO studies of 4-nitroaniline by density functional method. Ind. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 48, 20–30 (2010)
R.V. Hoffman, Organic Chemistry: An Intermediate Text (Wiley, New York, 2004)
N.A. Elmarzugi, T. Adali, A.M. Bentaleb, E.I. Keleb, A.T. Mohamed, A.M. Hamza, Spectroscopic characterization of PEG-DNA biocomplexes by FTIR. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 4(8), 6 (2014)
N. Arsalani, H. Fattahi, M. Nazarpoor, Synthesis and characterization of PVP-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an MRI contrast agent. Express Polym. Lett. 4(6), 329–338 (2010)
D. Kumar, S.K. Jat, P.K. Khanna, N. Vijayan, S. Banerjee, Synthesis, characterization, and studies of PVA/Co-Doped ZnO nanocomposite films. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 4(3), 408–416 (2012)
A.P. Indolia, M.S. Gaur, Optical properties of solution grown PVDF-ZnO nanocomposite thin films. J. Polym. Res. 20(1), 43 (2013)
G.A.M. Amin, M.H. Abd-El Salam, Optical, dielectric and electrical properties of PVA doped with Sn nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 1(2), 025024 (2014)
A. Hashim, Q. Hadi, Structural, electrical and optical properties of (biopolymer blend/titanium carbide) nanocomposites for low cost humidity sensors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 11598–11604 (2018)
A. Hashim, Q. Hadi, Synthesis of novel (polymer blend-ceramics) nanocomposites: structural, optical and electrical properties for humidity sensors. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(4), 1394–1401 (2018)
I.R. Agool, K.J. Kadhim, A. Hashim, Fabrication of new nanocomposites:(PVA–PEG–PVP) blend-zirconium oxide nanoparticles) for humidity sensors. Int. J. Plast. Technol. 21(2), 397–403 (2017)
A.M. Abdelghany, E.M. Abdelrazek, D.S. Rashad, Impact of in situ preparation of CdS filled PVP nano-composite. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 130, 302–308 (2014)
A. Hashim, A. Hadi, Novel lead oxide polymer nanocomposites for nuclear radiation shielding applications. Ukr. J. Phys. 62(11), 978–983 (2017)
N.B. Kumar, V. Crasta, B.M. Praveen, Advancement in microstructural, optical, and mechanical properties of PVA (Mowiol 10-98) doped by ZnO nanoparticles. Phys. Res. Int. 2014 (2014)
A. Hashim, I.R. Agool, K.J. Kadhim, Novel of (polymer blend-Fe3O4) magnetic nanocomposites: preparation and characterization for thermal energy storage and release, gamma ray shielding, antibacterial activity and humidity sensors applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29(12), 10369–10394
S.C. Nagaraju, A.S. Roy, J.B. Prasanna Kumar, K.R. Anilkumar, G. Ramagopal, Humidity sensing properties of surface modified polyaniline metal oxide composites. J. Eng. 2014, Article ID 925020 (2014)
A. Hashim, A. Hadi, Novel pressure sensors made from nanocomposites (biodegradable polymers–metal oxide nanoparticles): fabrication and characterization. Ukr. J. Phys. 63(8), 754–758 (2018)
A. Hashim, M.A. Habeeb, Synthesis and characterization of polymer blend-CoFe2O4 nanoparticles as a humidity sensors for different temperatures. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-018-0081-1
R. Srivastava, Effect of poly ethylene glycolon moisture sensing of copper ferrite nanocomposite. Am. J. Sens. Technol. 3(1), 1–4 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University of Babylon-Iraq (College of Education for Pure Sciences, Department of Physics and College of Science, Department of Physics).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, H., Abduljalil, H.M. & Hashim, A. Analysis of Structural, Optical and Electronic Properties of Polymeric Nanocomposites/Silicon Carbide for Humidity Sensors. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 20, 206–217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00100-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-019-00100-2