Abstract
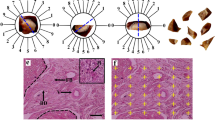
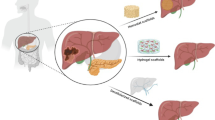
Problems associated with the treatment of liver failure necessitate more research on advanced strategies like cell-based therapy and tissue engineering. Since cell therapy approaches suffer from some limitations, tissue engineering and material science converge the sight onto stem cell-biomaterial based therapy. In this study, the human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAd-MSCs), carrying ectopic fluorescent reporter genes, were encapsulated in the chitosan-β-glycerol phosphate hydroxyethyl cellulose (β-GP-HEC) and transplanted into the right lobe of the intact liver of Wistar rats (as cell-laden scaffolds). In addition, labeled hAd-MSCs were injected into the liver (as scaffold-free groups). All experimental groups were monitored after 15, 45, 90, and 180 days of transplantation. Fluorescence microscopy and histological evaluations were used to monitor the migration and distribution of cells within the two test groups along with their related controls, during the 6-month follow-up. Moreover, the ability of cells to migrate to other tissues was detected by quantitative PCR. Macroscopic inspection during this period showed no evidence of pathological inflammatory responses. Microscopic observations revealed that the injected cells were detectable at the target organ, for at least 6 months in both scaffold and scaffold-free groups. However, the scaffold-free samples showed signs of reduction in cellular augmentation over time. The molecular assessment also confirmed that the application of scaffold in vivo reduced unnecessary cell migration into other organs. In conclusion, the application of cell-seeded β-GP-HEC scaffold not only improved cell survival but also reduced the rate of cellular escape from the target area of transplantation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Marcellin, B.K. Kutala, Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 38, 2–6 (2018)
C. Hu, Z. Wu, L. Li, Pre-treatments enhance the therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cells in liver diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24(1), 40–49 (2020)
A. Sun, W. Gao, T. Xiao, Autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation via the hepatic artery for the treatment of hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis based on the Chinese population. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1), 1–17 (2020)
V. Iansante, R.R. Mitry, C. Filippi, E. Fitzpatrick, A. Dhawan, Human hepatocyte transplantation for liver disease: Current status and future perspectives. Pediatr. Res. 83(1), 232–240 (2018)
L.J. Wang, Y.M. Chen, D. George, F. Smets, E.M. Sokal, E.G. Bremer, H.E. Soriano, Engraftment assessment in human and mouse liver tissue after sex-mismatched liver cell transplantation by real-time quantitative PCR for Y chromosome sequences. Liver Transpl. 8(9), 822–828 (2002)
C. Hu, L. Li, In vitro culture of isolated primary hepatocytes and stem cell-derived hepatocyte-like cells for liver regeneration. Protein Cell 6(8), 562–574 (2015)
M.F. Pittenger et al., Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284(5411), 143–147 (1999)
K. Bieback, S. Kern, H. Klüter, H. Eichler, Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells 22(4), 625–634 (2004)
S.A. Scherjon et al., Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells 22(7), 1338–1345 (2004)
D.T.b. Shih et al., Isolation and characterization of neurogenic mesenchymal stem cells in human scalp tissue. Stem Cells 23(7), 1012–1020 (2005)
P. De Coppi et al., Isolation of amniotic stem cell lines with potential for therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 25(1), 100–106 (2007)
P.A. Zuk, M. Zhu, H. Mizuno, J. Huang, J.W. Futrell, A.J. Katz, P. Benhaim, H.P. Lorenz, M.H. Hedrick, Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 7(2), 211–228 (2001)
K. Furuhashi, N. Tsuboi, A. Shimizu, T. Katsuno, H. Kim, Y. Saka, T. Ozaki, Y. Sado, E. Imai, S. Matsuo, S. Maruyama, Serum-starved adipose-derived stromal cells ameliorate crescentic GN by promoting immunoregulatory macrophages. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 24(4), 587–603 (2013)
Y. Fu, J. Deng, Q. Jiang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, Y. Yao, F. Cheng, X. Chen, F. Xu, M. Huang, Y. Yang, S. Zhang, D. Yu, R.C. Zhao, Y. Wei, H. Deng, Rapid generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells from human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 7(1), 105 (2016)
H. Okura, M. Soeda, M. Morita, M. Fujita, K. Naba, C. Ito, A. Ichinose, A. Matsuyama, Therapeutic potential of human adipose tissue-derived multi-lineage progenitor cells in liver fibrosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 456(4), 860–865 (2015)
N. Liao et al., Poly (dopamine) coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanocluster for noninvasive labeling, tracking, and targeted delivery of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Sci. Rep. 6, 18746 (2016)
M.-J. Chen, Y. Lu, N.E. Simpson, M.J. Beveridge, A.S. Elshikha, M.A. Akbar, H.Y. Tsai, S. Hinske, J. Qin, C.R. Grunwitz, T. Chen, M.L. Brantly, S. Song, In situ transplantation of alginate bioencapsulated adipose tissues derived stem cells (ADSCs) via hepatic injection in a mouse model. PLoS One 10(9), e0138184 (2015)
H. Li, B. Zhang, Y. Lu, M. Jorgensen, B. Petersen, S. Song, Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-based liver gene delivery. J. Hepatol. 54(5), 930–938 (2011)
M. Saheli et al., Generation of transplantable three-dimensional hepatic-patch to improve the functionality of hepatic cells in vitro and in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 29(5), 301–313 (2020)
C. Siltanen, M. Diakatou, J. Lowen, A. Haque, A. Rahimian, G. Stybayeva, A. Revzin, One step fabrication of hydrogel microcapsules with hollow core for assembly and cultivation of hepatocyte spheroids. Acta Biomater. 50, 428–436 (2017)
N. Mobarra, M. Soleimani, F. Kouhkan, Z. Hesari, R. Lahmy, M. Mossahebi-Mohammadi, E. Arefian, Z. Jaafarpour, H. Nasiri, R. Pakzad, R. Tavakoli, P. Pasalar, Efficient differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) derived hepatocyte-like cells on hMSCs feeder. Int. J. Hematol.-Oncol Stem Cell Res. 8(4), 20–29 (2014)
M. Saheli, M. Sepantafar, B. Pournasr, Z. Farzaneh, M. Vosough, A. Piryaei, H. Baharvand, Three-dimensional liver-derived extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes liver organoids function. J. Cell. Biochem. 119(6), 4320–4333 (2018)
J.F. Prudden, P. Migel, P. Hanson, L. Friedrich, L. Balassa, The discovery of a potent pure chemical wound-healing accelerator. Am. J. Surg. 119(5), 560–564 (1970)
R. Muzzarelli, V. Baldassarre, F. Conti, P. Ferrara, G. Biagini, G. Gazzanelli, V. Vasi, Biological activity of chitosan: Ultrastructural study. Biomaterials 9(3), 247–252 (1988)
P.J. VandeVord, H.W.T. Matthew, S.P. DeSilva, L. Mayton, B. Wu, P.H. Wooley, Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a chitosan scaffold in mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59(3), 585–590 (2002)
C. Hoemann et al., Cytocompatible gel formation of chitosan-glycerol phosphate solutions supplemented with hydroxyl ethyl cellulose is due to the presence of glyoxal. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 83(2), 521–529 (2007)
A. Chenite, C. Chaput, D. Wang, C. Combes, M.D. Buschmann, C.D. Hoemann, J.C. Leroux, B.L. Atkinson, F. Binette, A. Selmani, Novel injectable neutral solutions of chitosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials 21(21), 2155–2161 (2000)
C. Hoemann et al., Tissue engineering of cartilage using an injectable and adhesive chitosan-based cell-delivery vehicle. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 13(4), 318–329 (2005)
J. Gimble, F. Guilak, Adipose-derived adult stem cells: Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cytotherapy 5(5), 362–369 (2003)
H. Naderi-Meshkin, K. Andreas, M.M. Matin, M. Sittinger, H.R. Bidkhori, N. Ahmadiankia, A.R. Bahrami, J. Ringe, Chitosan-based injectable hydrogel as a promising in situ forming scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. Cell Biol. Int. 38(1), 72–84 (2014)
A. Seki, Y. Sakai, T. Komura, A. Nasti, K. Yoshida, M. Higashimoto, M. Honda, S. Usui, M. Takamura, T. Takamura, T. Ochiya, K. Furuichi, T. Wada, S. Kaneko, Adipose tissue-derived stem cells as a regenerative therapy for a mouse steatohepatitis-induced cirrhosis model. Hepatology 58(3), 1133–1142 (2013)
A. Haddad-Mashadrizeh et al., Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility evaluation of chitosan-beta glycerol phosphate-hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel on adult rat liver for cell-based therapeutic applications. Int. J. Biomed. Eng. Technol. 12(3), 228–239 (2013)
A. Pirosa, R. Gottardi, P.G. Alexander, R.S. Tuan, Engineering in-vitro stem cell-based vascularized bone models for drug screening and predictive toxicology. Stem Cell Res Ther 9(1), 112 (2018)
M. Kim, I.E. Erickson, A.H. Huang, S.T. Garrity, R.L. Mauck, D.R. Steinberg, Donor variation and optimization of human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis in hyaluronic acid. Tissue Eng. A 24(21-22), 1693–1703 (2018)
T. Liu, J. Li, Z. Shao, K. Ma, Z. Zhang, B. Wang, Y. Zhang, Encapsulation of mesenchymal stem cells in chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for seeding on a novel calcium phosphate cement scaffold. Med. Eng. Phys. 56, 9–15 (2018)
F. Shahabipour, N. Ashammakhi, R.K. Oskuee, S. Bonakdar, T. Hoffman, M.A. Shokrgozar, A. Khademhosseini, Key components of engineering vascularized 3-dimensional bioprinted bone constructs. Transl. Res. 216, 57–76 (2020)
E. Jain, A. Damania, A. Kumar, Biomaterials for liver tissue engineering. Hepatol. Int. 8(2), 185–197 (2014)
L. Xu, S. Wang, X. Sui, Y. Wang, Y. Su, L. Huang, Y. Zhang, Z. Chen, Q. Chen, H. du, Y. Zhang, L. Yan, Mesenchymal stem cell-seeded regenerated silk fibroin complex matrices for liver regeneration in an animal model of acute liver failure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9(17), 14716–14723 (2017)
H. Naderi, M.M. Matin, A.R. Bahrami, Review paper: critical issues in tissue engineering: biomaterials, cell sources, angiogenesis, and drug delivery systems. J. Biomater. Appl. 26(4), 383–417 (2011)
M.A. Rizzo, M.W. Davidson, D.W. Piston, Fluorescent protein tracking and detection: Fluorescent protein structure and color variants. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2009(12), pdb. top63 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ehsan Bahramzadeh and Mohammadmahdi Esmail-Jami for their editing suggestions, as well as Hassan Tamadonipour, Mohammad Nakhaei, and Dr. Moein Farschian for their excellent technical assistance.
Funding
The study was financed by grants from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad and Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) and performed in the Institute of Biotechnology, Ferdowsi University of Mashhad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHM, MMM, and ARB were responsible for the design of experiments and data acquisition, and data interpretation; FS, SE, and AZ contributed to data analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors declare that the research was conducted with the approval from Ferdowsi University of Mashhad Ethics Committee (IR.UM.REC.1399.069). Written informed consents were obtained from the patients.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad-Mashadrizeh, A., Matin, M.M., Shahabipour, F. et al. Effects of chitosan-glycerol phosphate hydrogel on the maintenance and homing of hAd-MSCs after xenotransplantation into the rat liver. emergent mater. 5, 519–528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00167-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00167-9