Abstract
Ion exchange is widely used for the removal of selected ions from water streams. Within oil & gas, one application is boiler feedwater treatment to remove hardness, i.e. calcium and magnesium. Weak acid cation (WAC) resins are typically used and advances in material science, polymer chemistry and manufacturing methods have resulted in new resins being introduced to the market. These new resins can lower operating costs through higher capacity, reduced chemical consumption during regeneration or improved physical properties.
In this research, the performance of a WAC resin used for boiler feedwater treatment in oil & gas operations (resin A) was compared with two new commercial resins (resins B & C).
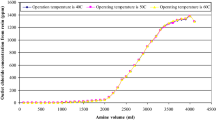
The results indicated that resin B had the highest operational capacity in comparison to A & C. During regeneration, resin B was the most efficient with 0.43 meq of calcium and magnesium removed from the feed per meq of HCl consumed during regeneration, slightly higher than resins A & C at 0.38 and 0.30 meq/meq respectively. All three resins demonstrated preferential affinity for calcium over magnesium. As breakthrough approached, previously adsorbed magnesium ions were released back to the water resulting in a spike in effluent magnesium that was ≈3× higher than in the feed stream. In full-scale systems, breakthrough can be determined by measuring only the effluent magnesium concentration which can be more sensitive parameter than total hardness and/or calcium.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Clifford, Water Qual. Treat. 4, 561 (1999)
C.J. Brown, C.J. Brown, M. Sheedy, M. Sheedy, System 2 (2002)
R.J. Jan, T.G. Reed Jr., SPE Prod. Engineeering (1992)
Q. Jiang, J. Rentschler, R. Perrone, K. Liu, J. Membr. Sci. 431, 55 (2013)
S. Adham, A. Hussain, J. Minier-Matar, A. Janson, R. Sharma, Desalination 440, 2 (2018)
G.J. Millar, S.J. Couperthwaite, C.D. Moodliar, Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 57, 669 (2016)
Y. Hu, T.H. Boyer, Water Res. 115, 40 (2017)
J.N. Apell, T.H. Boyer, Water Res. 44, 2419 (2010)
M. Arias-Paic, K.M. Cawley, S. Byg, F.L. Rosario-Ortiz, Water Res. 88, 981 (2016)
J.A. Korak, R. Huggins, M. Arias-Paic, Water Res. 118, 141 (2017)
A.M. Bergquist, J.K. Choe, T.J. Strathmann, C.J. Werth, Water Res. 96, 177 (2016)
S. Ebrahimi, D.J. Roberts, Water Res. 88, 766 (2016)
K.A. Landry, P. Sun, C.H. Huang, T.H. Boyer, Water Res. 68, 510 (2015)
W. Beita-Sandí, T. Karanfil, Water Res. 124, 20 (2017)
M.D. LeVan, G. Carta, C.M. Yon, Energy 16, 17 (1997)
D. Reichenberg, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75, 589 (1953)
G.E. Boyd, A.W. Adamson, L.S. Myers Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 69, 2836 (1947)
I.M. Abrams, J.R. Millar, React. Funct. Polym. 35, 7 (1997)
Q. Li, L. Fu, Z. Wang, A. Li, C. Shuang, C. Gao, J. Clean. Prod. 165, 801 (2017)
Y. Sun, P. Zuo, J. Luo, R.P. Singh, J. Environ. Sci. 54, 40 (2017)
G.M. Hale, M.R. Querry, Appl. Opt. 12, 555 (1973)
S.N. Kasarova, N.G. Sultanova, C.D. Ivanov, I.D. Nikolov, Opt. Mater. (Amst) 29, 1481 (2007)
H. M. F. Freundlich and others, J. Phys. Chem 57, 1100 (1906)
G.J. Millar, G.L. Miller, S.J. Couperthwaite, S. Papworth, Sep. Purif. Technol. 163, 79 (2016)
H.C. Thomas, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 66, 1664 (1944)
H.C. Thomas, Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 49, 161 (1948)
R.S. Juang, H.C. Kao, W. Chen, Sep. Purif. Technol. 49, 36 (2006)
M. Kalaruban, P. Loganathan, W.G. Shim, J. Kandasamy, G. Naidu, T.V. Nguyen, S. Vigneswaran, Sep. Purif. Technol. 158, 62 (2016)
S. Belaïd, G. Boiteux, P. Cassagnau, Rheol. Acta 52, 75 (2013)
DOW Liquid Separations, March (2006)
K.W. Pepper, D. Reichenberg, D.K. Hale, J. Chem. Soc. 3129 (1952)
H.P. Gregor, F. Gutoff, J. Bregman, J. Colloid Sci. 6, 245 (1951)
H. Ashjian, Q. N. Le, D. O. Marler, J. Shim, and S. S. Wong, (1991)
Y. Marcus, Chem. Rev. 88, 1475 (1988)
L.P. Mazur, T.A. Pozdniakova, D.A. Mayer, R.A.R. Boaventura, V.J.P. Vilar, Water Res. 90, 354 (2016)
J.R. Couper, W.R. Penney, J.R. Fair, S.M. Walas, J.R. Couper, W.R. Penney, J.R. Fair, S.M. Walas, Chem. Process Equip, 529–559 (2012)
V.J. Inglezakis, A. Zorpas, in Ion Exch. Technol. I Theory Mater, ed. by I. DR, M. Luqman. (Springer, Netherlands, 2012), pp. 121–161
Acknowledgements
The research team would like to acknowledge Samir Gharfeh, Aida Rafat and Nabin Upadhyay for their feedback and contributions to the project, as well as the resin manufacturers for providing the resins used on this study.
This evaluation is a contribution to science and does not constitute an endorsement of any particular vendor’s resins.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janson, A., Minier-Matar, J., Al-Shamari, E. et al. Evaluation of new ion exchange resins for hardness removal from boiler feedwater. emergent mater. 1, 77–87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-018-0006-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-018-0006-0