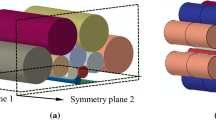
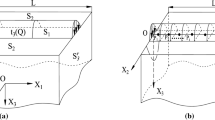
Abstract
To achieve stable rolling, the influence of a tension mechanism of a large diameter ratio roll system on the rolling process of a strip flatness electromagnetic control rolling mill is studied. Through the analysis of the rolling deformation zone, the deformation zone composition form of a large diameter ratio roll system and a calculation formula of neutral angle under tension are proposed. To analyze the effect of front and post tensions on the rolling characteristic and the strip flatness control characteristic, a three-dimensional rolling finite element (FE) model of a large diameter ratio roll system with the function of roll profile electromagnetic control is established by FE software and verified by a strip flatness electromagnetic control rolling mill. Based on the model, the strip thickness characteristic, metal transverse flow, strip flatness state, and adjustment range of the loaded roll gap are analyzed for different front and post tensions setting values. The results show that changing the front or post tension setting values can improve the single-pass reduction rate of a large diameter ratio roll system and have little effect on the flatness control ability of the strip flatness electromagnetic control rolling mill.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a 0, a 2, a 4 :
-
Polynomial coefficients of loaded roll gap shape curve
- B :
-
Strip width value (mm)
- C x :
-
Strip crown
- C w :
-
Electromagnetic control roll crown (μm)
- C w2 :
-
Quadratic crown
- C w4 :
-
Quartic crown
- D w(x):
-
Worn roll profile
- D v(x):
-
Variation of roll profile
- E d :
-
Edge drop value
- F :
-
Bending force (kN)
- F r :
-
Rolling force (kN)
- f :
-
Front slip value
- g(x):
-
Loaded roll gap shape curve
- H :
-
Inlet strip thickness (mm)
- h :
-
Outlet strip thickness (mm)
- Δh :
-
Single-pass reduction (mm)
- Δh 1 :
-
Equivalent reduction of upper working roll (mm)
- Δh 2 :
-
Equivalent reduction of lower working roll (mm)
- h c :
-
Strip thickness of middle point of strip
- h D :
-
Strip edge thickness
- h x :
-
Strip thickness of side marking point
- h xd :
-
Strip thickness of marking point of transmission side
- h xw :
-
Strip thickness of marking point of operating side
- h γ 1 :
-
Strip thickness of neutral surface of back slip zone (mm)
- h γ 2 :
-
Strip thickness of neutral surface of front slip zone (mm)
- l :
-
Length of rolling deformation zone (mm)
- p :
-
Contact stress on surface of contact zone (MPa)
- p(x):
-
Distribution function of rolling force (MPa)
- R 1 :
-
Roll radius of upper working roll (mm)
- R 2 :
-
Roll radius of lower working roll (mm)
- T F :
-
Front tension setting value (MPa)
- T P :
-
Post tension setting value (MPa)
- V 0 :
-
Linear velocity of lower working roll (m s−1)
- V 1 :
-
Exit velocity of rolled piece (m s−1)
- V 2 :
-
Entrance velocity of rolled piece (m s−1)
- V 3 :
-
Linear velocity of upper working roll (m s−1)
- V γ 1 :
-
Metal flow velocity on neutral surface of back slip zone (m s−1)
- V γ 2 :
-
Metal flow velocity on neutral surface of front slip zone (m s−1)
- x :
-
Strip width coordinate, [− B/2, B/2]
- ΣX :
-
Resultant force in horizontal direction
- ΣX F :
-
Sum of horizontal forces in front slip zone
- ΣX C :
-
Sum of horizontal forces in cross shear zone
- ΣX B :
-
Sum of horizontal forces in back slip zone
- ΣY :
-
Resultant force in vertical direction
- ΣY F :
-
Sum of vertical forces in front slip zone
- ΣY C :
-
Sum of vertical forces in cross shear zone
- ΣY B :
-
Sum of vertical forces in back slip zone
- α 1 :
-
Bite angle of upper working roll (°)
- α 2 :
-
Bite angle of lower working roll (°)
- β :
-
Back slip value
- γ 1 :
-
Neutral angle of upper working roll (°)
- γ 2 :
-
Neutral angle of lower working roll (°)
- τ :
-
Shear stress on surface of contact zone (MPa)
- μ :
-
Friction coefficient
- σ 1 :
-
Front tension preset value
- σ 2 :
-
Post tension preset value
References
T. Yang, Q. Chen, Y. Feng, Y. Hai, F. Du, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 120 (2022) 5741–5754.
Y. Zheng, T. Yang, T. Qu, F. Du, Z. Xu, Iron and Steel 56 (2021) No. 5, 80–90+112.
T. Yang, Y. Bai, Z. Lei, Z. Xu, F. Du, Iron and Steel 57 (2022) No. 5, 81–89.
M. Borghesi, G. Chiozzi, in: Proceedings of International Conference on Steel Rolling, ICSR Tokyo, Japan, 1980, pp. 760–771.
M. Okado, T. Arimura, F. Fujita, H. Kuwamoto, Y. Sakaguchi, M. Mikami, Iron and Steel Engineer 59 (1982) 25–29.
T. Tarnopolskaya, W.Y.D. Yuen, ISIJ Int. 45 (2005) 1316–1321.
M.S. Dyshel’, Int. Appl. Mech. 42 (2006) 589–592.
X. Wang, Y. Liu, X. Zhao, X. Jin, Steel Rolling 23 (2007) No. 6, 12–14.
E.A. Maksimov, Metallurgist 54 (2011) 753–757.
S. Abdelkhalek, H. Zahrouni, N. Legrand, M. Potier-Ferry, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 104 (2015) 126–137.
E.A. Garber, A.E. Aleshin, S.S. Degtev, A.I. Traino, Russ. Metall. 2016 (2016) 1108–1111.
Z.K. Ren, H. Xiao, C. Yu, J. Wang, Procedia Eng. 207 (2017) 1326–1331.
Y.M. Hwang, G.Y. Tzou, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2 (1993) 597–606.
Y.M. Hwang, G.Y. Tzou, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 4 (1995) 265–274.
Y.M. Hwang, G.Y. Tzou, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 39 (1997) 289–303.
S.H. Zhang, D.W. Zhao, C.R. Gao, G.D. Wang, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 65 (2012) 168–176.
M. Salimi, M. Kadkhodaei, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 150 (2004) 215–222.
Y. Feng, W. Liu, T. Yang, F. Du, J. Sun, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 104 (2019) 2925–2937.
W. Liu, Y. Feng, T. Yang, F. Du, J. Sun, Appl. Therm. Eng. 145 (2018) 277–286.
Y. Feng, W. Liu, T. Yang, F. Du, J. Sun, Metall. Res. Technol. 116 (2019) 405.
T. Yang, Y. Wang, J. Liu, F. Du, Z. Xu, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 114 (2021) 1065–1074.
T. Yang, J. Liu, H. Zhou, Z. Xu, F. Du, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 116 (2021) 403–415.
M. Stolbchenko, O. Grydin, A. Samsonenko, V. Khvist, M. Schaper, Forsch. Im Ingenieurwesen 78 (2014) 121–130.
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (Grant No. E2021203129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Ts., Yuan, Th., Sun, Wq. et al. Theoretical and numerical research on effect of tension mechanisms in strip flatness electromagnetic control rolling mills. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-024-01195-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-024-01195-5