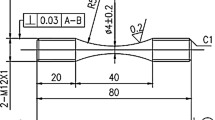
Abstract
Spring steel is an indispensable basic part manufacturing material in mechanical equipment, which is widely used in transportation tools such as automobiles, railways, construction machinery and other industries. The effects of rare earth (RE) on inclusions, microstructure, carbides and impact toughness of 50CrV spring steel were studied by means of optical microscope, scanning electron microscope, transmission electron microscope and impact tester. The results show that the addition of rare earth can modify the main MnS and Al2O3 inclusions in steel to form spherical or near-spherical rare earth inclusions, and the size of inclusions is significantly reduced. In the quenched structure, the size of martensite slab becomes smaller and the structure is refined. After tempering, the carbide changes from sheet to ellipse, which makes it easier for spring steel to form stress concentration cracks under stress. VC becomes finer and more dispersed, which leads to better pinning of grain boundaries and smaller grain sizes. The impact toughness of 50CrV-RE spring steel increased from 21 to 41 J by 95% due to the improvement of inclusions, microstructure and carbides by rare earth. It is possible to improve the strength and toughness of spring steel for the improvement of railway running speed and the development of vehicle lightweight in China.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. Wang, X. Liu, F. Xie, C. Lai, H. Li, Q. Zhang, JOM 70 (2018) 2385–2391.
C.L. Zhang, Y.Z. Liu, C. Jiang, J.F. Xiao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 6, 49–53.
S. Liu, D. Liu, S. Liu, Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 52 (2010) 57–60.
W.J. Nam, C.S. Lee, D.Y. Ban, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 289 (2000) 8–17.
V.R.M. Gonçalves, B. Podgornik, V. Leskovšek, G.E. Totten, L. de Campos Franceschini Canale, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 28 (2019) 769–775.
O.P. Ostash, R.V. Chepil’, L.I. Markashova, V.I. Hrybovs’ka, V.V. Kulyk, O.M. Berdnikova, Mater. Sci. 53 (2018) 684–690.
L. Kucerova, Metals 7 (2017) 537.
L. Xu, L. Chen, W. Sun, Vacuum 154 (2018) 322–332.
Y. Harada, K. Mori, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 162–163 (2005) 498–503.
Z.F. Luo, Y.L. Liang, S.L. Long, Y. Jiang, Z.L. Wu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 690 (2017) 225–232.
B. Podgornik, V. Leskovšek, M. Godec, B. Senčič, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 599 (2014) 81–86.
B. Podgornik, M. Torkar, J. Burja, M. Godec, B. Senčič, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 638 (2015) 183–189.
L. Zhou, J. Liang, X.H. Wang, P. Zhang, X.F. Shi, J. Iron Steel Res. 29 (2017) 626–636.
K. Xu, L. Xiao, Iron and Steel 47 (2012) No. 10, 1–13.
C. Yang, Y. Luan, D. Li, Y. Li, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 (2019) 1298–1308.
H. Yan, Y. Hu, D. Zhao, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018 (2018) 1–9.
H. Liu, P. Fu, H. Liu, C. Sun, J. Gao, D. Li, Metals 7 (2017) 436.
X. Zhang, W. Wei, L. Cheng, J. Liu, K. Wu, M. Liu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 475 (2019) 83–93.
L. Chen, X. Ma, L. Wang, X. Ye, Mater. Des. 32 (2011) 2206–2212.
X. Zhou, X. Yin, F. Fang, J. Jiang, W. Zhu, J. Rare Earths 30 (2012) 1075–1078.
H.G. Fu, Q. Xiao, Y.X. Li, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 395 (2005) 281–287.
M.A. Hamidzadeh, M. Meratian, A. Saatchi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 571 (2013) 193–198.
Q.C. Zhou, Y.J. Pan, X.J. Wu, D.K. Chen, Chinese Rare Earths 28 (2007) No. 6, 66–70.
J.P. Buban, K. Matsunaga, J. Chen, N. Shibata, W.Y. Ching, T. Yamamoto, Y. Ikuhara, Science 311 (2006) 212–215.
Q.X. Yang, Z.Q. Cui, B. Liao, M. Yao, Journal of Rare Earths 17 (1999) 46–48.
R.M. Geng, J. Li, C.B. Shi, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29 (2022) 1659–1668.
Y. Cao, X. Wan, Y. Hou, C. Niu, Y. Liu, G. Li, Steel Res. Int. 90 (2019) 1900084.
N. Yan, S. Yu, Y. Chen, J. Rare Earths 35 (2017) 203–210.
C. Gallo, J.A. Álvarez, F. Gutiérrez-Solana, J.A. Polanco, European Structural Integrity Society 30 (2002) 271–278.
S. Cvetkovski, European Structural Integrity Society 30 (2002) 95–102.
B.Y. Chen, Y.W. Shi, Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 38 (1989) 275–292.
C.S. Wiesner, Int. J. Press. Vessels Pip. 69 (1996) 185–196.
A.F. Gourgues, H.M. Flower, T.C. Lindley, Mater. Sci. Technol. 16 (2000) 26–40.
M. Calcagnotto, D. Ponge, E. Demir, D. Raabe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527 (2010) 2738–2746.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52101165).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, Cl., Yang, Cy., Liu, P. et al. Effects of rare earth elements on inclusions, microstructure and impact toughness of spring steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 933–944 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01055-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01055-8