Abstract
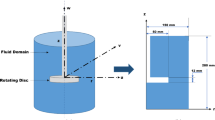
A mathematical model accounting for unsteady mass transfer across interface of a stationary iron droplet immersed into molten slag was established through the volume of fluid coupled with level set method. The Marangoni effect induced by mass transfer was reproduced successfully, and the hydrodynamic instability phenomena at the interface, such as the Marangoni convection flow, the evolution of the interfacial tension during the mass transfer, and the influence of Marangoni effect on the mass transfer rate, were revealed. The results show that the Marangoni convection flow develops quickly and behaves as an ordered structure in the forms of four pairs of the convection cell at the edge of the droplet once the oxygen transfer across the interface starts. The average convection flow velocity along the interface is high, even more than 0.025 m/s, depending on the droplet diameter, which facilitates the mass transfer. The Marangoni convection flow of the large droplet develops more easily than that of the small droplet, and the larger the droplet diameter is, the higher the convection flow velocity and the mass transfer rate are. Moreover, it is shown that the droplet diameter influences the impacting region of the Marangoni convection flow and its duration period.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.V. Riboud, L.D. Lucas, Can. Metall. Quart. 20 (1981) 199–208.
Y. Chung, A.W. Cramb, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31 (2000) 957–971.
A. Sharan, A.W. Cramb, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 26 (1995) 87–94.
T. Tanaka, H. Goto, M. Nakamoto, M. Suzuki, M. Hanao, M. Zeze, H. Yamamura, T. Yoshikawa, ISIJ Int. 56 (2016) 944–952.
P. Ni, T. Tanaka, M. Suzuki, M. Nakamoto, P.G. Jönsson, ISIJ Int. 58 (2018) 1979–1988.
M.A. Rhamdhani, K.S. Coley, G.A. Brooks, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 36 (2005) 219–227.
C. Solans, D. Morales, M. Homs, Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 22 (2016) 88–93.
T. Fabritius, J. Riipi, M. Järvinen, O. Mattila, E.P. Heikkinen, A. Kärnä, J. Kurikkala, P. Sulasalmi, J. Härkki, ISIJ Int. 50 (2010) 797–803.
M.A. Rhamdhani, G.A. Brooks, in: Indonesian Process Metallurgy Conference and Workshop (IPM), Indonesian, Bandung, 2008, pp. 1–12.
M.A. Rhamdhani, K.S. Coley, G.A. Brooks, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 36 (2005) 591–604.
M.A. Rhamdhani, G.A. Brooks, K.S. Coley, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 37 (2006) 1087–1091.
S. Spooner, A.N. Assis, J. Warnett, R. Fruehan, M.A. Williams, S. Sridhar, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47 (2016) 2123–2132.
S.M. Kang, D.Y. Kim, J.S. Kim, H.G. Lee, ISIJ Int. 43 (2003) 1683–1690.
A. Jakobsson, S. Du, S. Seetharaman, N.N. Viswanathan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31 (2000) 973–980.
L. Muhmood, N.N. Viswanathan, S. Seetharaman, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 42 (2011) 460–470.
W. Cao, L. Muhmood, S. Seetharaman, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43 (2012) 363–369.
A.N. Assis, J. Warnett, S. Spooner, R.J. Fruehan, M.A. Williams, S. Sridhar, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 46 (2015) 568–576.
J.U. Brackbill, D.B. Kothe, C. Zemach, J. Comput. Phys. 100 (1992) 335–354.
M. Sussman, P. Smereka, S. Osher, J. Comput. Phys. 114 (1994) 146–159.
S.C. Park, H. Gaye, H.G. Lee, Ironmak. Steelmak. 36 (2009) 3–11.
D. Darmana, N.G. Deen, J.A.M. Kuipers, Chem. Eng. Technol. 29 (2006) 1027–1033.
Y. Renardy, M. Renardy, J. Comput. Phys. 183 (2002) 400–421.
Z.S. Mao, J. Chen, Chem. Eng. Sci. 59 (2004) 1815–1828.
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904062), the Fundamental Research Funds of the Central Universities of China (No. N2225021), and the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Liaoning Institute of Science and Technology (No. 2107B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Mm., Wu, Zq., Li, L. et al. Numerical simulation of Marangoni effect induced by species transfer across iron droplet–molten slag interface. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 1109–1116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00977-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00977-7