Abstract
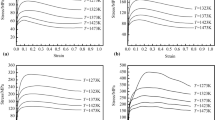
Primary γ′ phase instead of carbides and borides plays an important role in suppressing grain growth during solution at 1433 K of Ni-based FGH98 superalloys. Results illustrate that as-fabricated FGH98 superalloy has equiaxed grain structure, and after heat treatment, grains remain equiaxed but grow larger. In order to clarify the effects of the size and volume fraction of the primary γ′ phase on the grain growth during heat treatment, a 2D cellular automata (CA) model was established based on the thermal activation and the lowest energy principle. The CA results are compared with the experimental results and show a good fit with an error less than 10%. Grain growth kinetics are depicted, and simulations in real time for various sizes and volume fractions of primary γ′ particles work out well with the Zener relation. The coefficient n value which reflects the pinning ability in Zener relation is theoretically calculated, and its minimum value is 0.23 when the radius of primary γ′ phase is 2.8 μm.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.S.S. Kumar, T. Raghu, P.P. Bhattacharjee, G. Appa Rao, U. Borah, Mater. Charact. 146 (2018) 217–236.
J.C. Williams, E.A. Starke, Acta Mater. 51 (2003) 5775–5799.
C. Dong, Z. Liu, Z. Chen, H. Bao, X. Wang, Z. Liu, J. Alloy. Compd. 825 (2020) 154106.
T. Osada, Y. Gu, N. Nagashima, Y. Yuan, T. Yokokawa, H. Harada, Acta Mater. 61 (2013) 1820–1829.
Y. Brechet, M. Militzer, Scripta Mater. 52 (2006) 1299–1303.
L. Du, S. Yang, P. Zhang, H. Du, Compos. Interfaces 25 (2018) 357–368.
K. Song, M. Aindow, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 479 (2008) 365–372.
T.M. Rodgers, J.D. Madison, V. Tikare, Comput. Mater. Sci. 135 (2017) 78–89.
D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 48 (2000) 1617–1628.
C.S. Zhu, S. Xu, L. Feng, D. Han, K.M. Wang, Comput. Mater. Sci. 160 (2019) 53–61.
I. Toda-Caraballo, C. Capdevila, G. Pimentel, C.G. DeAndres, Comput. Mater. Sci. 68 (2013) 95–106.
M. Bakhtiari, M. Seyed Salehi, Comput. Mater. Sci. 149 (2018) 1–13.
M.S. Chen, Z.H. Zou, Y.C. Lin, H.B. Li, G.Q. Wang, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 35 (2019) 1403–1411.
O. Zinovieva, V. Romanova, R. Balokhonov, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 832 (2022) 142447.
Z. Li, J. Wang, H. Huang, J. Alloy. Compd. 791 (2019) 411–422.
Y. He, H. Ding, L. Liu, K. Shin, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 429 (2006) 236–246.
P. Nie, O.A. Ojo, Z. Li, Acta Mater. 77 (2014) 85–95.
C. Zheng, N. Xiao, D. Li, Y. Li, Comput. Mater. Sci. 44 (2008) 507–514.
V. Marx, F.R. Reher, G. Gottstein, Acta Mater. 47 (1999) 1219–1230.
Y.X. Liu, Y.C. Lin, H.B. Li, D.X. Wen, X.M. Chen, M.S. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 626 (2015) 432–440.
Y.J. Lan, D.Z. Li, Y.Y. Li, Acta Mater. 52 (2004) 1721–1729.
D. Raabe, L. Hantcherli, Comput. Mater. Sci. 34 (2005) 299–313.
F. Han, B. Tang, H. Kou, J. Li, Y. Feng, Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 23 (2015) 065010.
D. Weygand, Y. Bréchet, J. Lépinoux, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 292 (2000) 34–39.
G. Huang, G.Q. Liu, M. Feng, M. Zhang, B. Hu, H. Wang, J. Alloy. Compd. 747 (2018) 1062–1072.
S. Liu, Y.C. Shin, Comput. Mater. Sci. 183 (2020) 109889.
E.A. Holm, N. Zacharopoulos, D.J. Srolovitz, Acta Mater. 46 (1998) 953–964.
M. Wang, Y. Yin, J. Zhou, H. Nan, T. Wang, W. Li, Canad. J. Phys. 94 (2016) 1353–1364.
X. Song, G. Liu, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 14 (1998) 506–510.
K. Song, M. Aindow, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38 (2007) 1–6.
R. Li, E.R. Homer, C. Hong, Y. Zhang, D.J. Jensen, Scripta Mater. 211 (2022) 114489.
B.R. Patterson, Y. Liu, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 23 (1992) 2481–2482.
O. Hundert, E. Nes, N. Ryum, Acta Metall. 37 (1989) 129–133.
M.P. Anderson, G.S. Grest, R.D. Doherty, K. Li, D.J. Srolovitz, Scripta Metall. 23 (1989) 753–758.
A. Mallick, Comput. Mater. Sci. 67 (2013) 27–34.
C. Schwarze, R.D. Kamachali, I. Steinbach, Acta Mater. 106 (2016) 59–65.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by National Major Science and Technology Project (2017-VI-0009-0079) and Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (2020B0301030001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interests in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Yl., Liu, Ss., Lu, Rg. et al. Cellular automata simulation of grain growth of powder metallurgy Ni-based superalloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 838–848 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00921-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-00921-9