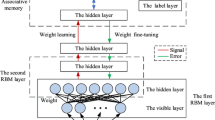
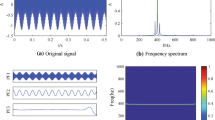
Abstract
Online monitoring and diagnosis of production processes face great challenges due to the nonlinearity and multivariate of complex industrial processes. Traditional process monitoring methods employ kernel function or multilayer neural networks to solve the nonlinear mapping problem of data. However, the above methods increase the model complexity and are not interpretable, leading to difficulties in subsequent fault recognition/diagnosis/location. A process monitoring and diagnosis method based on the free energy of Gaussian–Bernoulli restricted Boltzmann machine (GBRBM-FE) was proposed. Firstly, a GBRBM network was established to make the probability distribution of the reconstructed data as close as possible to the probability distribution of the raw data. On this basis, the weights and biases in GBRBM network were used to construct F statistics, which represents the free energy of the sample. The smaller the energy of the sample is, the more normal the sample is. Therefore, F statistics can be used to monitor the production process. To diagnose fault variables, the F statistic for each sample was decomposed to obtain the Fv statistic for each variable. By analyzing the deviation degree between the corresponding variables of abnormal samples and normal samples, the cause of process abnormalities can be accurately located. The application of converter steelmaking process demonstrates that the proposed method outperforms the traditional methods, in terms of fault monitoring and diagnosis performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.W. Xu, Quality control theory and method of metallurgical production process, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2015.
Z. Wu, M. Shamsuzzaman, J. Manuf. Syst. 24 (2005) 302–314.
A. Salmasnia, A. Rahimi, B. Abdzadeh, Neural Comput. Appl. 31 (2019) 1173–1194.
J.F. MacGregor, H. Yu, S. García Muñoz, J. Flores-Cerrillo, Comput. Chem. Eng. 29 (2005) 1217–1223.
S. Han, N. Mannan, D.C. Stein, K.R. Pattipati, G.M. Bollas, J. Manuf. Syst. 61 (2021) 45–53.
X. Xiu, Y. Yang, L. Kong, W. Liu, J. Process Control. 92 (2020) 212–219.
L. Shi, Z.L. Li, T. Yu, J.P. Li, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 10, 13–16.
J. Kivinen, A.J. Smola, R.C. Williamson, IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 52 (2004) 2165–2176.
M. Onel, C.A. Kieslich, Y.A. Guzman, C.A. Floudas, E.N. Pistikopoulos, Comput. Chem. Eng. 115 (2018) 46–63.
L.M. Liu, M.X. Chu, R.F. Gong, X.Y. Qi, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 1407–1419.
C. Gao, M.G. Shen, X.P. Liu, N.N. Zhao, M.X. Chu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27 (2020) 42–54.
Q. Dong, R. Kontar, M. Li, G. Xu, J. Xu, J. Manuf. Syst. 53 (2019) 291–304.
Q. Qian, X. Fang, J. Xu, M. Li, J. Manuf. Syst. 61 (2021) 375–390.
R. Fezai, M. Mansouri, O. Taouali, M. F. Harkat, N. Bouguila, J. Process Control. 61 (2018) 1–11.
O. Taouali, I. Elaissi, H. Messaoud, Neural Comput. Appl. 21 (2012) 161–169.
B. Cai, X. Sun, J. Wang, C. Yang, Z. Wang, X. Kong, Z. Liu, Y. Liu, J. Manuf. Syst. 57 (2020) 148–157.
M. Yuan, P. Zhou, M.L. Li, R.F. Li, H. Wang, T.Y. Chai, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) 487–495.
Y. Tang, X. Wu, IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26 (2017) 1509–1520.
Y. Du, D. Du, Comput. Chem. Eng. 115 (2018) 1–21.
K. Zhong, M. Han, T. Qiu, B. Han, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31 (2020) 1581–1591.
X. Xie, W. Sun, K.C. Cheung, IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 63 (2016) 2587–2594.
K.X Peng, L. Ma, K. Zhang, Acta Autom. Sin. 43 (2017) 349–365.
P. Wu, S. Lou, X. Zhang, J. He, Y. Liu, J. Gao, IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 17 (2021) 3324–3334.
J.H. Cho, J.M. Lee, S. Wook Choi, D. Lee, I.B. Lee, Chem. Eng. Sci. 60 (2005) 279–288.
S.W. Choi, C. Lee, J.M. Lee, J.H. Park, I.B. Lee, Chemometrics Intell. Lab. Syst. 75 (2005) 55–67.
G. Li, S.J. Qin, Y. Ji, D. Zhou, Control Eng. Practice 18 (2010) 1211–1219.
C.F. Alcala, S.J. Qin, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 49 (2010) 7849–7857.
K. Demertzis, L. Iliadis, E. Pimenidis, P. Kikiras, Neural Comput. Appl. 34 (2022) 15207–15220.
G.E. Hinton, in: G. Montavon, G.B. Orr, K.R. Müller (Eds.), Neural Networks: Tricks of the Trade, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2012, pp. 599–619.
G.E. Hinton, Neural Comput. 14 (2002) 1771–1800.
J. Yang, W. Bao, X. Li, Y. Liu, neural Comput. Appl. 34 (2022) 9885–9899.
H. Huang, L. Zhao, H. Huang, S. Guo, IEEE Commun. Mag. 58 (2020) 40–46.
H. Huang, S. Ding, L. Zhao, H. Huang, L. Chen, H. Gao, S.H. Ahmed, IEEE Internet Things J. 7 (2020) 5713–5722.
P. Peng, Y. Wu, Y. Zhang, in: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 2019, 1349–1354.
A. Fischer, C. Igel, Pattern Recognit. 47 (2014) 25–39.
G.E. Hinton, S. Osindero, Y.W. Teh, Neural Comput. 18 (2006) 1527–1554.
W. Hu, J. Gao, B. Li, O. Wu, J. Du, S. Maybank, IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 32 (2020) 218–233.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant No. 2020YFA0405700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 A. Deduction of relationship between F and Fv statistic
There is a linear correlation between the sample free energy F and the variable free energy Fv. The proof is as follows.
The first term of Eq. (5) can be written as Eq. (14), that is, the first term of Eq. (5) is the linear addition of the first term of p Eq. (9).
The exponential term in the second term of Eq. (5) can be expanded as:
The exponential term in the second term of Eq. (9) can be unfolded as:
Therefore, the relationship between Eqs. (15) and (16) is shown in Eq. (17):
Let \(A = - \left( {p - 1} \right)\sum\limits_{{{j}} = 1}^{{q}}b_{j}\), and then the exponential term of Eq. (5) is the linear addition of p exponent terms of Eq. (9) plus a constant A.
In summary, the F statistic is the linear addition of the Fv statistics of all variables plus a constant C.
where constant \(C \approx - \left( {p - 1} \right)\sum\limits_{{{j}} = 1}^{{q}}b_{j}\).
1.2 B. Monitoring results of traditional methods
See Fig. 7.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Qq., Qian, Qt., Li, M. et al. Monitoring and diagnosis of complex production process based on free energy of Gaussian–Bernoulli restricted Boltzmann machine. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 30, 971–984 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00867-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-022-00867-4