Abstract
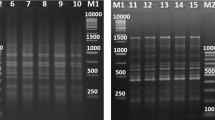
Changing environmental conditions can cause diseases in plants, leading to novel interactions between plants and stress factors. In this respect, the relationships between pathogens and plants regarding epigenetics have still been investigated. Our aim is to examine the effect of leaf blight bacterial causal agent, Pantoea ananatis isolate PaTo34a1, on barley- and rice-specific retrotransposons’ (Nikita, Osr30 and RIRE1, respectively) movements in different rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L. cv. Tosya, Cameo, Arize, Ronaldo, Osmancik-97, Kale, Baldo, Bafra, Hakkari and Vasco) collected from different localities in Turkey. The activation order of retrotransposons was observed as Osr30 > Nikita = RIRE1. Osr30 shows polymorphism in Ronaldo and Cameo cultivars when compared to the control. After, amplified Ranoldo and Cameo fragments were sequenced and aligned with rice genome. The result showed that sequence was homologous to Oryza sativa chromosome 12. It is worth noting that this is the first report detailing barley- and rice-specific LTR retrotransposons in pathogen-infected rice cultivars. Hence, it may offer better insights into the retrotransposon movements of a P. ananatis in rice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal G, Choudhary D, Stice SP, Myers BK, Gitaitis RD, Venter SN, Kvitko BH, Dutta B (2021) Pan-genome-wide analysis of Pantoea ananatis identified genes linked to pathogenicity in onion. Front Microbiol 12:684756
Aksoy HM, Bölük E (2019) First report of Pantoea ananatis in japonia rice varieties in Turkey. J Plant Pathol 101:409
Arayaskul N, Poompouang S, Lıthanatudom P, Lithanatudom SK (2020) First report of a leaf blight in rice (Oryza sativa) caused by Pantoea ananatis and Pantoea stewartii in Thailand. Plant Dis 104(2):562
Arvas YE, Yolcı MS, Marakli S (2023) Investigation the effect of drought stress on tolerant and resistant rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties in terms of morphologic and genetic characters. Genet Resour Crop Evol 70:427–436
Azizi MMF, Zulperi D, Rahman MAA, Abdul-Basir B, Othman NA, Ismail SI, Hata EM, Ina-Salwany MY, Abdullah MAF (2019) First report of Pantoea ananatis causing leaf blight disease of rice in Peninsular Malaysia. Plant Dis 103(8):2122
Bichsel M, Barbour AD, Wagner A (2010) The early phase of a bacterial insertion sequence infection. Theor Popul Biol 78:278–288
Bing XL, Wan YY, Liu HH, Ji R, Zhao DS, Niu YD, …, Hong XY (2022) Characterization of Pantoea ananatis from rice planthoppers reveals a clade of rice-associated P. ananatis undergoing genome reduction. Microb Genomics 8(12)
Camargo-Ramirez R, Val-Torregrosa B, San Segundo B (2018) MiR858-mediated regulation of flavonoid-specific MYB transcription factor genes controls resistance to pathogen infection in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 59(1):190–204
Chen Y, Wang J, Yang N, Wen Z, Sun X, Chai Y, Ma Z (2018) Wheat microbiome bacteria can reduce virulence of a plant pathogenic fungus by altering histone acetylation. Nat Commun 9(1):1–14
Cheng C, Gao X, Feng B, Sheen J, Shan L, He P (2013) Plant immune response to pathogens differs with changing temperatures. Nat Commun 4:2530
Comertpay G, Baloch FS, Derya M, Andeden EE, Alsaleh A, Sürek H, Özkan H (2016) Population structure of rice varieties used in Turkish rice breeding programs determined using simple-sequence repeat and inter-primer binding site-retrotransposon data. Genet Mol Res 15(1):1–14
Cortesi P, Pizzatti C (2007) Palea browning, a new disease of rice in Italy caused by Pantoea ananatis. J Phytopathol 89:S76
Cother EJ et al (2010) Bacterial pathogens of rice in the Kingdom of Cambodia and description of a new pathogen causing a serious sheath rot disease. Plant Pathol 59:944–953
Coutinho TA, Venter SN (2009) Pantoea ananatis: an unconventional plant pathogen. Mol Plant Pathol 10:325–335
Coutinho TA, Preisig O, Mergaert J, Cnockaert MC, Riedel KH, Swings J, Wingfield MJ (2002) Bacterial blight and dieback of Eucalyptus species, hybrids, and clones in South Africa. Plant Dis 86:20–25
De Maayer P, Chan WY, Rubagotti E, Venter SN, Toth IK et al (2014) Analysis of the Pantoea ananatis pan-genome reveals factors underlying its ability to colonize and interact with plant, insect and vertebrate hosts. BMC Genomics 15:404
Durrant MG, Li MM, Siranosian BA, Montgomery SB, Bhatt AS (2020) A bioinformatic analysis of integrative mobile genetic elements highlights their role in bacterial adaptation. Cell Host Microbe 27(1):140–153
Eğerci Y, Kınay-Teksür P, Uysal-Morca A (2021) First report of Bakanae disease caused by Fusarium proliferatum on rice in Turkey. J Pant Dis Prot 128(2):577–582
Egorova M, Mazurin E, Ignatov AN (2015) First report of Pantoea ananatis causing grain discolouration and leaf blight of rice in Russia. New Disease Reports 32:21
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Int J Org Evol 39:783–791
Fouché S, Badet T, Oggenfuss U, Plissonneau C, Francisco CS, Croll D (2020) Stress-driven transposable element de-repression dynamics and virulence evolution in a fungal pathogen. Mol Biol Evol 37(1):221–239
Ghonaim MM, Mohamed HI, Omran AA (2021) Evaluation of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) salt stress tolerance using physiological parameters and retrotransposon-based markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68:227–242
Gitaitis RD, Walcott RD, Culpepper S, Sandres FH, Zolobowska L, Langston D (2002) Recovery of Pantoea ananatis, causal agent of center rot of onion, from weeds and crops in Georgia. USA Crop Protection 21:983–989
Giarrocco LE, Marassi MA, Salerno GL (2007) Assessment of the genetic diversity in Argentine rice cultivars with SSR markers. Crop Sci 47:853–858
Goszczynska T, Venter SN, Coutinho TA (2007) Isolation and identification of the causal agent of brown stalk rot, a new disease of corn in South Africa. Plant Dis 91:711–718
Hsu C et al (2020) Identification of high-copy number long terminal repeat retrotransposons and their expansion in Phalaenopsis orchids. BMC Genomics 21(1):1–13
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Société Vaudoise Sci Nat 44:223–270
Jeon J et al (202) Alternative splicing diversifies the transcriptome and proteome of the rice blast fungus during host infection. RNA Biol 19(1):373–385
Jomova K, Feszterova M, Morovic M (2021) Expression of pathogenesis-related protein genes and changes of superoxide dismutase activity induced by toxic elements in Lupinus luteus L. J Microbiol Biotechnol Food Sci 2021:437–445
Kadu TP, Kale SS, Chayan NR, Agarwal T, Verulkar SB (2015) Pyramiding of three bacterial blight resistance in Dubraj rice cultivar using marker-assisted selection. The Ecoscan 7:07–12
Kauffman HE, Reddy APK, Hsıeh SPY, Merca SD (1973) An improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Disease Reporter 56:537–541
Khan AS, Imran M, Ashfaq M (2009) Estimation of genetic variability and correlation for grain yield components in rice (Oryza sativa L). J Agric Environ Sci 6:585–590
Kim CY et al (2022) A rice gene encoding glycosyl hydrolase plays contrasting roles in immunity depending on the type of pathogens. Mol Plant Pathol 23(3):400–416
Kini K, Lefeuvre P, Poulin L, Silué D, Koebnik R (2020) Genome resources of three west african strains of Pantoea ananatis causing bacterial blight and grain discoloration of rice. Phytopathology 110:1500–1502
Krawczyk K, Wıelkopolan B, Obrepalska-Steplowskaa (2020) Pantoea ananatis, a new bacterial pathogen affecting wheat plants (Triticum L.) in Poland. Pathogens 9(12):1079
Kumar AS, Aiyanathan KEA, Nakkeeran S, Manickam S (2018) Documentation of virulence and races of Xanthomonas citri pv. malvacearum in India and its correlation with genetic diversity revealed by repetitive elements (REP, ERIC, and BOX) and ISSR markers. 3Biotech 8:479
Leigh F, Kalendar R, Lea V, Lee D, Donini P, Schulman AH (2003) Comparison of the utility of barley retrotransposon families for genetic analysis by molecular marker techniques. Mol Genet Genomics 269:464–474
Letunic I, Bork P (2007) Interactive tree of life (iTOL): an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Bioinformatics 23(1):127–128
Lin H et al (2022) An MKP-MAPK protein phosphorylation cascade controls vascular immunity in plants. Sci Adv 8(10):eabg8723
Lorrain C, Feurtey A, Moller M, Haueısen J, Stukenbrock EH (2020) Dynamics of transposable elements in recently diverged fungal pathogens: lineage-specific transposable element content and efficiency of genome defences. BioRxiv G3(4):jkab068
Lv L, Luo J, Ahmed T, Zaki HE, Tian Y, Shahid MS, …, Li B (2022) Beneficial effect and potential risk of Pantoea on rice production. Plants 11(19):2608
Ma J, Zhang K, Huang M, Hector SB, Liu B, Tong C, Liu Q, Zeng J, Gao Y, Xu T (2016) Involvement of fenton chemistry in rice straw degradation by the lignocellulolytic bacterium Pantoea ananatis Sd-1. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod 9:1–13
Maeda S, Hayashi N, Sasaya T, Mori M (2016) Overexpression of BSR1 confers broad-spectrum resistance against two bacterial diseases and two major fungal diseases in rice. Breed Sci 66:396–406
Mamede MC et al (2018) Detection of Pantoea ananatis in corn seeds on semi-selective medium. Trop Plant Pathol 43(3):254–256
Melotto M, Underwood W, Koczan J, He SY (2006) Plant stomata function in innate immunity against bacterial invasion. Cell 126:969–980
Mondal KK, Manı C, Singh J (2011) A new leaf blight of rice caused by Pantoea ananatis in India. Plant Dis 95:1582
Mongiano G, Titone P, Bregaglio S, Tamborini L (2021) Susceptibility of novel Italian rice varieties to panicle blast under field conditions. Eur J Plant Pathol 160(2):427–440
Nei M (2000) In: Kumar S (ed) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York, NY. ISBN 0-19-513585-7
Nie Q, Qıao G, Peng L, Wen X (2019) Transcriptional activation of long terminal repeat retrotransposon sequences in the genome of pitaya under abiotic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 135:460–468
Resende RS, Araujo DE, Klabunde ER, G. H. F., Rossato M (2022) First report of Pantoea ananatis causing a foliar and bulb disease on onion in Brazil. J Plant Pathol 104(1):463–464
Sahin O, KAarlık E, Merc S, Ari S, Gozukirmizi N (2020) Genome organization changes in GM and non-GM soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] under salinity stress by retro-transposition events. Genetic Resour Crop Evoltion 67(6):1551–1566
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Serrano F (1928) Bacterial fruitlet brown-rot of pineapple in the Philippines. Philippine J Sci 36:271–305
Sheibani-Tezerji R, Naveed M, Jehl MA, Sessitsch A, Rattei T, Mitter B (2015) The genomes of closely related Pantoea ananatis maize seed endophytes having different effects on the host plant differ in secretion system genes and mobile genetic elements. Front Microbiol 6:440
Singh P et al (2020) Biotic stress management in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through conventional and molecular approaches. New Frontiers in Stress Management for Durable Agriculture, Springer, Singapore, pp. 609–644
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027
The Rice Chromosomes 11 and 12 Sequencing Consortia (2005) The sequence of rice chromosomes 11 and 12, rich in disease resistance genes and recent gene duplications. BMC Biol 3:20
Thomas T et al (2020) Identification of rice genotypes for seedling stage multiple abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol Rep 25(4):697–706
Thomson MJ, Septiningsıh EM, Suwardjo F, Santoso TJ (2007) Genetic diversity analysis of traditional and improved indonesian rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 114:559–568
Veltman MA, Flowers JM, Van Andel TR, Schranz ME (2019) Origins and geographic diversification of African rice (Oryza glaberrima), PLoS ONE, 14(2019), e0203508
Vemireddy LR et al (2015) Molecular profiling of major indian rice cultivars using a set of eight hypervariable microsatellite markers. Cereal Res Commun 43:189–203
Weller-Stuart T, De Maayer P, Coutinho T (2017) Pantoea ananatis: genomic insights into a versatile pathogen. Mol Plant Pathol 18:1191–1198
Xu Y, Zhu XF, Zhou MG, Kuang J, Zhang Y, Shang Y, Wang JX (2010) Status of streptomycin resistance development in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola in China and their resistance characters. J Phytopathol 158:601–608
Yan H, Yu SH, Xıe GL (2010) Grain discoloration of rice caused by Pantoea ananatis (synonym Erwinia uredovora) in China. Plant Dis 94:482–482
Yüzbaşıoğlu G, Yılmaz S, Gözükırmızı N (2016) Houba retrotransposon-based molecular markers: a tool for variation analysis in rice. Turkish J Agric Forestry 40:456–464
Zhang D, Zhang H, Wang M, Sun J (2009) Genetic structure and differentiation of Oryza sativa L. in China revealed by microsatellites. Theor Appl Genet 119:1105–1117
Zhang SJ, Liu L, Yang R, Wang X (2020) Genome size evolution mediated by gypsy retrotransposons in Brassicaceae. Genomics Proteom Bioinf 8(3):321–332
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by project grant from Ondokuz Mayis University, OMU-PYO.ZRT.1901.18.015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HMA and EB contributed running the laboratory work. HMA, EB, YK and SM contributed to evaluated results. HMA and SM contributed to bioinfomatics analyses. HMA, YK and SM contributed to critical reading of the manuscript. All the authors have read the final manuscript and approved the submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aksoy, H.M., Boluk, E., Kaya, Y. et al. The effect of leaf blight disease of rice caused by Pantoea ananatis on Nikita, Osr30 and RIRE1 retrotransposons’ movements. J Plant Pathol 105, 1629–1636 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-023-01514-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-023-01514-x