Abstract
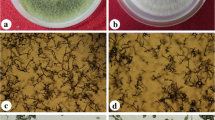
As a devastating disease, leaf spot of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa subsp. pekinensis) caused by Alternaria could render the edible leaves unusable and lead to yield loss. Till now, no research related to Alternaria species causing leaf spot on Chinese cabbage was recorded in the Shanxi province of China. In the current study, 246 Alternaria isolates were recovered from diseased leaves of Chinese cabbage with the symptoms of leaf spot and identified based on morphological traits and phylogenetic analysis of the sequences of the internal transcribed spacer regions of ribosomal DNA (rDNA ITS) and the partial coding sequence of the histone 3 gene. These isolates were grouped into four Alternaria species, of which A. tenuissima was predominant (175 isolates, 71.2%), followed by A. alternata (67 isolates, 27.2%), A. brassicicola (three isolates, 1.2%), and A. solani (one isolate, 0.4%). All the tested Alternaria isolates were pathogenic to detached leaves of Chinese cabbage with the disease incidence and disease index ranging from 73.3% to 100.0% and 20.8 to 99.1, respectively. To our knowledge, it is the first comprehensive study of Alternaria species inciting leaf spot on Chinese cabbage in Shanxi province of China; also, this is the first report of A. tenuissima, A. alternata, and A. solani infecting Chinese cabbage in Shanxi province of China. This study provides important information on the Alternaria species associated with leaf spot of Chinese cabbage, which can help design the strategies for managing Alternaria leaf spot disease on Chinese cabbage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Nadabi HH, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Agrama H, Al-Azri M, Nasehi A, Al-Sadi AM (2018) Molecular characterization and pathogenicity of Alternaria species on wheat and date palms in Oman. Eur J Plant Pathol 152:577–588
Andersen B, Kroger E, Roberts RG (2001) Chemical and morphological segregation of Alternaria alternata, A. gaisen and A. longipes. Mycol Res 105:291–299
Armitage AD, Barbara DJ, Harrison RJ, Lane CR, Sreenivasaprasad S, Woodhall JW, Clarkson LP (2015) Discrete lineages within Alternaria alternata species group: identification using new highly variable loci and support from morphological characters. Fungal Biol 119:994–1006
Bensassi F, Zid M, Rhouma A, Bacha H, Hajlaoui MR (2009) First report of Alternaria species associated with black point of wheat in Tunisia. Ann Microbiol 59:465
Bordoloi M, Saikia S, Bordoloi PK, Kolita B, Dutta PP, Bhuyan PD, Dutta SC, Rao PG (2017) Isolation, characterization and antifungal activity of very long chain alkane derivatives from Cinnamomum obtusifolium, Elaeocarpus lanceifolius and Baccaurea sapida. J Mol Struct 1142:200–210
Chen LY, Price TV, Park-Ng Z (2003) Conidial dispersal by Alternaria brassicicola on Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis) in the field and under simulated conditions. Plant Pathol 52:536–545
Corlett M, Corlett ME (1999) Alternaria japonica. Can J Plant Pathol 21:298–300
Dillard HR, Cobb AC, Lamboy JS (1998) Transmission of Alternaria brassicicola to cabbage by flea beetles (Phyllotreta cruciferae). Plant Dis 82:153–157
Foolad M, Zhang L, Khan AA, Nino-Liu D, Lin G (2002) Identification of QTLs for early blight (Alternaria solani) resistance in tomato using backcross populations of a Lycopersicon esculentum × L. hirsutum cross. Theor Appl Genet 104:945–958
Fu Y, Zhang XF, Liu SJH, Hu KL, Wu XH (2020) Characterization of Alternaria species associated with black spot of strawberry in Beijing municipality of China. Can J Plant Pathol 42:235–242
Glass NL, Donaldson GC (1995) Development of primer sets designed for use with the PCR to amplify conserved genes from filamentous ascomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1323–1330
Hu DQ, Fan YY, Tan YL, Tian Y, Liu N, Wang L, Zhao DY, Wang C, Wu AB (2017) Metabolic profiling on Alternaria toxins and components of Xinjiang jujubes incubated with pathogenic Alternaria alternata and Alternaria tenuissima via orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 65:8466–8474
Kang JC, Crous PW, Schoch CL (2001) Species concepts in the Cylindrocladium floridanum and Cy. spathiphylli complexes (Hypocreaceae) based on multi-allelic sequence data, sexual compatibility and morphology. Syst Appl Microbiol 24:206–217
Kang JC, Crous PW, Mchau GRA, Serdani M, Song SM (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of Alternaria spp. associated with apple core rot and citrus black rot in South Africa. Mycol Res 106:1151–1162
Kumar D, Maurya N, Bharati YK, Kumar A, Kumar K, Srivastava K, Chand G, Kushwaha C, Singh SK, Mishra RK (2014) Alternaria blight of oilseed brassicas: a comprehensive review. Afr J Microbiol Res 8:2816–2829
Lawrence DP, Gannibal PB, Peever TL, Pryor BM (2013) The sections of Alternaria: formalizing species-group concepts. Mycologia 105:530–546
Lee YH, Jang SJ, Han JH, Bae JS, Shin H, Park HJ, Sang MK, Han SH, Kim KS, Han SW, Hong JK (2018) Enhanced tolerance of Chinese cabbage seedlings mediated by Bacillus aryabhattai H26–2 and B. siamensis H30–3 against high temperature stress and fungal infections. Plant Pathology J 34:555–566
Li Y, Zhang D, Xu W, Wu Z, Guo M, Cao A (2011) Alternaria tenuissima causing leaf spot and fruit rot on pepper (Capsicum annuum): first report in China. New Dis Rep 24:3
Liu HR, Ke GL (1992) The component and the perennial change of population of black spot pathogen in Cruciferae vegetable crops. Acta Agric Bor-Occid Sin, 1:6–10 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Guan XY, Kong XD, Wu XL, Liu SN, Ren JH, Guo M, Zhang YW (2019) First report of bacterial leaf spot caused by Pseudomonas viridiflava on Chinese cabbage in China. Plant Dis 103:1764
Loganathan M, Venkataravanappa V, Saha S, Rai AB, Tripathi S, Rai RK, Pandey AK, Chowdappa P (2016) Morphological, pathogenic and molecular characterizations of Alternaria species causing early blight of tomato in northern India. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India Sect B Biol Sci 86:325–330
Luan YS, Feng L, Xia XY, An LJ (2007) First report of Alternaria tenuissima causing disease on blueberry in China. Plant Dis 91:1947
Ma GP, Bao SW, Zhao J, Sui Y, Wu XH (2020) Morphological and molecular characterization of Alternaria species causing leaf blight on watermelon in China. Plant Dis, https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-01-20-0130-RE
Michereff SJ, Noronha MA, Xavier Filha MS, Câmara MPS, Reis A (2012) Survey and prevalence of species causing Alternaria leaf spots on brassica species in Pernambuco. Hortic Bras 30:345–348
Nowakowska M, Wrzesińska M, Kamiński P, Szczechura W, Lichocka M, Tartanus M, Kozik EU, Nowicki M (2019) Alternaria brassicicola - Brassicaceae pathosystem: insights into the infection process and resistance mechanisms under optimized artificial bio-assay. Eur J Plant Pathol 153:131–151
Nowicki M, Nowakowska M, Niezgoda A, Kozik EU (2012) Alternaria black spot of crucifers: symptoms, importance of disease, and perspectives of resistance breeding. Veget Crops Res Bull 76:5–19
Pryor BM, Michailides TJ (2002) Morphological, pathogenic, and molecular characterization of Alternaria isolates associated with Alternaria late blight of pistachio. Phytopathology 92:406–416
Rang JC, Crous PW, Mchau GRA, Serdani M, Song SM (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of Alternaria spp. associated with apple core rot and citrus black rot in South Africa. Mycol Res 106:1151–1162
Ren XX, Zhang GZ, Dai WA (2012) First report of damping-off caused by Alternaria japonica on Chinese cabbage seedlings in China. Plant Dis 96:1378
Selvamani R, Pandian RTP, Sharma P (2014) Role of weather on Alternaria leaf spot development in crucifers. Indian Phytopath 67:285–290
Simmons EG (2007) Alternaria: an identification manual. CBS Biodiversity Series. CBS Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, p 6
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tsuge T, Harimoto Y, Akimitsu K, Ohtani K, Kodama M, Akagi Y, Egusa M, Yamamoto M, Otani H (2013) Host-selective toxins produced by the plant pathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:44–66
Valkonen JPT, Koponen H (1990) The seed-borne fungi of Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis), their pathogenicity and control. Plant Pathol 39:510–516
Wang FM, Zhang LG, Liu J, Zhang HM, Hui MX, Zhang MK (2007) Pathogen identification of black leaf spot in spring summer Chinese cabbage and comparison of the resistance identification methods. J Plant Prot, 34:614–618 (in Chinese)
Wang TY, Zhao J, Sun P, Wu XH (2014) Characterization of Alternaria species associated with leaf blight of sunflower in China. Eur J Plant Pathol 140:301–315
Wang TY, Zhao J, Ma GP, Bao SW, Wu XH (2019) Leaf blight of sunflower caused by Alternaria tenuissima and A. alternata in Beijing, China. Can J Plant Pathol 41:372–378
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 315–322
Woudenberg JHC, Seidl MF, Groenewald JZ, de Vries M, Stielow JB, Thomma BPHJ, Crous PW (2015) Alternaria section Alternaria: species, formae speciales or pathotypes? Stud Mycol 82:1–21
Xiao CK, Wu XH, Li JQ, Zheng JQ, Zhang WH, Bolkan H (2004) Comparison of culture conditions for three Alternaria species causing black spot of cabbage. Mycosystema, 23:573–579 (in Chinese)
Yamagishi D, Akamatsu H, Otani H, Kodama M (2006) Pathological evaluation of host-specific AAL-toxins and fumonisin mycotoxins produced by Alternaria and Fusarium species. J Gen Plant Pathol 72:323–327
Zhang SX, Cui CS, Xu LB (1998) Study on the population composition and pathogenic types of black spot in Chinese cabbage in Heilongjiang province. In: Hou X, Chang Y (eds) Advances in horticulture (II). Southeast University Press, Nanjing, Jiangsu, pp 532–535 (in Chinese)
Zhao J, Bao SW, Ma GP, Wu XH (2016a) Characterization of Alternaria species associated with muskmelon foliar diseases in Beijing municipality of China. J Gen Plant Pathol 82:29–32
Zhao J, Bao SW, Ma GP, Wu XH (2016b) Characterization of Alternaria species associated with watermelon leaf blight in Beijing municipality of China. J Plant Pathol 98:135–138
Zhao J, Ma GP, Liu YY, Wu XH (2018) Alternaria species infecting potato in southern China. Can J Plant Pathol 40:312–317
Zheng HH, Wu XH (2013) First report of Alternaria blight of potato caused by Alternaria tenuissima in China. Plant Dis 97:1246
Zheng HH, Zhao J, Wang TY, Wu XH (2015) Characterization of Alternaria species associated with potato foliar diseases in China. Plant Pathol 64:425–433
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Scientific and Technological Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi (2019 L0832). Mention of trade names or commercial products in this report is solely for the purposes of providing specific information and does not imply a recommendation or endorsement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal studies
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 444 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, X., Zeng, K., Wang, X. et al. Characterization of Alternaria species causing leaf spot on Chinese cabbage in Shanxi province of China. J Plant Pathol 103, 283–293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-020-00740-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-020-00740-x