Abstract
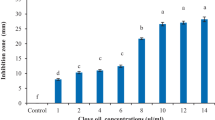
A peroxyacetic acid mixture (CH3CO3H) has been used as a disinfectant for a low environmental impact. In this study, we investigated whether a commercial peroxyacetic acid mixture, Perosan, can be applied as a green chemical to control bacterial and fungal pathogens, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo) and Rhizoctonia solani in rice plants. Paper discs carrying 25% Perosan caused obvious chlorosis on rice leaves. Ion leakage caused by the phytotoxicity was obviously observed at 5% and higher concentrations of Perosan. Perosan treatment resulted in a slightly decreased pH in rice growing water. In a bacterial growth inhibition assay using optical density measurements, 0.007% of Perosan almost completely inhibited the Xoo growth for 36 h. In an agar dilution assay for antifungal activity, mycelial growth inhibition of R. solani was observed with 0.05% addition of Perosan. In planta antimicrobial activity assay with 5% of Perosan inhibited the lesion lengths in Xoo-inoculated rice plants. A spray of 0.5% Perosan significantly inhibited the lesion developments on the leaves inoculated with an agar disc of R. solani. Our results suggest that Perosan can be applied to rice plants to control the pathogens, Xoo and R. solani, as a green chemical.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alasri A, Valverde M, Roques C, Michel G, Cabassud C, Aptel P (1993) Sporocidal properties of peracetic acid and hydrogen peroxide, alone and in combination, in comparison with chlorine and formaldehyde for ultrafiltration membrane disinfection. Can J Microbiol 39:52–60
Arikan S (2007) Current status of antifungal susceptibility testing methods. Med Mycol 45:569–587. https://doi.org/10.1080/13693780701436794
Arturo-Schaan M, Sauvager F, Mamez C, Gougeon A, Cormier M (1996) Use of peracetic acid as a disinfectant in a water-treatment plant: effect on the plasmid contents of Escherichia coli strains. Curr Microbiol 32:43–47
Ayoub F, Ben Oujji N, Chebli B, Ayoub M, Hafidi A, Salghi R, Jodeh S (2017) Antifungal effectiveness of fungicide and peroxyacetic acid mixture on the growth of Botrytis cinerea. Microb Pathog 105:74–80
Bai J, Choi SH, Ponciano G, Leung H, Leach JE (2000) Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae avirulence genes contribute differently and specifically to pathogen aggressiveness. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:1322–1329
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: a review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79
Beuchat LR, Adler BB, Lang MM (2004) Efficacy of chlorine and a peroxyacetic acid sanitizer in killing Listeria monocytogenes on iceberg and Romaine lettuce using simulated commercial processing conditions. J Food Prot 67:1238–1242
Bonadonna L et al (1999) Reduction of microorganisms in sewage effluent using hypochlorite and peracetic acid as disinfectants. Cent Eur J Public Health 7:130–132
Bouman B (2009) How much water does rice use. Rice Today 8:28–29
Bounoure F, Fiquet H, Arnaud P (2006) Comparison of hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid as isolator sterilization agents in a hospital pharmacy. Am J Health Syst Pharm 63:451–455
Carrasco G, Urrestarazu M (2010) Green chemistry in protected horticulture: the use of peroxyacetic acid as a sustainable strategy. Int J Mol Sci 11:1999–2009
Carrasco G, Moggia C, Osses IJ, Alvaro JE, Urrestarazu M (2011) Use of peroxyacetic acid as green chemical on yield and sensorial quality in watercress (Nasturtium officinale R. Br.) under soilless culture. Int J Mol Sci 12:9463–9470
Cinquerrui A, Abriano S, Dimartino MA, Myrta A, Vitale A, Cirvilleri G, Polizzi G (2014) Efficacy of peracetic acid and hydrogen peroxide in controlling bacterial spot and pith necrosis caused by Xanthomonas perforans on tomato. Atti Giornate Fitopatologiche 2:443–446
Delventhal R, Loehrer M, Weidenbach D, Schaffrath U (2016) Inoculation of rice with different pathogens: sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani), damping off disease (Pythium graminicola) and barley powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei). Bio-protocol 6:e2070
Gonzalez JF, Degrassi G, Devescovi G, De Vleesschauwer D, Hofte M, Myers MP, Venturi V (2012) A proteomic study of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice xylem sap. J Proteome 75:5911–5919
Guerreiro-Tanomaru JM, Morgental RD, Faria-Junior NB, Berbert FL, Tanomaru-Filho M (2011) Antibacterial effectiveness of peracetic acid and conventional endodontic irrigants. Braz Dent J 22:285–287
Hong JK et al (2018) Reduced bacterial wilt in tomato plants by bactericidal Peroxyacetic acid mixture treatment. Plant Pathol J 34:78–84
Hopkins DL, Thompson CM, Hilgren J, Lovic B (2003) Wet seed treatment with peroxyacetic acid for the control of bacterial fruit blotch and other seedborne diseases of watermelon. Plant Dis 87:1495–1499
Jia Y, Liu G, Park DS, Yang Y (2013) Inoculation and scoring methods for rice sheath blight disease. Methods Mol Biol 956:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-194-3_19
Kenyon WH, Duke SO, Vaughn KC (1985) Sequence of effects of acifluorfen on physiological and ultrastructural parameters in cucumber cotyledon discs. Pestic Biochem Physiol 24:240–250
Keskinen LA, Annous BA (2011) Efficacy of adding detergents to sanitizer solutions for inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 on Romaine lettuce. Int J Food Microbiol 147:157–161
Kim SI, Song JT, Jeong JY, Seo HS (2016) Niclosamide inhibits leaf blight caused by Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Sci Rep 6:21209
Liu J, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Deng H (2015) Trade-off between water pollution prevention, agriculture profit, and farmer practice--an optimization methodology for discussion on land-use adjustment in China. Environ Monit Assess 187:4104
Meinelt T, Phan TM, Behrens S, Wienke A, Pedersen LF, Liu D, Straus DL (2015) Growth inhibition of Aeromonas salmonicida and Yersinia ruckeri by disinfectants containing peracetic acid. Dis Aquat Org 113:207–213
Mestres R (2005) Green chemistry--views and strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 12:128–132
Meyer E (1976) Disinfection of sewage waters from rendering plants by means by peracetic acid. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 21:266–273
Moss B (2008) Water pollution by agriculture. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 363:659–666
Nadarajah K, Mat Razali N, Cheah BH, Sahruna NS, Ismail I, Tathode M, Bankar K (2017) Draft genome sequence of Rhizoctonia solani anastomosis group 1 subgroup 1A strain 1802/KB isolated from rice. Genome Announc 5. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.01188-17
Nino-Liu DO, Ronald PC, Bogdanove AJ (2006) Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: model pathogens of a model crop. Mol Plant Pathol 7:303–324
Norton GJ, Travis AJ, Danku JMC, Salt DE, Hossain M, Islam MR, Price AH (2017) Biomass and elemental concentrations of 22 rice cultivars grown under alternate wetting and drying conditions at three field sites in Bangladesh. Food Energy Secur 6:98–112
Paik SB, Sim SC, Ku HM, Yoe WG (1998) Screening for antifungal medicinal plants against brown patch and large patch diseases of turfgrass. Korean Turf Sci 12:183–194
Picon-Camacho SM, Marcos-Lopez M, Bron JE, Shinn AP (2012) An assessment of the use of drug and non-drug interventions in the treatment of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet, 1876, a protozoan parasite of freshwater fish. Parasitology 139:149–190
Salzberg SL et al (2008) Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genomics 9:204
Schindelin J et al (2012) Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9:676–682
Sha J, Zhang C (2016) Antibacterial activity identification of pCM19 and pCM12 derived from hGlyrichin. Springerplus 5:1382. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-3025-4
Song WY et al (1995) A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 270:1804–1806
Stalons DR, Thornsberry C (1975) Broth-dilution method for determining the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 7:15–21
Su S, Zhou X, Liao G, Qi P, Jin L (2016) Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of new sulfone derivatives containing 2-Aroxymethyl-1,3,4-oxadiazole/thiadiazole moiety. Molecules 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010064
Taheri P, Gnanamanickam S, Hofte M (2007) Characterization, genetic structure, and pathogenicity of Rhizoctonia spp. associated with rice sheath diseases in India. Phytopathology 97:373–383
Vines JRL, Jenkins PD, Foyer CH, French MS, Scott IM (2003) Physiological effects of peracetic acid on hydroponic tomato plants. Ann Appl Biol 143:153–159
Wiegand I, Hilpert K, Hancock RE (2008) Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances. Nat Protoc 3:163–175
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Todd Tate (Sejong University, Korea) for critically reading this manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries through the Agri-Bio industry Technology Development Program (315091–03 and 316087–4) and the Advanced Production Technology Development Program (115051–2), funded by MAFRA, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HJ, HM, HJK, JKH, and CJP conceived and designed the experiments. HJ and HM performed the experiments and analyzed the data. HJ, HM, JKH, and CJP wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors HJ, HM, HJK, JKH, and CJP declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, H., Moon, H., Kim, H.J. et al. Effect of a peroxyacetic acid mixture as green chemical on rice bacterial and fungal pathogens. J Plant Pathol 101, 661–669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-019-00260-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-019-00260-3