Abstract
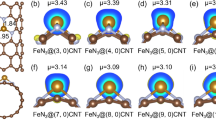
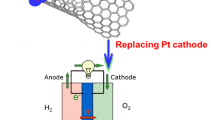
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been widely investigated to develop efficient ORR catalysts. Here we demonstrate that CNTs with 2–7 inner tubes are better supports to develop highly efficient ORR catalysts. Macrocyclic compounds and metal particle loading can dramatically improve the activity for ORR, and the CNTs composed of 2–7 inner tubes functionalized with cobalt phthalocyanine (CoPc) or supported with Pt nanoparticles (NPs) universally demonstrated better activity for ORR, demonstrating that CNTs composed of between 2 and 7 concentric tubes were proved the best supports to develop CNT hybrids for ORR in alkaline condition. The new discovery provides guidance to develop highly efficient catalysts by selecting carbon nanotubes as supports.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The average OD was abtain from the statistical data according to the TEM micrographs.
References
Debe MK (2012) Electrocatalyst approaches and challenges for automotive fuel cells. Nature 486:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11115
Chen Z, Higgins D, Yu A, Zhang L, Zhang JJ (2011) A review on non-precious metal electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells. Energy Environ Sci 4:3167–3192. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ee00558d
Lefèvre M, Proietti E, Jaouen F, Dodelet JP (2009) Iron-based catalysts with improved oxygen reduction activity in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Science 324:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1126/science
Proietti E, Jaouen F, Lefèvre M, Larouche N, Tian J, Herranz J, Dodelet JP (2011) Iron-based cathode catalyst with enhanced power density in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Nat Commun 2:416. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1427
Bashyam R, Zelenay P (2006) A class of non-precious metal composite catalysts for fuel cells. Nature 443:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05118
Yang L, Jiang S, Zhao Y, Zhu L, Chen S, Wang X, Wu Q, Ma J, Ma Y, Hu Z (2011) Boron-doped carbon nanotubes as metal-free electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:7132–7135. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201101287
Gong K, Du F, Xia Z, Durstock M, Dai L (2009) Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Science 323:760–764. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1168049
Wang S, Yu D, Dai L (2011) Polyelectrolyte functionalized carbon nanotubes as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. J Am Chem Soc 133:5182–5185. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1112904
Chen Z, Higgins D, Tao H, Hsu RS, Chen Z (2009) Highly active nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes for oxygen reduction reaction in fuel cell applications. J Phys Chem C 113:21008–21013. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp908067v
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/354056a0
Volder MD, Tawfick SH, Baughman RH, Hart AJ (2013) Carbon nanotubes: present and future commercial applications. Science 339:535–539. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1222453
Eder D (2010) Carbon nanotube-inorganic hybrids. Chem Rev 110:1348–1385. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr800433k
Wu J, Xue Y, Yan X, Yan W, Cheng Q, Xie Y (2012) Co3O4 nanocrystals on single-walled carbon nanotubes as a highly efficient oxygen-evolving catalyst. Nano Res 5:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-012-0237-y
Toma FM, Sartorel A, Iurlo M, Carraro M, Parisse P, Maccato C, Rapino S, Gonzalez BR, Amenitsch H, Da Ros T, Casalis L, Goldoni A, Marcaccio M, Scorrano G, Scoles G, Paolucci F, Prato M, Bonchio M (2010) Efficient water oxidation at carbon nanotube-polyoxometalate electrocatalytic interfaces. Nat Chem 2:826–831. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.761
Toma FM, Sartorel A, Iurlo M, Carraro M, Rapino S, Hoober-Burkhardt L, Da Ros T, Marcaccio M, Scorrano G, Paolucci F, Bonchio M, Prato M (2011) Tailored functionalization of carbon nanotubes for electrocatalytic water splitting and sustainable energy applications. Chemsuschem 4:1447–1451. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201100089
Rutherglen C, Jain D, Burke P (2009) Nanotube electronics for radiofrequency applications. Nat Nanotech 4:811–819. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.355
Ando T (2009) The electronic properties of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Npg Asia Mater 1:17–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/10.1038/asiamat.2009.1
Gong M, Li Y, Wang H, Liang Y, Wu JZ, Zhou J, Wang J, Regier T, Wei F, Dai H (2013) An advanced Ni-Fe layered double hydroxide electrocatalyst for water oxidation. J Am Chem Soc 135:8452–8455. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4027715
Xiang Y, Lu S, Jiang SP (2012) Layer-by-layer self-assembly in the development of electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices from fuel cells to supercapacitors. Chem Soc Rev 41:7291–7321. D https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35048c
Ye W, Hu H, Zhang H, Zhou F, Liu W (2010) Multi-walled carbon nanotube supported Pd and Pt nanoparticles with high solution affinity for effective electrocatalysis. Appl Surf Sci 256:6723–6728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.04.080
Lee HY, Vogel W, Chu PPJ (2011) Nanostructure and surface composition of Pt and Ru binary catalysts on polyaniline-functionalized carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 27:14654–14661. https://doi.org/10.1021/la202169j
Bambagioni V, Bianchini C, Marchionni A, Filippi J, Vizza F, Teddy J, Serp P, Zhiani M (2009) Pd and Pt-Ru anode electrocatalysts supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and their use in passive and active direct alcohol fuel cells with an anion-exchange membrane (alcohol=methanol, ethanol, glycerol). J Power Sources 190:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.01.044
Hu C, Cao Y, Yang L, Bai Z, Guo Y, Wang K, Xu P, Zhou J (2011) Preparation of highly dispersed Pt-SnOx nanoparticles supported on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for methanol oxidation. Appl Surf Sci 257:7968–7974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.04.010
Wang S, Wang X, Jiang SP (2008) PtRu nanoparticles supported on 1-aminopyrene-functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their electrocatalytic activity for methanol oxidation. Langmuir 24:10505–10512. https://doi.org/10.1021/la800925t
Wang D, Lu S, Jiang SP (2010) Tetrahydrofuran-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as effective support for Pt and PtSn electrocatalysts of fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 55:2964–2971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.01.031
Liang Y, Li Y, Wang H, Dai H (2013) Strongly coupled inorganic/nanocarbon hybrid materials for advanced electrocatalysis. J Am Chem Soc 135:2013–2036. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja3089923
Shi Q, Peng F, Liao S, Wang H, Yu H, Liu Z, Zhang B, Su D (2013) Sulfur and nitrogen co-doped carbon nanotubes for enhancing electrochemical oxygen reduction activity in acidic and alkaline media. J Mater Chem A 1:14853–14857. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta12647a
Zhu J, Jiang SP, Wang R, Shi K, Shen PK (2014) One-pot synthesis of a nitrogen and phosphorus-dual-doped carbon nanotube array as a highly effective electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. J Mater Chem A 2:15448–15453. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta02427c
Miller TS, Macpherson JV, Unwin PR (2014) Electrochemical activation of pristine single walled carbon nanotubes: impact on oxygen reduction and other surface sensitive redox processes. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:9966–9973. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp53717j
Waki K, Wong RA, Oktaviano HS, Fujio T, Nagai T, Kimoto K, Yamada K (2014) Non-nitrogen doped and non-metal oxygen reduction electrocatalysts based on carbon nanotubes: mechanism and origin of ORR activity. Energy Environ Sci 7:1950–1958. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee43743d
Cheng Y, Memar A, Saunders M, Pan J, Liu C, Gale JD, Demichelis R, Shen PK, Jiang SP (2016) Dye functionalized carbon nanotubes for photoelectrochemical water splitting-role of inner tubes. J Mater Chem A 4:2473–2483. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA00143B
Cheng Y, Zhang J, Jiang SP (2015) Are metal-free pristine carbon nanotubes electrocatalytically active? Chem Comm 51:13764–13767. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC02218E
Yuan W, Cheng Y, Shen PK, Li CM, Jiang SP (2015) Significance of wall number on the carbon nanotube support-promoted electrocatalytic activity of Pt NPs towards methanol/formic acid oxidation reactions in direct alcohol fuel cells. J Mater Chem A 3:1961–1971. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA04613G
Liu Y, Zhang J, Cheng Y, Jiang SP (2018) Effect of carbon nanotubes on direct electron transfer and electrocatalytic activity of immobilized glucose oxidase. ACS Omega 3:667–676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega
Cheng Y, Xu C, Jia L, Gale JD, Zhang L, Liu C, Shen PK, Jiang SP (2015) Pristine carbon nanotubes as non-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction of water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 163:96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.07.049
Zhang J, Cheng Y, Lu S, Jia L, Shen PK, Jiang SP (2014) Significant promotion effect of carbon nanotubes on the electrocatalytic activity of supported Pd NPs for ethanol oxidation reaction of fuel cells: the role of inner tubes. Chem Commun 50:13732–13734. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc06185c
Cheng Y, Jiang SP (2013) Highly effective and CO-tolerant PtRu electrocatalysts supported on poly(ethyleneimine) functionalized carbon nanotubes for direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim Acta 99:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.03.081
Tackley DR, Dent G, Ewen Smith W (2000) IR and Raman assignments for zinc phthalocyanine from DFT calculations. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:3949–3955. https://doi.org/10.1039/b005091l
Murray C, Dozova N, McCaffrey JG, FitzGerald S, Shafizadeh N, Crepin C (2010) Infra-red and Raman spectroscopy of free-base and zinc phthalocyanines isolated in matrices. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:10406–10422. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cp00055h
Funding
This work was supported by the Key R&D project of Hubei Province, China (2021AAA006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51976143) and the Guangdong Key Areas Research and Development Program (2020B090904001 and 2019B090909003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tian Tian and Yi Cheng wrote the main manuscript text, Zhenfan Sun and Kai Huang prepared figures 1-8, Ming Lei and Haolin Tang edited the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript."
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, T., Cheng, Y., Sun, Z. et al. Carbon nanotubes supported oxygen reduction reaction catalysts: role of inner tubes. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 6, 7 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00592-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-022-00592-2