Abstract
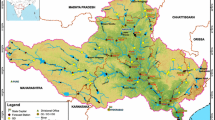
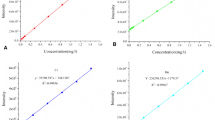
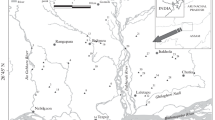
Water is a universal solvent that has the ability to dissolve any compound. It is of great importance to the existence of mankind, as it serves as a means of drinking, clean energy, irrigation, recreation, livestock farming and many more. However, Human activities such as industrialization and the improper waste management around water body introduce toxic metallic substances which could have great effect on human health and aquatic life when in high concentration (above standard). Hence, this study was carried out to determine the level of pollution of the river waters in and around Abuja city as rapid emerging city in Nigeria and to detect the concentration of ten (10) heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Ni, Zn, Cr, Co, Cd, Fe, Mn, and Mg), respectively. The four water samples were collected along rivers at different points and analyzed at the Chemistry Advanced Laboratory, Sheda Technology and Generation complex, Abuja. Atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS) was used to detect the concentration of heavy metals in the water samples. The results indicated the low level concentration in Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd and Mn when compared with the World Health Organization standard. The maximum desirable concentration specified for Ni and Cr by World Health Organization is exceeded in the river waters, while Mg is very low comparable with World Health Organization standard. This study shows that the river waters are not suitable for human consumption and hence recommended that microbiological investigation should be carried out on the river waters as soon as possible to save both lives and aquatic livings.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abimbola, A. F., Odukoya, A. M., & Olatunji, A. S. (2002). Influence of bedrock on the hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in Northern part of Ibadan metropolis, SW Nigeria. Water Resources Journal,9, 195–202.
Adelekan, B. A., & Abegunde, K. D. (2011). Heavy metals contamination of soil and groundwater at automobile mechanic villages in Ibadan, Nigeria. International Journal of the Physical Sciences,6(5), 1045–1058. https://doi.org/10.5897/IJPS10.495.
Aderinola, O. J., Clarke, E. O., Olarinmoye, O. M., Kusemiju, V., & Anatekhai, M. A. (2009). Heavy metal in surface water, sediments, fish and periwinkles of Lagos, Lagoon. American-Eurasian Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences,5(5), 609–617.
APHA (2008) Standard methods for examination of water and waste water, (20th Ed.). Washington DC: American Public Health Association 136th Annual Meeting, October 25–29, 2008; San Diego, California.
Bhagure, G. R., & Mirgane, S. R. (2010). Heavy metals contaminations in groundwater and soils of Thane region of Maharashtra, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,173(1–4), 643–652. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1412-9.
Ene, A., Bosneaga, A., & Georgescu, L. (2010). Determination of heavy metals in soils using XRF technique. Romanian Journal of Physics,55(7–8), 815–820.
Finch, L. E., Hillyer, M. M., & Leopold, M. C. (2015). Quantitative analysis of heavy metals in children's toys and jewelry: A multi-instrument, multi-technique exercise in analytical chemistry and public health. Journal of Chemical Education,92, 849–854.
IARC. (1990). Chromium, nickel and welding. International Agency for Research on Cancer monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans, vol. 49, Lyon, France. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Islam, M. S., Ahmed, M. K., Raknuzzaman, M., Habibullah-Al-Mamun, M., & Islam, M. K. (2015). Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecological Indicators,48(2015), 282–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.08.016.
Jarup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin,68(1), 167–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032.
Khan, S., Cao, Q., Zheng, Y. M., Huang, Y. Z., & Zhu, Y. G. (2008). Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environmental Pollution,152(3), 682–692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.056.
Kumar, A., & Rao, S. R. (2010). Cytological investigations in some important tree species of Rajasthan II. Male meiosis studies in the genus Anogeissus (DC.) Guill P. and Rich A. Caryologia,55, 63–72.
Lenntech Water Treatment and Air Purification. (2004). Water treatment, Published by Lenntech, Rotterdamseweg, Netherlands. http://www.excelwater.com/thp/filters/Water-Purification.htm.
Lide, D. R. (1992). CRC handbook of chemistry and physics (73rd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
NGSA. (2004). Modified Geological map of Abuja, Nigerian Geological Survey Agency, 2004.
Obaje, N. G. (2009). Geology and mineral resources of Nigeria. Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92685-6.
Obaroh, I. O., Elinge, C. M., & Nwankwo, C. (2012). Assessment of some heavy metals and physico-chemical parameters of Jega River, North Western Nigeria. International Journal of Natural and Applied Sciences,8, 78–81.
Obodai, E. A., Boamponsem, L. K., Adokoh, C. K., Essumang, D. K., Villawoe, B. O., Aheto, D. W., et al. (2011). Concentration of heavy metals in two Ghanaian Lagoons. Archives of Applied Science Research,3(3), 177–187.
Offodile, M. E. (2002). Groundwater Study and development in Nigeria (2nd ed., pp. 239–244). Jos, Nigeria: Mecon Geology and Engineering Service Limited.
Suciu, I., Cosma, C., Todica, M., Bolboaca, S. D., & Jantschi, L. (2008). Analysis of soil heavy metal pollution and pattern in Central Transylvania. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,9(4), 434–453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9040434.
Wilson, B., & Pyatt, F. B. (2007). Heavy metal dispersion, persistence and bioaccumulation around an ancient copper mine situated in Anglesey, UK. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,66(2), 224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.02.015.
World Health Organization WHO (2006). Guidelines for the safe use of waste, excreta and grey water: waste water use in Agriculture. Recommendations, World Health Organization, Geneva. 2, p. 219
Yahaya, A., Adegbe, A. A., & Emurotu, J. E. (2012). Assessment of heavy metal content in the surface water of Oke-Afa canal Isolo Lagos, Nigeria. Archives of Applied Science Research,4(6), 2322–2326.
Yu, G. B., Liu, Y., Yu, S., Wu, S. C., Leung, A. O., Luo, W. X. S., et al. (2011). Inconsistency and comprehensiveness of risk assessments for heavy metals in urban surface sediments. Chemosphere,85(6), 1080–1087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.039.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talabi, A.T., Odunaike, K.O., Akinyemi, L.P. et al. Investigation for heavy metals in river waters in the federal capital territory, North Central of Nigeria. Int J Energ Water Res 4, 213–219 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00063-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-020-00063-8