Abstract
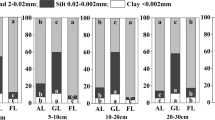
The soil physical-chemical changes in different land uses in a Tropical Cambisol at Apodi Plateau, Northeastern Brazil, were investigated between May 2017 and April 2018. Soil samples were collected at three soil layers (0–5, 5–15, and 15–25 cm) under three land uses: a 6-year agroecological farming system, a 10-year fruticulture farming system, and a 6-year conventional farming system. We evaluated: bulk density, soil porosity, weighted average diameter (WAD), geometric mean diameter (GMD), soil pH, soil organic carbon (SOC), P, and sum of bases. Soil quality index was built by considering four main functions: Water supply and storage, root growth capacity, nutrient cycling, and soil conservation. Our results emphasized the land use influence on the soil physical-chemical traits in a Tropical Cambisol. The PCA analyses showed that SOC, soil porosity, bulk density, WAD, GMD, soil pH, sum of bases, and soil P content were the main factors contributing to the data variance. We found the highest values of soil quality index in the conventional farming system (0.57 ± 0.03). The results highlight the importance to consider land uses that increase the sum of bases, WAD, GMD, and SOC content, and decrease bulk density. Our findings suggest that (1) a conventional farming system with liming and fertilizers’ input positively changed soil physical-chemical traits, which in turn improved soil quality in a tropical Cambisol; and (2) by altering soil functions land uses may create a sustainable cycle into the soil profile thus promoting soil quality.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Alam, S., Ginting, S., Hemon, M. T., Leomo, S., Kilowasid, L. M. H., Karim, J., & Nugroho, Y. (2022). Influence of land cover types on soil quality and carbon storage in Moramo Education Estate, Southeast Sulawesi, Indonesia. Biodiv, 23, 4371–4376. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d230901.
Alkharabsheh, H. M., Seleiman, M. F., Battaglia, M., Shami, A., Jalal, R. S., Alhammad, B. A., Almutairi, K. F., & Al-Saif, A. M. (2021). Biochar and Its Broad Impacts in Soil Quality and Fertility, Nutrient Leaching and Crop Productivity: A Review. Agron. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11050993.
Antisari, L. V., William, T., Mauro, F., Gianluca, B., & Gloria, F. (2021). Soil quality and Organic Matter pools in a temperate climate (Northern Italy) under different land uses. Agron. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091815.
Bald, E. (2021). Soil–Plant Interaction: Effects on Plant Growth and Soil Biodiversity. Agron. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122378.
Biswas, S., Hazra, G. C., Purakayastha, T. J., Saha, N., Mitran, T., Roy, S. S., Basak, N., & Mandal, B. (2017). Establishment of critical limits of indicators and indices of soil quality in rice-rice cropping systems under different soil orders. Geoderma, 292, 34–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.01.003.
Black, C. A. (1965). Methods of soil analysis. In C. A. Black (Ed.), Agronomy Monograph No. 9 (pp. 771–1572). Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Cavalli, J. P., Reichert, J. M., Rodrigues, M. F., & Araújo, E. F. (2020). Composition and functional soil properties of arenosols and acrisols: Effects on eucalyptus growth and productivity. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.104439.
Chamkhi, I., Cheto, S., Geistlinger, J., Zeroual, Y., Kouisni, L., Bargaz, A., & Ghoulam, C. (2022). Legume-based intercropping systems promote beneficial rhizobacterial community and crop yield under stressing conditions. Industrial Crops And Products. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114958.
Cherubin, M. R., Tormena, C. A., & Karlen, D. L. (2017). Soil quality evaluation using the Soil Management Assessment Framework (SMAF) in brazilian oxisols with contrasting texture. Rev Bras Cienc Solo. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20160148.
Choudhary, M., Jat, H. S., Datta, A., Yadav, A. K., Sapkota, T. B., Mondal, S., Meena, R. P., Sharma, P. C., & Jat, M. L. (2018). Sustainable intensification influences soil quality, biota, and productivity in cereal-based agroecosystems. Applied Soil Ecology, 126, 189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.041.
Coban, O., De Deyn, G. B., & Der Ploeg, M. V. (2022). Soil microbiota as game-changers in restoration of degraded lands. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abe072.
Cortez, J. W., Silva, R. P. D., Furlani, C. E., Olszevski, N., & Nagahama, H. D. J. (2019). Soil attributes and initial corn development as a function of fertilization and intercropping systems. Eng Agric, 39, 257–264. https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-4430-Eng.Agric.v39n2p257-264/2019.
da Silva, L. J. R., Souza, T., Laurindo, L. K., Nascimento, G. D. S., de Lucena, E. O., & Freitas, H. (2022). Aboveground Biomass, Carbon Sequestration, and yield of Pyrus pyrifolia under the management of Organic residues in the subtropical ecosystem of Southern Brazil. Agron. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12020231.
Dai, L., Yuan, Y., Guo, X., Du, Y., Ke, X., Zhang, F., Li, Y., Li, Q., Lin, L., Zhou, H., & Cao, G. (2020). Soil water retention in alpine meadows under different degradation stages on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal Of Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125397.
Dijkstra, F. A., Zhu, B., & Cheng, W. (2021). Root effects on soil organic carbon: A double-edged sword. New Phytologist, 230(1), 60–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.17082.
dos Reis, A. M. H., Auler, A. C., Armindo, R. A., Cooper, M., & Pires, L. F. (2021). Micromorphological analysis of soil porosity under integrated crop-livestock management systems. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104783.
Drewry, J. J., Cavanagh, J. A. E., McNeill, S. J., Stevenson, B. A., Gordon, D. A., & Taylor, M. D. (2021). Long-term monitoring of soil quality and trace elements to evaluate land use effects and temporal change in the Wellington region, New Zealand. Geoderma Regional. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2021.e00383.
Du, X., Jian, J., Du, C., & Stewart, R. D. (2022). Conservation management decreases surface runoff and soil erosion. Int Soil Water Conserv Res, 10(2), 188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.08.001.
Faloye, O. T., Ajayi, A. E., Zink, A., Fleige, H., Dörner, J., & Hornd, R. (2021). Effective stress and pore water dynamics in unsaturated soils: Influence of soil compaction history and soil properties. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.104997.
Fortin, M. J., & Dale, M. R. T. (2005). Spatial analysis: A guide for ecologists. New York: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511542039.
Gava, C. A. T., Giongo, V., Signor, D., & Fernandes-Júnior, P. I. (2021). Land-use change alters the stocks of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in a haplic cambisol in the brazilian semi-arid region. Soil Use And Management, 38(1), 953–963. https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12716.
Grossman, R. B., & Reinsch, T. G. (2002). The solid phase. In J. H. Dane, & G. C. Topp (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Physical methods (pp. 201–414). Soil Science Society of America.
Guhra, T., Stolze, K., & Totsche, K. U. (2022). Pathways of biogenically excreted organic matter into soil aggregates. Soil Biology & Biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2021.108483.
Gura, I., & Mnkeni, P. N. S. (2019). Crop rotation and residue management effects under no till on the soil quality of a haplic cambisol in Alice, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Geoderma, 337, 927–934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2018.10.042.
Husein, H. H., Lucke, B., Bäumler, R., & Sahwan, W. (2021). A contribution to Soil Fertility Assessment for Arid and Semi-Arid Lands. Soil Syst. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems5030042.
IITA (1979). Selected methods for soil and plant analysis. IITA (International Institute of Tropical Agriculture) Manual Series no.1, Ibadan.
INMET (2018). Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia. Dados de precipitação pluviométrica, Rio Grande do Norte, Brasil. https://portal.inmet.gov.br/.
Iqbal, A., Khan, A., Green, S. J., Ali, I., He, L., Zeeshan, M., Luo, Y., Wu, X., Wei, S., & Jiang, L. (2021). Long-term straw mulching in a no‐till field improves soil functionality and rice yield by increasing soil enzymatic activity and chemical properties in paddy soils. J Plant Nut Soil Sci, 184(6), 622–634. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.202100089.
Kadiri, W. O. J., Fasina, A. S., & Babalola, T. S. (2021). Soil organic carbon concentration and stock of arable land use of two agro-ecological zones of Nigeria. J Saudi Society Agric Sci, 20(3), 180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2021.01.004.
Karlen, D. L., & Stott, D. E. (1994). A framework for evaluating physical and chemical indicators of soil quality. Defining soil quality for a sustainable environment, 35, 53–72. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaspecpub35.c4.
Kemper, W. D., & Chepil, W. S. (1965). Size distribution of aggregates. Methods of soil analysis: Part 1 physical and mineralogical properties. including statistics of measurement and sampling, 9, 499–510. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.1.c39.
Klopp, H. W., Arriaga, F. A., Daigh, A. L. M., & Bleam, W. F. (2021). Development of functions to predict soil hydraulic properties that account for solution sodicity and salinity. Catena. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2021.105389.
Kurniawan, S., Agustina, M. P., Wiwaha, R. A., Wijaya, A. Y., & Fitria, A. D. (2021). Soil quality degradation under horticulture practices in volcanic slope soil, East Java – Indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/648/1/012062.
Latvala, T., Regina, K., & Lehtonen, H. (2021). Evaluating Non-Market values of Agroecological and Socio-Cultural benefits of Diversified Cropping Systems. Environ Manag, 67(5), 988–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-021-01437-2.
Li, X. F., Wang, Z. G., Bao, X. G., Sun, J. H., Yang, S. C., Wang, P., Wang, C. B., Wu, J. P., Liu, X. R., Tian, X. L., Wang, Y., Li, J. P., Wang, Y., Xia, H. Y., Mei, P. P., Wang, X. F., Zhao, J. H., Yu, R. P., Zhang, W. P., Che, Z. X., Gui, L. G., Callaway, R. M., Tilman, D., & Li, L. (2021). Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping. Nat Sustain, 4(11), 943–950. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-021-00767-7.
Livesley, S. J., Bristow, M., Grover, S. P., Beringer, J., Arndt, S. K., & Hutley, L. B. (2021). Soil carbon density can increase when australian savanna is converted to pasture, but may not change under intense cropping systems. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107527.
Ma, L., Shao, M. A., Fan, J., Wang, J., & Li, Y. (2021). Effects of earthworm (Metaphire guillelmi) density on soil macropore and soil water content in typical Anthrosol soil. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107338.
Mamuye, M., Nebiyu, A., Elias, E., & Berecha, G. (2021). Combined Use of Organic and Inorganic Nutrient Sources Improved Maize Productivity and Soil Fertility in Southwestern Ethiopia. Int J Plant Prod, 15, 407–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-021-00144-6.
Martínez-Mena, M., Perez, M., Almagro, M., Garcia-Franco, N., & Díaz-Pereira, E. (2021). Long-term effects of sustainable management practices on soil properties and crop yields in rainfed Mediterranean almond agroecosystems. European Journal of Agronomy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2020.126207.
Melo Filho, J. F., Souza, A. L. V., & Souza, L. S. (2007). Determinação do índice de qualidade subsuperficial em um Latossolo Amarelo Coeso dos Tabuleiros Costeiros, sob floresta natural. Rev Bras Cienc Soil. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-06832007000600036.
Mortensen, E., De Notaris, C., Peixoto, L., Olesen, J. E., & Rasmussen, J. (2021). Short-term cover crop carbon inputs to soil as affected by long-term cropping system management and soil fertility. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107339.
Muhammad, I., Wang, J., Sainju, U. M., Zhang, S., Zhao, F., & Khan, A. (2021). Cover cropping enhances soil microbial biomass and affects microbial community structure: A meta-analysis. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114696.
Mutuku, E. A., Vanlauwe, B., Roobroeck, D., Boeckx, P., & Cornelis, W. M. (2021). Physico-chemical soil attributes under conservation agriculture and integrated soil fertility management. Nut Cyc Agroecosyst, 120(2), 145–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-021-10132-x.
Nandan, R., Singh, V., Singh, S. S., Kumar, V., Hazra, K. K., Nath, C. P., Poonia, S., Malik, R. K., Bhattacharyya, R., & McDonald, A. (2019). Impact of conservation tillage in rice–based cropping systems on soil aggregation, carbon pools and nutrients. Geoderma, 340, 104–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2019.01.001.
Nascimento, G. S., Souza, T. A. F., da Silva, L. J. R., & Santos, D. (2021). Soil physico-chemical properties, biomass production, and root density in a green manure farming system from tropical ecosystem, North-eastern Brazil. Journal Of Soils And Sediments, 21, 2203–2211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-021-02924-z.
Navarro-Pedreño, J., Almendro-Candel, M. B., & Zorpas, A. A. (2021). The Increase of Soil Organic Matter Reduces Global Warming, Myth or Reality? Science. https://doi.org/10.3390/sci3010018.
Ni, H., Su, W., Fan, S., & Chu, H. (2021). Effects of intensive management practices on rhizosphere soil properties, root growth, and nutrient uptake in Moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. For Ecol Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2021.119083.
Okalebo, J. R., Gathua, K. W., & Woomer, P. L. (1993). Laboratory Methods of Plant and Soil Analysis: A Working Manual. Technical Bulletin No. 1 Soil Science Society East Africa. http://hdl.handle.net/11295/85257.
Oliveira, D. P., Sartor, L. R., Souza Júnior, V. S., Corrêa, M. M., Romero, R. E., Andrade, G. R. P., & Ferreira, T. O. (2018). Weathering and clay formation in semi-arid calcareous soils from northeastern Brazil. Catena, 162, 325–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.030.
Oliveira, J. A., Cássaro, F. A., & Pires, L. F. (2021). Estimating soil porosity and pore size distribution changes due to wetting-drying cycles by morphometric image analysis. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104814.
Pratibha, G., Rao, K. V., Srinivas, I., Raju, B. M. K., Shanker, A. K., Madhavi, M., Indoria, A. K., Rao, M. S., Murthy, K., Reddy, K. S., Rao, C. S., Biswas, A. K., & Chaudhari, S. K. (2021). Weed shift and community diversity in conservation and conventional agriculture systems in pigeonpea- castor systems under rainfed semi-arid tropics. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021.105075.
R Core Team. (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/.
Reichert, J. M., Albuquerque, J. A., Peraza, J. E. S., & Costa, A. (2020). Estimating water retention and availability in cultivated soils of southern Brazil. Geoderma Regional, 21, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2020.e00277.
Reichert, J. M., Gubiani, P. I., Santos, D. R., Reinert, D. J., Sandro, C. A., & Giacomini, J. (2021). Soil properties characterization for land-use planning and soil management in watersheds under family farming. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 10, 119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2021.05.003.
Rudiyanto, M. B., Shah, R. M., Setiawan, B. I., & van Genuchten, M. T. (2020). Simple functions for describing soil water retention and the unsaturated hydraulic conductivity from saturation to complete dryness. Journal Of Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125041.
Sainju, U. M., Liptzin, D., Allen, B. L., & Rana-Dangi, S. (2021). Soil health indicators and crop yield in a long‐term cropping system experiment. Agronomy Journal, 113(4), 3675–3687. https://doi.org/10.1002/agj2.20673.
Santos, P. G., Almeida, J. A., & Sequinatto, L. (2017). Mineralogy of the Clay Fraction and Chemical Properties of Soils developed from Sedimentary Lithologies of Pirambóia, Sanga-the-Cabral and Guará Geological Formations in Southern Brazil. Rev Bras Ciênc Solo, 41. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20160344.
Serri, D. L., Pérez-Brandan, C., Meriles, J. M., Salvagiotti, F., BacigaluppoS, Malmantile, A., & Vargas-Gil, S. (2022). Development of a soil quality index for sequences with different levels of land occupation using soil chemical, physical and microbiological properties. Applied Soil Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2022.104621.
Silva, A. C., Armindo, R. A., Minasny, B., & Prevedello, C. L. (2021a). Evaluating the Splintex model for estimating the soil water retention curve for a wide range of soils. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021a.104974.
Silva, T. G. F., Queiroz, M. G., Zolnier, S., Souza, L. S. B., Souza, C. A. A., Moura, M. S. B., Araújo, G. G. L., Steidle Neto, A. J., Santos, T. S., Melo, A. L., Cruz Neto, J. F. C., Silva, M. J., & Alves, H. K. M. N. (2021b). Soil properties and microclimate of two predominant landscapes in the brazilian semiarid region: Comparison between a seasonally dry tropical forest and a deforested area. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2020.104852.
Silva-Olaya, A. M., Mora-Motta, D. A., Cherubin, M. R., Grados, D., Somenahally, A., & Ortiz-Morea, F. A. (2021). Soil enzyme responses to land use change in the tropical rainforest of the colombian Amazon region. Plos One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0255669.
Solgi, A., Najafi, A., Page-Dumroese, D. S., & Zenner, E. K. (2020). Assessment of topsoil disturbance caused by different skidding machine types beyond the margins of the machine operating trail. Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114238.
Soto, R. L., Martínez-Mena, M., Padilla, M. C., & Vente, J. (2021). Restoring soil quality of woody agroecosystems in Mediterranean drylands through regenerative agriculture. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107191.
Stratton, A. E., Comin, J. J., Siddique, I., Zak, D. R., Filipini, L. D., Lucas, R. R., & Blesh, J. (2022). Assessing cover crop and intercrop performance along a farm management gradient. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2022.107925.
Sun, X., Ye, Y., Ma, Q., Guan, Q., & Jones, D. L. (2021). Variation in enzyme activities involved in carbon and nitrogen cycling in rhizosphere and bulk soil after organic mulching. Rhizosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100376.
Tasser, E., Gamper, S., Walde, J., Obojes, N., & Tappeiner, U. (2021). Evidence for the importance of land use, site characteristics and vegetation composition for rooting in European Alps. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90652-2.
Taucare, M., Daniele, L., Viguier, B., Vallejos, A., & Arancibia, G. (2020). Groundwater resources and recharge processes in the western Andean Front of Central Chile. Science Of The Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137824.
Teixeira, P. C., Donagemma, G. K., Fontana, A., & Teixeira, W. G. (2017). Manual de métodos de análise do solo. Brasília: Embrapa Solos.
Teixeira, H. M., Bianchi, F. J. J. A., Cardoso, I. M., Tittonell, P., & Peña-Claros, M. (2021). Impact of agroecological management on plant diversity and soil-based ecosystem services in pasture and coffee systems in the Atlantic forest of Brazil. Agric Ecosyst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2020.107171.
Thapa, V. R., Ghimire, R., Acosta-Martínez, V., Marsalis, M. A., & Schipanski, M. E. (2021). Cover crop biomass and species composition affect soil microbial community structure and enzyme activities in semiarid cropping systems. Applied Soil Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103735.
Torres, J. L. R., Mazetto Júnior, J. C., Silveira, B. S., Loss, A., Santos, G. L., Assis, R. L., Lemes, E. M., & Vieira, D. M. S. (2022). Physical attributes of an Irrigated Oxisol after Brassicas crops under No-Tillage System. Agron. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12081825.
Trinchera, A., Testani, E., Roccuzzo, G., Campanelli, G., & Ciaccia, C. (2021). Agroecological service crops drive Plant Mycorrhization in Organic Horticultural Systems. Microorganisms 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020410.
Tuchtenhagen, I. K., Lima, C. L. R. D., Bamberg, A. L., Guimarães, R. M. L., & Mansonia, P. M. (2018). Visual evaluation of the soil structure under different management systems in lowlands in southern Brazil. Rev Bras Cienc Solo. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20170270.
Usowicz, B., & Lipiec, J. (2021). Spatial variability of saturated hydraulic conductivity and its links with other soil properties at the regional scale. Scientific Reports, 11, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86862-3.
van Oort, F., Paradelo, R., Baize, D., Chenu, C., Delarue, G., Guérin, A., & Proix, N. (2022). Can long-term fertilization accelerate pedogenesis? Depicting soil processes boosted by annual NPK-inputs since 1928 on bare loess Luvisol (INRAE-Versailles). Geoderma. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.115808.
Wymore, A. W. (1993). Model-based systems engineering: An introduction to the mathematical theory of discrete systems and to the tricotyledon theory of system design. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203746936.
Yee, S. H., Paulukonis, E., Simmons, C., Russell, M., Fulford, R., Harwell, L., & Smith, L. M. (2021). Projecting effects of land use change on human well-being through changes in ecosystem services. Ecological Modelling. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2020.109358.
Yinga, O. E., Kumar, K. S., Chowlani, M., Tripathi, S. K., Khanduri, V. P., & Singh, S. K. (2020). Influence of land-use pattern on soil quality in a steeply sloped tropical mountainous region, India. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2020.1858478.
Zhang, Y., Xu, X., Lia, Z., Xu, C., & Luo, W. (2021). Improvements in soil quality with vegetation succession in subtropical China karst. Science Of The Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145876.
Zhao, X., Tong, M., He, Y., Han, X., & Wang, L. (2021a). A comprehensive, locally adapted soil quality indexing under different land uses in a typical watershed of the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021a.107445.
Zhao, Z., Gao, S., Lu, C., Xiaoyu, L. I., Li, F., & Wang, T. (2021b). Effects of different tillage and fertilization management practices on soil organic carbon and aggregates under the rice–wheat rotation system. Soil Till Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2021b.105071.
Zhou, J., & Fong, J. J. (2021). Strong agricultural management effects on soil microbial community in a non-experimental agroecosystem. Applied Soil Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2021.103970.
Acknowledgements
We thank the GEBIOS (Soil Biology Research Group) for practical support. We thank CAPES and the Postgraduate Program of Soil Science of the Federal University of Paraiba for facilitating the master and pos-doc studies of the first, and second author, respectively. Tancredo Souza is supported by a Research fellowship from FAPESQ-Brazil.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We declare that all the authors made substantial contributions to the conception, design, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. All the authors participated in drafting the article, revising it critically for important intellectual content; and finally, the authors gave final approval of the version to be submitted to International Journal of Plant Production.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to Publish
We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal. All Authors have approved the manuscript and agree with submission to International Journal of Plant Production. We have read and have abided by the statement of ethical standards for manuscripts submitted to International Journal of Plant Production.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gondim, J.E.F., Souza, T., Portela, J.C. et al. Soil Physical-chemical Traits and Soil Quality Index in a Tropical Cambisol as Influenced by Land Uses and Soil Depth at Apodi Plateau, Northeastern Brazil. Int. J. Plant Prod. 17, 491–501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-023-00256-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-023-00256-1