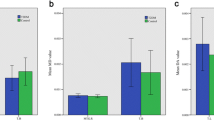
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a risk factor for mild cognitive dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease, but the related neural mechanisms are still unknown. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can quantitatively evaluate the microstructure changes of the white matter of the brain. Although some studies have reported findings for white matter changes related to T2DM, the results were inconsistent. This review summarized 28 T2DM-related DTI studies from home and abroad. We found that the studies reported a wide range of white matter microstructure abnormalities in T2DM patients, and that changes in white matter structure in different regions in T2DM patients are related to specific cognitive functions. DTI is of great value in exploring the relationship between T2DM and white matter microstructure changes and cognitive dysfunction, which might provide imaging evidence in revealing the neural mechanisms underlying T2DM-related cognitive dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seaquist ER. The final frontier: how does diabetes affect the brain? Diabetes. 2010;59(1):4–5.
Moran C, Phan TG, Chen J, et al. Brain atrophy in type 2 diabetes: regional distribution and influence on cognition. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(12):4036–42.
Crane PK, Walker R, Larson EB. Glucose levels and risk of dementia. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(19):1863–4.
Cheng G, Huang C, Deng H, et al. Diabetes as a risk factor for dementia and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Intern Med J. 2012;42(5):484–91.
Basser PJ, Mattiello J, Lebihan D. MR diffusion tensor spectroscopy and imaging. Biophys J. 1994;66(1):259–67.
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ. Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36(6):893–906.
Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Cercignani M. About, “axial” and “radial” diffusivities. Magn Reson Med. 2009;61(5):1255–60.
Yau PL, Javier DC, Ryan CM, et al. Preliminary evidence for brain complications in obese adolescents with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2010;53(11):2298–306.
Rofey DL, Arslanian SA, El Nokali NE, et al. Brain volume and white matter in youth with type 2 diabetes compared to obese and normal weight, non-diabetic peers: a pilot study. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2015;46:88–91.
Van Bloemendaal L, Ijzerman RG, Ten Kulve JS, et al. Alterations in white matter volume and integrity in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Metab Brain Dis. 2016;31(3):621–9.
Nouwen A, Chambers A, Chechlacz M, et al. Microstructural abnormalities in white and gray matter in obese adolescents with and without type 2 diabetes. Neuroimage Clin. 2017;16:43–51.
Yoon S, Cho H, Kim J, et al. Brain changes in overweight/obese and normal-weight adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2017;60(7):1207–17.
Yau PL, Hempel R, Tirsi A, et al. Cerebral white matter and retinal arterial health in hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Hypertens. 2013;2013:329602.
Yu X, Jiaerken Y, Xu X, et al. Abnormal corpus callosum induced by diabetes impairs sensorimotor connectivity in patients after acute stroke. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(1):115–23.
Zhuo Y, Fang F, Lu L, et al. White matter impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without microvascular disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;24:101945.
Hoogenboom WS, Marder TJ, Flores VL, et al. Cerebral white matter integrity and resting-state functional connectivity in middle-aged patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2014;63(2):728–38.
Tan X, Fang P, An J, et al. Micro-structural white matter abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients: a DTI study using TBSS analysis. Neuroradiology. 2016;58(12):1209–16.
Zhang J, Wang Y, Wang J, et al. White matter integrity disruptions associated with cognitive impairments in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes. 2014;63(11):3596–605.
Zhang A, Ajilore O, Zhan L, et al. White matter tract integrity of anterior limb of internal capsule in major depression and type 2 diabetes. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(8):1451–9.
Hsu JL, Chen YL, Leu JG, et al. Microstructural white matter abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Neuroimage. 2012;59(2):1098–105.
Reijmer YD, Brundel M, De Bresser J, et al. Microstructural white matter abnormalities and cognitive functioning in type 2 diabetes: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(1):137–44.
Sun Q, Chen GQ, Wang XB, et al. Alterations of white matter integrity and hippocampal functional connectivity in type 2 diabetes without mild cognitive impairment. Front Neuroanat. 2018;12:21.
Xie Y, Zhang Y, Qin W, et al. White matter microstructural abnormalities in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a diffusional kurtosis imaging analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017;38(3):617–25.
Xiong Y, Sui Y, Xu Z, et al. A Diffusion tensor imaging study on white matter abnormalities in patients with type 2 diabetes using tract-based spatial statistics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37(8):1462–9.
Kim DJ, Yu JH, Shin MS, et al. Hyperglycemia reduces efficiency of brain networks in subjects with type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(6):e0157268.
Zhang J, Liu Z, Li Z, et al. Disrupted white matter network and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes patients. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;53(1):185–95.
Xiong Y, Sui Y, Zhang S, et al. Brain microstructural alterations in type 2 diabetes: diffusion kurtosis imaging provides added value to diffusion tensor imaging. Eur Radiol. 2019;29(4):1997–2008.
Yau PL, Javier D, Tsui W, et al. Emotional and neutral declarative memory impairments and associated white matter microstructural abnormalities in adults with type 2 diabetes. Psychiatry Res. 2009;174(3):223–30.
Yau PL, Kluger A, Borod JC, et al. Neural substrates of verbal memory impairments in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2014;36(1):74–87.
Raffield LM, Cox AJ, Freedman BI, et al. Analysis of the relationships between type 2 diabetes status, glycemic control, and neuroimaging measures in the Diabetes Heart Study Mind. Acta Diabetol. 2016;53(3):439–47.
Falvey CM, Rosano C, Simonsick EM, et al. Macro- and microstructural magnetic resonance imaging indices associated with diabetes among community-dwelling older adults. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(3):677–82.
Qi D, Wang A, Chen Y, et al. Default mode network connectivity and related white matter disruption in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients concurrent with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(11):1238–46.
Fang P, An J, Tan X, et al. Changes in the cerebellar and cerebro-cerebellar circuit in type 2 diabetes. Brain Res Bull. 2017;130:95–100.
Van Bussel FC, Backes WH, Hofman PA, et al. Altered hippocampal white matter connectivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus and memory decrements. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016;28(3):12366.
Groeneveld O, Reijmer Y, Heinen R, et al. Brain imaging correlates of mild cognitive impairment and early dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;28(12):1253–60.
Remy F, Vayssiere N, Saint-Aubert L, et al. White matter disruption at the prodromal stage of Alzheimer’s disease: relationships with hippocampal atrophy and episodic memory performance. Neuroimage Clin. 2015;7:482–92.
Stahl R, Dietrich O, Teipel SJ, et al. White matter damage in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: assessment with diffusion-tensor MR imaging and parallel imaging techniques. Radiology. 2007;243(2):483–92.
Hasan KM, Iftikhar A, Kamali A, et al. Development and aging of the healthy human brain uncinate fasciculus across the lifespan using diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Res. 2009;1276:67–76.
Diehl B, Busch RM, Duncan JS, et al. Abnormalities in diffusion tensor imaging of the uncinate fasciculus relate to reduced memory in temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia. 2008;49(8):1409–18.
Van Der Werf YD, Jolles J, Witter MP, et al. Contributions of thalamic nuclei to declarative memory functioning. Cortex. 2003;39(4–5):1047–62.
Papma JM, De Groot M, De Koning I, et al. Cerebral small vessel disease affects white matter microstructure in mild cognitive impairment. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35(6):2836–51.
Zheng Z, Shemmassian S, Wijekoon C, et al. DTI correlates of distinct cognitive impairments in Parkinson’s disease. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014;35(4):1325–33.
Levitt JJ, Alvarado JL, Nestor PG, et al. Fractional anisotropy and radial diffusivity: diffusion measures of white matter abnormalities in the anterior limb of the internal capsule in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2012;136(1–3):55–62.
Jung RE, Chavez RS, Flores RA, et al. White matter correlates of neuropsychological dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(1):e28373.
Xia W, Wang S, Rao H, et al. Disrupted resting-state attentional networks in T2DM patients. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11148.
Miller EK, Cohen JD. An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:167–202.
Reijmer YD, Leemans A, Brundel M, et al. Disruption of the cerebral white matter network is related to slowing of information processing speed in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2013;62(6):2112–5.
Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A. Diffusion tensor imaging and aging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2006;30(6):749–61.
Kennedy KM, Raz N. Aging white matter and cognition: differential effects of regional variations in diffusion properties on memory, executive functions, and speed. Neuropsychologia. 2009;47(3):916–27.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81270416, 81801327, 81801327), the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province of China (2018ZDXM-SF-038), and the Social Development Science and Technology Research Project of Shaanxi Province of China (2019SF-131).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Gao, J., Zhang, D. et al. Correlation between white matter microstructure changes and cognitive function in type 2 diabetes assessed using diffusion tensor imaging. Chin J Acad Radiol 4, 9–20 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-021-00057-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42058-021-00057-3