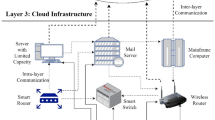
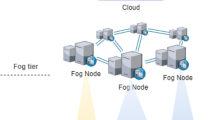
Abstract
The emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) has paved the way for numerous activities leading to smart life, such as health care, surveillance, and smart cities. Since many IoT applications are real-time, they need prompt processing and actuation. To enable this, a network of Fog devices has been developed to provide services close to the data generation points, i.e., the network's edge. Designing a feasible Fog network for managing the explosion of data from the edge to the Cloud requires intelligent monitoring. This work develops a model to address the issue of Fog node placement in a geographical area. The proposed model determines the location of the Fog devices and how to connect them to the Cloud in the best feasible way. Using a multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA), the proposed model minimizes the Deployment Cost (DC) and network latency (NL). The simulation setting is designed in Spyder (Anaconda3) using Python programming.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not Applicable.
References
Ajmera K, Tewari TK (2023) Energy-efficient virtual machine scheduling in IaaS cloud environment using energy-aware green-particle swarm optimization. Int J Inf Technol 15(4):1927–1935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01227-5
Arora U, Singh N (2021) IoT application modules placement in heterogeneous fog–cloud infrastructure. Int J Inf Technol 13(5):1975–1982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00672-4
Balfaqih M et al (2021) Design and development of smart parking system based on fog computing and internet of things. Electron 10(24):1–18. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10243184
Celaya-Echarri M et al (2020) Building decentralized fog computing-based smart parking systems: from deterministic propagation modeling to practical deployment. IEEE Access 8:117666–117688. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004745
Coello, C.A.C. et al.: Evolutionary algorithms for solving multi-objective problems. Springer.
Haider F et al (2021) On the planning and design problem of fog computing networks. IEEE Trans Cloud Comput 9(2):724–736. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2018.2874484
Hurbungs V et al (2021) Fog and edge computing: concepts, tools and focus areas. Int J Inf Technol 13(2):511–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-020-00588-5
OpenfogConsortium: OpenFog Reference Architecture for Fog Computing Produced. Ref Arch. February, 1–162,.
Pahlavan K, Krishnamurthy P (2011) Principles of wireless networks: a unified approach. Prentice Hall PTR, USA
Rahmani AM et al (2018) Exploiting smart e-Health gateways at the edge of healthcare internet-of-things: a fog computing approach. Futur Gener Comput Syst 78:641–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2017.02.014
Sen AAA, Yamin M (2021) Advantages of using fog in IoT applications. Int J Inf Technol 13(3):829–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-020-00514-9
Sham EE, Vidyarthi DP (2022) Admission control and resource provisioning in fog-integrated cloud using modified fuzzy inference system. J Supercomput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04483-7
Sharma M et al (2022) An optimistic approach for task scheduling in cloud computing. Int J Inf Technol 14(6):2951–2961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-022-01045-1
Da Silva RAC, Da Fonseca NLS (2020) Location of fog nodes for reduction of energy consumption of end-user devices. IEEE Trans Green Commun Netw 4(2):593–605. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGCN.2020.2986753
Singh S, Vidyarthi DP (2023) Designing Fog Device Network for Digitization of University Campus. In: Patel KK et al (eds) Soft computing and its engineering applications. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham, pp 123–134
Sohag MU, Podder AK (2020) Smart garbage management system for a sustainable urban life: An IoT based application. Internet of Things 11:100255. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IOT.2020.100255
Srikanth CS et al (2019) Smart waste management using internet-of-things (IoT). Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 8(9):2518–2522. https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.g5334.078919
Vilela PH et al (2019) Performance evaluation of a Fog-assisted IoT solution for e-Health applications. Futur Gener Comput Syst 97:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.02.055
Yadav P, Vidyarthi DP (2023) An efficient fuzzy-based task offloading in edge-fog-cloud architecture. Concurr Comput Pract Exp. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.7843
Zhang D et al (2019) Model and algorithms for the planning of fog computing networks. IEEE Internet Things J 6(2):3873–3884. https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2019.2892940
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi, INDIA, for the facility in carrying out the experiments. One of the authors would acknowledge UGC, India, for the SRF fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Vidyarthi, D.P. Fog node placement using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Int. j. inf. tecnol. 16, 713–719 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01530-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-023-01530-1