Abstract
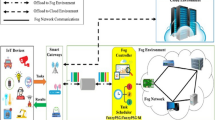
Due to the increasing demands of minimizing the delay for Internet of things (IoT) applications, cloud computing researchers are now moving towards the research in fog computing and edge computing area. Fog computing serves the purpose of bringing devices closer to the proximity of data centre by performing some specific possible tasks nearest to the vicinity of devices requiring the services and ultimately reduces the delay. Thus the complete infrastructure becomes combined fog–cloud in itself. Furthermore, Fog computing serves the need of running the IoT applications by placing the application modules on to the devices available in the said fog–cloud infrastructure. For this purpose, various module placement and scheduling approaches have been developed, but considering the heterogeneous and dynamic nature in the environment is the primary concern of our work. The purpose of this paper is to present the Heterogeneous Shortest Module First (HSMF) Algorithm for placement of the modules of an application in the heterogeneous fog–cloud computing environment. Using this algorithm, we place heterogeneous modules on to the different Fog devices available in the network. The proposed approach is then compared to the available cloud-only and edge-ward application module placement approach. The results obtained from our presented framework clearly state improvement in the total execution time and total network usage.





Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Algorithm included in manuscript.
References
Gupta H, Vahid Dastjerdi A, Ghosh SK, Buyya R (2017) iFogSim: a toolkit for modeling and simulation of resource management techniques in the Internet of Things, Edge and Fog computing environments. Softw Pract Exp 47(9):1275–1296
Mahmud R, Ramamohanarao K, Buyya R (2018) Latency-aware application module management for Fog computing environments. ACM Trans Internet Technol (TOIT) 19(1):1–21
Rahbari D, Nickray M (2019) Low-latency and energy-efficient scheduling in Fog-based IoT applications. Turk J Electr Eng Comput Sci 27(2):1406–1427
Mahmud R, Srirama SN, Ramamohanarao K, Buyya R (2019) Quality of Experience (QoE)-aware placement of applications in Fog computing environments. J Parallel Distrib Comput 132:190–203
Tran MQ, Nguyen DT, Le VA, Nguyen DH, Pham TV (2019) Task placement on fog computing made efficient for iot application provision. Wirel Commun Mob Comput 2019:6215454
Taneja M, Davy A (2017) Resource aware placement of IoT application modules in fog–cloud computing paradigm. In: 2017 IFIP/IEEE symposium on integrated network and service management (IM), pp. 1222–1228
Natesha BV, Guddeti RMR (2018) Heuristic-based IoT application modules placement in the fog–cloud computing environment. In: 2018 IEEE/ACM international conference on utility and cloud computing companion (UCC Companion), IEEE, pp. 24–25
Rezazadeh Z, Rahbari D, Nickray M (2018) Optimized module placement in IoT applications based on fog computing. In: Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Iranian Conference on, IEEE, pp. 1553–1558
Souza VBC, Ramírez W, Masip-Bruin X, Marín-Tordera E, Ren G, Tashakor G (2016) Handling service allocation in combined fog–cloud scenarios. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), IEEE, pp 1–5
Skarlat O, Nardelli M, Schulte S, Dustdar S (2017) Towards qos-aware fog service placement. In: 2017 IEEE 1st international conference on fog and edge computing (ICFEC), IEEE, pp. 89–96
Fan Q, Ansari N (2018) Workload allocation in hierarchical cloudlet networks. IEEE Commun Lett 22(4):820–823
Abbasi M, Yaghoobikia M, Rafiee M, Jolfaei A, Khosravi MR (2020) Efficient resource management and workload allocation in fog–cloud computing paradigm in IoT using learning classifier systems. Comput Commun 153:217–228
Zhang W, Zhang Z, Zeadally S, Chao HC, Leung VC (2020) Energy-efficient workload allocation and computation resource configuration in distributed cloud/edge computing systems with stochastic workloads. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 38(6):1118–1132
Niu X, Shao S, Xin C, Zhou J, Guo S, Chen X, Qi F (2019) Workload allocation mechanism for minimum service delay in edge computing-based power internet of things. IEEE Access 7:83771–83784
Atapattu S, Weeraddana C, Ding M, Inaltekin H, Evans J (2020) Latency minimization with optimum workload distribution and power control for fog computing. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2001.11648.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Availability of data and material
Attached with manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, U., Singh, N. IoT application modules placement in heterogeneous fog–cloud infrastructure. Int. j. inf. tecnol. 13, 1975–1982 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00672-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-021-00672-4