Abstract
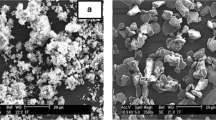
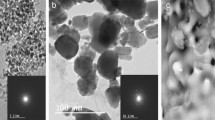
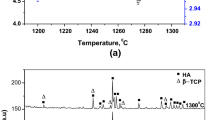
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of lanthanum oxide (La2O3) additive on the microstructural, physical, mechanical, and in vitro bioactivity properties of hydroxyapatite (HA)-alpha alumina (α-Al2O3) composite. The monolithic HA as well as composites of HA-5 wt% α-Al2O3 and HA-5 wt% Al2O3-(0.5 wt%, 1.5 wt%, and 2.5 wt%) La2O3 were uniaxially pelleted at 350 MPa with a size of ∅11 and 11 mm2 and sintered at the temperatures ranging from 1100 to 1300 °C for 4 h. The highest mechanical strength values of 130.20 ± 6.22 MPa, 60.27 ± 9.93 MPa, and 0.96 ± 0.05 MPa m1/2 for compressive strength (σcompressive), three-point bending strength (σthree-point bending), and fracture toughness (Kıc) were obtained for monolithic HA, respectively. While the decomposition (transformation of HA to secondary phases such as beta-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP), alpha-tricalcium phosphate (α-TCP), and calcium oxide (CaO)) ratio was about 5.7% for monolithic HA, it attained to 27.4% for HA-5wt% α-Al2O3 composite. However, addition of La2O3 to HA-5 wt% α-Al2O3 composite contributed to decreasing of decomposition from 27.4 to 22.0%. The mechanical strength values of σcompressive of 214 ± 32.50 MPa, σthree-point bending of 75.70 ± 2.40 MPa, and Kıc of 1.95 ± 0.10 MPa m1/2 were obtained for HA-5wt% α-Al2O3 composite. SEM images exhibited that α-Al2O3 led to decreasing the in vitro bioactivity of HA. However, La2O3 additive contributed to improvement of the mechanical as well as bioactivity properties of HA-5 wt% α-Al2O3 composite. HA-5 wt% α-Al2O3-0.5 wt% La2O3 composite can be used as a bioceramic in human body, because it has enough mechanical properties as well as its desirable in vitro bioactivity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prakasam, M., Locs, J., Salma-Ancane, K., Loca, D., Largeteau, A., Berzina-Cimdina, L.: Fabrication, properties and applications of dense hydroxyapatite: a review. J. Funct. Biomater. 6, 1099–1140 (2015)
Ghazanfari, S.M.H., Zamanian, A.: Phase transformation, microstructural and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite/alumina nanocomposite scaffolds produced by freeze casting. Ceram. Int. 39, 9835–9844 (2013)
Champion, E., Gautier, S., Bernache-Assollant, D.: Characterization of hot pressed Al2O3-platelet reinforced hydroxyapatite composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 7, 125–130 (1996)
Brzezińska-Miecznik, J., Haberko, K., Sitarz, M., Bućko, M.M., Macherzyńska, B., Lach, R.: Natural and synthetic hydroxyapatite/zirconia composites: a comparative study. Ceram. Int. 42, 11126–11135 (2016)
Lih-Jyh, F., Ya-Jing, H., Wen-Cheng, C., Dan-Jae, L.: Preparation of micro-porous bioceramic containing silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite and beta-tricalcium phosphate. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 75, 798–806 (2017)
Hannora, A.E., Ataya, S.: Structure and compression strength of hydroxyapatite/titania nanocomposites formed by high energy ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 658, 222–233 (2016)
Bozkurt, Y., Gokce, H., Pazarlioglu, S., Salman, S.: The effect of yttrium oxide reinforcement on the microstructural and mechanical properties of biologically derived hydroxyapatite. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 127(4), 1403–1406 (2015)
Bartonickova, E., Vojtisek, J., Tkacz, J., Porizka, J., Masilko, J., Moncekova, M., Parizek, L.: Porous Ha/alumina composites intended for bone-tissue engineering. Mater. Technol. 51(4), 631–636 (2017)
Aminzare, M., Eskandari, A., Baroonian, M.H., Berenov, A., Hesabi, Z.R., Taheri, M., Sadrnezhaad, S.K.: Hydroxyapatite nanocomposites: synthesis, sintering and mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 39, 2197–2206 (2013)
Afzal, M.A.F., Kesarwani, P., Reddy, K.M., Kalmodia, S., Basu, B., Balani, K.: Functionally graded hydroxyapatite-alumina-zirconia biocomposite: synergy of toughness and biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 32, 1164–1173 (2012)
Li, J., Fartash, B., Herrnansson, L.: Hydroxyapatite-alumina composites and bone-bonding. Biomater. 16, 417–422 (1995)
Sivaperumal, V.R., Mani, R., Nachiappan, M.S., Arumugam, K.: Direct hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/alumina nanocomposite. Mater. Charact. 134, 416–421 (2017)
Tayebi, S., Mirjalili, F., Samadi, H., Nemati, A.: The effect of additives on the properties of HAp-Al2O3 nano-composite powders. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 17(10), 1033–1041 (2016)
Evis, Z., Doremus, R.H.: Effect of AlF3, CaF2 and MgF2 on hot-pressed hydroxyapatite-nanophase alpha-alumina composites. Mater. Res. Bull. 43, 2643–2651 (2008)
Sung-Jin, K., Hee-Gon, B., Jun-Ho, S., Sang-Yeup, P.: Effect of fluoride additive on the mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite/alumina composites. Ceram. Int. 35, 1647–1650 (2009)
Hae-Won, K., Young-Hag, K., Seung-Beom, S., Hyoun-Ee, K.: Properties of fluoridated hydroxyapatite-alumina biological composites densified with addition of CaF2. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 23, 515–521 (2003)
Bulut, B., Erkmen, Z.E., Kayali, E.S.: Biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite-alumina and hydroxyapatite-zirconia composites including commercial inert glass (CIG) as a ternary component. J. Ceram. Sci. Tech. 07(03), 263–276 (2016)
Kalkandelen, C., Gunduz, O., Akan, A., Oktar, F.N.: Part 1: clinoptilolite-alumina-hydroxyapatite composites for biomedical engineering. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 53, 91–99 (2017)
Li-Li, W., Xiu-Feng, W., Xu, D., Hong-Tao, J.: Preparation of HA-bioglass-Al2O3 biological composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 28, 980–983 (2013)
Yelten, A., Yilmaz, S., Oktar, F.N.: Sol-gel derived alumina-hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate porous composite powders. Ceram. Int. 38, 2659–2665 (2012)
Guidara, A., Chaari, K., Bouaziz, J.: Effect of titania additive on structural and mechanical properties of alumina-fluorapatite composites. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28(12), 1130–1136 (2012)
Branda, F., Arcobello-Varlese, F., Costantini, A., Luciani, G.: Effect of the substitution of M2O3 (M=La, Y, In, Ga, Al) for CaO on the bioactivity of 2.5CaO.2SiO2 glass. Biomater. 23, 711–716 (2002)
Shin-Ike, M., Tsutsui, J., Tanaka, A., Murayama, S., Fujita, A.: Attempts to improve the strength of sintered lanthanum-containing hydroxyapatites. J. Osaka Dent. Uni. 52, 854–861 (1989)
Tanaka, A., Nishimura, Y., Sakaki, T., Fujita, A., Shin-Ike, T.: Histologic evaluation of tissue response to sintered lanthanum-containing hydroxyapatites subcutaneously implanted in rats. J. Osaka Dent. Uni. 23, 111–116 (1989)
Bozkurt, Y., Pazarlioglu, S., Gokce, H., Gurler, I., Salman, S.: Hydroxyapatite lanthanum oxide composites. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 127(4), 1407–1409 (2015)
Khoshsima, S., Yilmaz, B., Tezcaner, A., Evis, Z.: Structural, mechanical and biological properties of hydroxyapatite-zirconia-lanthanum oxide composites. Ceram. Int. 42, 15773–15779 (2016)
Khoshsima, S., Alshemary, A.Z., Tezcaner, A., Surdem, S., Evis, Z.: Impact of B2O3 and La2O3 addition on structural, mechanical and biological properties of hydroxyapatite. Process. Appl. Ceram. 12(2), 143–152 (2018)
Sato, K., Yugami, H., Hashida, T.: Effect of rare-earth oxides on fracture properties of ceria ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 5765–5770 (2004)
Majling, J., Znáik, P., Palová, A., Stevĭk, S., Kovalĭk, S., Agrawal, D.K., Roy, R.: Sintering of the ultrahigh pressure densified hydroxyapatite monolithic xerogels. J. Mater. Res. 12(1), 198–202 (1997)
Rahimiana, M., Ehsani, N., Parvin, N., reza Baharvandi, H.: The effect of particle size, sintering temperature and sintering time on the properties of Al-Al2O3 composites, made by powder metallurgy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 5387–5393 (2009)
Kwon, J., Dai, M., Halls, M.D., Langereis, E., Chabal, Y.J., Gordon, R.G.: In situ infrared characterization during atomic layer deposition of lanthanum oxide. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113, 654–660 (2009)
ASTM C1161-94 (1996) Standard test method for flexural strength of advanced ceramics at ambient temperature. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, USA
Kokubo, T., Yamamuro, T., Hench, L.L., Wilson, J.: Handbook on bioactive ceramics: bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics, vol. 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1990)
ASTM F 1185-88 (1993) Standard specification for composition of ceramic hydroxylapatite for surgical implants. American Society for Testing and Materials, 2000, West Conshohocken, PA, USA
Steele, F.A., Davey, W.P.: The crystal structure of tricalcium aluminate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51(8), 2283–2293 (1975)
Palchesko, R.N., McGowan, K.A., Gawalt, E.S.: Surface immobilization of active vancomycin on calcium aluminum oxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 31, 637–642 (2011)
Tas, C.A.: Chemical preparation of the binary compounds in the calcia-alumina system by self-propagating combustion synthesis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81(11), 2853–2863 (1998)
Evis, Z., Doremus, R.H.: A study of phase stability and mechanical properties of hydroxylapatite-nanosize α-alumina composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 27, 421–425 (2007)
Viswanath, B., Ravishankar, N.: Interfacial reactions in hydroxyapatite/alumina nanocomposites. Scr. Mater. 55, 863–866 (2006)
Ueda, J., Shinoda, T., Tanabe, S.: Evidence of three different Eu2+ sites and their luminescence quenching processes in CaAl2O4:Eu2+. Opt. Mater. 41, 84–89 (2015)
Kazin, P.E., Pogosova, M.A., Trusov, L.A., Kolesnik, I.V., Magdysyuk, O.V., Dinnebier, R.E.: Crystal structure details of La- and Bi-substituted hydroxyapatites: evidence for LaO+ and BiO+ with a very short metal-oxygen bond. J. Solid State Chem. 237, 349–357 (2016)
Choi, M., Janotti, A., Van de Walle, C.G.: Native point defects and dangling bonds in α-Al2O3. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 044501 (2013)
Krishna, R.H., Nagabhushana, B.M., Nagabhushana, H., Chakradhar, R.P.S., Murthy, N.S., Sivaramakrishna, R., Shivakumara, C., Rao, J.L., Thomas, T.: Combustion synthesis approach for spectral tuning of Eu doped CaAl2O4 phosphors. J. Alloys Compd. 589, 596–603 (2014)
Mansour, S.F., Hemeda, O.M., El-Dek, S.I., Salem, B.I.: Influence of La doping and synthesis method on the properties of CoFe2O4 nanocrystals. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 420, 7–18 (2016)
Cerrillo, J.G., Mendoza, A.N.C., Romero, P.M.M., Granadosa, A.H., Hu, H.: Improvement of the morphological and electrical characteristics of Al3+, Fe3+ and Bi3+-doped TiO2 compact thin films and their incorporation into hybrid solar cells. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 72, 106–114 (2017)
Chiba, A., Kimura, S., Raghukandan, K., Morizono, Y.: Effect of alumina addition on hydroxyapatite biocomposites fabricated by underwater-shock compaction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 350, 179–183 (2003)
Evis, Z.: Al3+ doped nano-hydroxyapatites and their sintering characteristics. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 114, 1001–1004 (2006)
Guo, D.G., Wang, A.H., Han, Y., Xu, K.W.: Characterization, physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of La-incorporated apatites. Acta Biomater. 5, 3512–3523 (2009)
Yang, H., Zhang, L., Xu, K.W.: Effect of fabrication processes on orientation growth of La/HAP crystal. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 207, 276–282 (2008)
Lou, W., Dong, Y., Zhang, H., Jin, Y., Hu, X., Ma, J., Liu, J., Wu, G.: Preparation and characterization of lanthanum-incorporated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 21070–21086 (2015)
Aykul, A., Kutbay, I., Evis, Z., Usta, M.: Effect of YF3 on the phase stability and sinterability of hydroxyapatite-partially stabilized zirconia composites. Ceram. Int. 39, 7869–7877 (2013)
Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M., Vallet-Regí, M., Ferreira, J.M.F.: Fabrication of hydroxyapatite bodies by uniaxial pressing from a precipitated powder. Biomater. 22, 583–588 (2001)
Gu, Y.W., Loh, N.H., Khor, K.A., Tor, S.B., Cheang, P.: Spark plasma sintering of hydroxyapatite powders. Biomater. 23, 37–43 (2002)
Khalil, K.A., Kim, S.W., Kim, H.Y.: Consolidation and mechanical properties of nanostructured hydroxyapatite-(ZrO2+3mol%Y2O3) bioceramics by high-frequency induction heat sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 456, 368–372 (2007)
Gu, Y.W., Khor, K.A., Cheang, P.: Bone-like apatite layer formation on hydroxyapatite prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS). Biomater. 25, 4127–4134 (2004)
Patel, N.R., Gohil, P.P.: A review on biomaterials: scope, applications & human anatomy significance. Int. J. Emerging Technol. Adv. Eng. 2(4), 91–101 (2012)
Kim, H.W., Noh, Y.J., Koh, Y.H., Kim, H.E.: Enhanced performance of flourine substituted hydroxyapatite composites for hard tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 14, 899–904 (2003)
Gautier, S., Champion, E., Bernache-Assollant, D.: Toughening characterization in alumina platelets-hydroxyapatite matrix composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 10, 533–540 (1999)
Kim, S., Kong, Y.M., Lee, I.S., Kim, H.E.: Effect of calcinations of starting powder on mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite-alumina bioceramic composite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 13, 307–310 (2002)
Thangamani, N., Chinnakali, K., Gnanam, F.D.: The effect of powder processing on densification, microstructure and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite. Ceram. Int. 28, 355–362 (2002)
Kobayashi, S., Kawai, W., Wakayama, S.: The effect of pressure during sintering on the strength and the fracture toughness of hydroxyapatite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 17, 1089–1093 (2006)
Kothapalli, C., Wei, M., Vasiliev, A., Shaw, M.T.: Influence of temperature and concentration on the sintering behavior and mechanical properties of hydroxyapatite. Acta Mater. 52, 5655–5663 (2004)
Zhang, J., Maeda, M., Kotobuki, N., Hirose, M., Ohgushi, H., Jiang, D., Iwasa, M.: Aqueous processing of hydroxyapatite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 99, 398–404 (2006)
Seo, D.S., Lee, J.K.: Dissolution-resistance of glass-added hydroxyapatite composites. Met. Mater. Int. 15(2), 265–271 (2009)
Chen, Q.Z., Rezwan, K., Armitage, D., Nazhat, S.N., Boccaccini, A.R.: The surface functionalization of 45S5 bioglass-based glass-ceramic scaffolds and its impact on bioactivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 17, 979–987 (2006)
Funding
The authors thank the economic support of Scientific Research Centre of Marmara University (Project No. FEN-K-150218-0051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pazarlioglu, S., Salman, S. Effect of lanthanum oxide additive on the sinterability, physical/mechanical, and bioactivity properties of hydroxyapatite-alpha alumina composite. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 1195–1209 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00336-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00336-4