Abstract
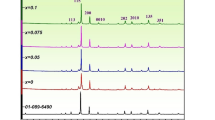
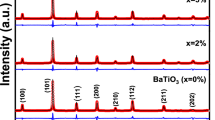
The present study reports detailed guidelines for the preparation of high-quality perovskite (Ba1-xCax)(Ti0.9Sn0.1)O3 (BCTS) (x = 0.0–0.1) lead-free ceramics by solid state reaction. The compositions (x = 0.0–0.04) exhibit orthorhombic–tetragonal phase transition (TO-T), except x ≥ 0.06 that shows a pure tetragonal structure phase which conformed by X-ray diffraction (XRD). The microstructure and purity of the sintered ceramics were examined using scanning electron microscope equipped with an energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM-EDS). Some pores existing in the grain boundary were observed at high concentrations of Ca content. Field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) was used to examine the morphology of sensing film of the calcined powder and it was prepared as a humidity sensor using screen-printing technique. All the compositions exhibited poor sensitivity toward the humidity sensing in the range of 0–98% RH at room temperature. Hot-stage microscope (HSM) has been used to investigate the sintering curve of the pure calcined powder and it was found that the suitable sintering temperature for obtaining a fully dense microstructure is 1400 °C. The highest values of permittivity (εr = 46,515, at 10 kHz) and piezoelectric coefficient (d33 = 510 pC/N) were achieved in the composition x = 0.02. The difference between alumina and platinum crucibles for the processing of the powders has been introduced, and by the aid of dispersive spectrometer analysis and it was indicated that use of alumina crucibles leads to the undesired presence of Al in the ceramics, which can be prevented by using a capped platinum crucibles.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe, B., Cook Jr., W.R., Jaffe, H.: Piezoelectric Ceramics. Academic Press, New York (1971)
Takahashi, T.: Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 69, 691 (1990)
Lines, M.E., Glass, A.M.: Principles and Applications of Ferroelectric and Related Materials. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1979)
Udomporn, A., Ananta, S.: J. Mater. Lett. 58, 1154 (2004)
Forrester, J.S., Zobec, J.S., Phelan, D., Kisi, E.H.: J. Solid State Chem. 177(10), 3553 (2004)
Wongmaneerung, R., Khamman, O., Yimnirun, R., Ananta, S.: J. Electroceram. 21, 798 (2008)
Hollenstein, E., Damjanovic, D., Setter, N.: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 4093 (2007)
Zhang, S.J., Xia, R., Shrout, T. R.: J. Appl. Phys. 100, 104108 (2006)
Zhao, L., Zhang, B.-P., Zhou, P.-F., Zhu, L.-F., Li, J.-F.: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 35, 533 (2015)
Li, W., Xu, Z., Chu, R., Peng, F., Zang, G.: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32, 517 (2012)
Bao, H., Zhou, C., Xue, D., Gao, J., Ren, X.: J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 43, 465401 (2010)
Li, W., Xu, Z., Chu, R., Fu, P., Zang, G.: J. Mater. Lett. 64, 2325 (2010)
Zhu, L.-F., Zhang, B.-P., Zhao, L., Li, J.-F.: J. Mater. Chem. C. 2, 4764 (2014)
Yao, Y.G., Zhou, C., Lv, D.C., Wang, D., Wu, H.J., Yang, Y. D., et al.: EPL. 98(2), 27008 (2012)
Fujii, I., Shimizu, S., Yamashita, K., Nakashima, K., Kumada, N., Moriyoshi, C., Kuroiwa, Y., Fujikawa, Y., Tanaka, D., Furukawa, M., Wada, S.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 99, 202902-1-3 (2011)
Wada, S., Nitta, M., Kumada, N., Tanaka, D., Furukawa, M., Ohno, S., Moriyoshi, C., Kuroiwa, Y.: Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 47, 7678 (2008)
Wang, J., Xu, B.K., Ruan, S.P., Wang, S.P.: Mater. Chem. Phys. 78, 746 (2003)
Jingbo, L., Wenchao, L., Yanxi, Z., Zhimin, W.: Sens. Actuators B Chem. 75, 11 (2001)
Mahmoud, A. E.-r., Viola, G., Afify, A.S., Babeer, A.M., Ferrairs M., J. Porous. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0315-8 (In progress)
Rodriguez-Navarro, C., Ruiz-Agudo, E., Luque, A., Rodriguez-Navarro, A.B., Ortega-Huertas, M.: Am. Mineral. 94, 578 (2009)
Arvanitidis, I., Siche, D., Seetharaman, S.: Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 27(3), 409 (1996)
Chen, M., Xu, Z., Chu, R., Qiu, H., Li, M., Liu, Y., Shao, L., Ma, S., Ji, W., Li, W., Gong, S., Li, G.: Physica B. 433, 43 (2014)
Li, W., Xu, Z., Chu, R., Fu, P., Zang, G.: J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94(12), 4131 (2011)
Zhu, X.N., Zhang, W., Chen, X.M.: J. AIP Adv. 3, 082125 (2013)
Zhu, L.-F., Zhang, B.-P., Zhao, X.-K., Zhao, L., Yao, F.-Z., Han, X., Zhou, P.-F., Jing-Feng: Appl. Phys. Lett. 103, 072905 (2013)
McCafferty, E., Zettlemoyer, A.: Discuss. Faraday Soc. 52, 239 (1971)
Traversa, E.: Sensors Actuators B Chem. 23, 135 (1995)
Seiyama, T., Yamazoe, N., Arai, H.: Sens. Actuators B Chem. 4, 85 (1983)
Lei, C., Bokov, A., Ye, Z.-G.: J. Appl. Phys. 101, 084105 (2007)
Mahmoud, A.E.-r., Afify, A.S., Mohamed, A.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 11591 (2017)
Mitsui, T., Westphal, W.B.: Phys. Rev. 124, 1354 (1961)
Yeo, D.L.Y., Lastochkin, D., Wang, S.-C., Chang, H.-C.: J. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 133902 (2004)
Selmi, A., Khaldi, O., Mascot, M., Jomni, F., Carru, J.C.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11299 (2016)
Wang, L., Wang, X., Li, B.: J. Solid State Commun. 149, 1877 (2009)
Acknowledgments
Authors are immensely grateful to Prof. Jean Marc Tulliani (DISAT, Politecnico di Torino, Italy) for his support and for Dr. A. Mohamed (Chemistry Department, Taibah University, Saudi Arabia) for his comments on an earlier version of the manuscript.
Funding
Abd El-razek and A. Afify received financial support from Erasmus-Mundus program (EMECW, WELCOME Project Action 2 (scholarship application number WELC1104035 and ELC11011869), respectively, Coordination Office: Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoud, A.Er., Afify, A.S., Saed, E.M. et al. Effect of processing conditions on (Ba1-xCax)(Ti0.9Sn0.1)O3 lead-free ceramics for the enhancement of structural, humidity sensing and dielectric properties. J Aust Ceram Soc 55, 933–942 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-00305-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-018-00305-3