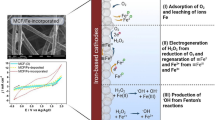
Abstract
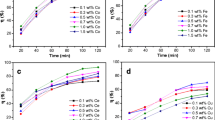
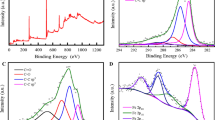
The objective of this study was to develop a carbon felt impregnated with iron (III) sulfate (CF-Fe) for its use both as a cathode and reusable heterogeneous catalyst source in the Fenton reaction for the elimination of sulfamethazine (SMT). The CF-Fe cathode was characterized with Scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive spectrometric (SEM–EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The results of morphology characterization with SEM–EDS revealed that the raw CF displayed a rod-like morphology with a clean and smooth surface. After the impregnation of CF with iron (III) sulfate, the surface of CF-Fe became rough and porous while retaining the raw CF structure well. Furthermore, some solid particles were clearly observed on the FC-Fe, suggesting that the iron species were loaded onto the CF–Fe surface, which contained 57.20% w of iron. The XRD indicated that iron species were successfully embedded in the CF. The effect of the current intensity and injected compressed air flow on the production of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was investigated. From the obtained results, it is shown that the highest concentrations of H2O2 are produced at I = 50 mA and 0.2 L min−1 compressed air flow rate. The effect of current intensity on the degradation and mineralization rate of SMT was investigated by varying the current intensity from 20 to 100 mA. At the optimal current applied (50 mA), the total degradation of SMT and a maximum of 70.2% mineralization were achieved after 120 min electrolysis. In addition, the biodegradability of the solutions electrolyzed under several experimental conditions was performed. The results revealed that the BOD5/COD ratio increased from 0 to 0.42 after 120 min when the solutions were electrolyzed at 100 mA; while, when the electrolysis was performed at 50 mA no biodegradability was observed. Finally, the stability of the CF–Fe cathode was evaluated during six consecutive cycles. The results showed that the total degradation of SMT was achieved in less than 120 min of treatment and remained the same even after six cycles. However, a significant decrease in the mineralization rate was observed, since the mineralization rate decreased from 70 to 36% after six cycles, due to the leaching of iron at the cathode, as demonstrated by the results of the evolution of total iron in solution. In view of the results obtained, the heterogeneous electro-Fenton process using CF-Fe cathode is promising to treat the SMT containing wastewater.
Highlights
-
Development of a carbon felt electrode impregnated with iron (III) sulfate
-
Use of the electrode both as a cathode and as a reusable heterogeneous catalyst source in the Fenton reaction for sulfamethazine (SMT) removal
-
Evaluation of the biodegradability of electrolyzed solutions for various EF experiments.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
References
Aboudalle A, Djelal H, Fourcade F et al (2018a) Metronidazole removal by means of a combined system coupling an electro-Fenton process and a conventional biological treatment: by-products monitoring and performance enhancement. J Hazard Mater 359:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.006
Aboudalle A, Fourcade F, Assadi AA et al (2018b) Reactive oxygen and iron species monitoring to investigate the electro-Fenton performances. Impact of the electrochemical process on the biodegradability of metronidazole and its by-products. Chemosphere 199:486–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.02.075
Ahmadi A, Zarei M, Hassani A et al (2021) Facile synthesis of iron(II) doped carbonaceous aerogel as a three-dimensional cathode and its excellent performance in electro-Fenton degradation of ceftazidime from water solution. Sep Purif Technol 278:119559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119559
Aissani T, Yahiaoui I, Boudrahem F et al (2018) The combination of photocatalysis process (UV/TiO2 (P25) and UV/ZnO) with activated sludge culture for the degradation of sulfamethazine. Sep Sci Technol 53:1423–1433. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1445109
Almansba A, Kane A, Nasrallah N et al (2021a) An engineering approach towards the design of an innovative compact photo-reactor for antibiotic removal in the frame of laboratory and pilot-plant scale. J Photochem Photobiol a: Chem 418:113445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113445
Almansba A, Kane A, Nasrallah N et al (2021b) Innovative photocatalytic luminous textiles optimized towards water treatment: performance evaluation of photoreactors. Chem Eng J 416:129195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129195
Arellano M, Oturan N, Pazos M et al (2020) Coupling electro-Fenton process to a biological treatment, a new methodology for the removal of ionic liquids? Sep Purif Technol 233:115990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115990
Bounab L, Iglesias O, González-Romero E et al (2015) Effective heterogeneous electro-Fenton process of m-cresol with iron loaded actived carbon. RSC Adv 5:31049–31056. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA03050A
Brillas E, Sirés I, Oturan MA (2009) Electro-Fenton process and related electrochemical technologies based on Fenton’s reaction chemistry. Chem Rev 109:6570–6631. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900136g
Caldwell DH, Adams RB (1946) Colorimetric determination of iron in water with o-Phenanthroline. J (am Water Works Assoc) 38:727–730
Chow LKM, Ghaly TM, Gillings MR (2021) A survey of sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics in the environment. J Environ Sci 99:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2020.05.030
Colades JI, Huang C-P, Retumban JD et al (2020) Electrochemically-driven dosing of iron (II) for autonomous electro-Fenton processes with in situ generation of H2O2. J Electroanal Chem 856:113639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113639
Cuerda-Correa EM, Alexandre-Franco MF, Fernández-González C (2020) Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of antibiotics from water. An overview. Water 12(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010102
Dibene K, Yahiaoui I, Yahia Cherif L et al (2020) Paracetamol degradation by photo-activated peroxydisulfate process (UV/PDS): kinetic study and optimization using central composite design. Water Sci Technol 82:1404–1415. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.412
Divyapriya G, Nidheesh PV (2020) Importance of graphene in the electro-Fenton process. ACS Omega 5(10):4725–4732. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04201
Dominguez CM, Oturan N, Romero A et al (2018) Optimization of electro-Fenton process for effective degradation of organochlorine pesticide lindane. Catal Today 313:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.10.028
El Kateb M, Trellu C, Darwich A et al (2019) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes using novel electrode materials for mineralization and biodegradability enhancement of nanofiltration concentrate of landfill leachates. Water Res 162:446–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.07.005
Fan Y, Ji Y, Kong D et al (2015) Kinetic and mechanistic investigations of the degradation of sulfamethazine in heat-activated persulfate oxidation process. J Hazard Mater 300:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.06.058
Fontmorin J-M, Siguié J, Fourcade F et al (2014) Combined electrochemical treatment/biological process for the removal of a commercial herbicide solution, U46D®. Sep Purif Technol 132:704–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.06.024
Fouad K, Gar Alalm M, Bassyouni M, Saleh MY (2020) A novel photocatalytic reactor for the extended reuse of W-TiO2 in the degradation of sulfamethazine. Chemosphere 257:127270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127270
Ganiyu SO, Le TXH, Bechelany M et al (2017) A hierarchical CoFe-layered double hydroxide modified carbon-felt cathode for heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. J Mater Chem A 5:3655–3666. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TA09100H
Ganzenko O, Huguenot D, van Hullebusch ED et al (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation and biological processes for wastewater treatment: a review of the combined approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8493–8524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2770-6
García-Galán MJ, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2012) Kinetic studies and characterization of photolytic products of sulfamethazine, sulfapyridine and their acetylated metabolites in water under simulated solar irradiation. Water Res 46:711–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.035
García-Rodríguez O, Bañuelos JA, El-Ghenymy A et al (2016) Use of a carbon felt–iron oxide air-diffusion cathode for the mineralization of Malachite Green dye by heterogeneous electro-Fenton and UVA photoelectro-Fenton processes. J Electroanal Chem 767:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.01.035
Ghanbari F, Hassani A, Wacławek S et al (2021) Insights into paracetamol degradation in aqueous solutions by ultrasound-assisted heterogeneous electro-Fenton process: key operating parameters, mineralization and toxicity assessment. Sep Purif Technol 266:118533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.118533
Hammouda SB, Fourcade F, Assadi A et al (2016) Effective heterogeneous electro-Fenton process for the degradation of a malodorous compound, indole, using iron loaded alginate beads as a reusable catalyst. Appl Catal B 182:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.09.007
Hammouda SB, Salazar C, Zhao F et al (2019) Efficient heterogeneous electro–Fenton incineration of a contaminant of emergent concern-Cotinine- in aqueous medium using the magnetic double perovskite oxide Sr2FeCuO6 as a highly stable catalayst: degradation kinetics and oxidation products. Appl Catal B 240:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.002
Hassani A, Malhotra M, Karim AV et al (2022) Recent progress on ultrasound-assisted electrochemical processes: a review on mechanism, reactor strategies, and applications for wastewater treatment. Environ Res 205:112463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.112463
Ikram M, Naeem M, Zahoor M et al (2022a) Biodegradation of azo dye methyl red by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: optimization of process conditions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19:9962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19169962
Ikram M, Naeem M, Zahoor M et al (2022b) Bacillus subtilis: as an efficient bacterial strain for the reclamation of water loaded with textile azo dye. Orange II Int J Mol Sci 23:10637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231810637
Kadji H, Yahiaoui I, Garti Z et al (2021) Kinetic degradation of amoxicillin by using the electro-Fenton process in the presence of a graphite rods from used batteries. Chin J Chem Eng 32:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.08.032
Karim AV, Hassani A, Eghbali P et al (2022) Nanostructured modified layered double hydroxides (LDHs)-based catalysts: a review on synthesis, characterization, and applications in water remediation by advanced oxidation processes. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 26:100965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2021.100965
Kaur P, Sangal VK, Kushwaha JP (2019) Parametric study of electro-Fenton treatment for real textile wastewater, disposal study and its cost analysis. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1696-9
Khavari Kashani MR, Kiani R, Hassani A et al (2022) Electro-peroxone application for ciprofloxacin degradation in aqueous solution using sacrificial iron anode: a new hybrid process. Sep Purif Technol 292:121026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121026
Ledjeri A, Yahiaoui I, Kadji H et al (2017) Combination of the Electro/Fe3+/peroxydisulfate (PDS) process with activated sludge culture for the degradation of sulfamethazine. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 53:34–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.04.022
Li Y, Dong H, Li L et al (2021) Recent advances in waste water treatment through transition metal sulfides-based advanced oxidation processes. Water Res 192:116850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116850
Liu J, Han L, An N et al (2017a) Enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity of carbonate-doped anatase TiO2 based on the electron-withdrawing bidentate carboxylate linkage. Appl Catal b: Environ 202:642–652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.09.057
Liu Y, Liu X, Dong W et al (2017b) Efficient adsorption of sulfamethazine onto modified activated carbon: a plausible adsorption mechanism. Sci Rep 7:12437. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12805-6
Liu Y, Wang J, Zhou Z et al (2020) The degradation, biodegradability and toxicity evaluation of sulfamethazine antibiotics by gamma radiation. Open Chem 18:1188–1194. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2020-0156
Lou Y-Y, Geneste F, Soutrel I et al (2020) Alachlor dechlorination prior to an electro-Fenton process: influence on the biodegradability of the treated solution. Sep Purif Technol 232:115936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115936
Mansour D, Fourcade F, Bellakhal N et al (2012) Biodegradability improvement of sulfamethazine solutions by means of an electro-Fenton process. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2023–2034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-1002-7
Mansour D, Fourcade F, Soutrel I et al (2015) Relevance of a combined process coupling electro-Fenton and biological treatment for the remediation of sulfamethazine solutions—application to an industrial pharmaceutical effluent. C R Chim 18:39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2014.05.005
Meijide J, Pazos M, Sanromán MÁ (2019) Heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst for 1-butylpyridinium chloride degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:3145–3156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0403-6
Mesa Medina S, Rey A, Durán-Valle C et al (2021) Performance of iron-functionalized activated carbon catalysts (Fe/AC-f) on CWPO wastewater treatment. Catalysts 11:337. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11030337
Miron SM, Brendlé J, Josien L et al (2019) Development of a new cathode for the electro-Fenton process combining carbon felt and iron-containing organic–inorganic hybrids. C R Chim 22:238–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crci.2018.11.012
Mirzaei A, Chen Z, Haghighat F, Yerushalmi L (2017) Removal of pharmaceuticals from water by homo/heterogonous Fenton-type processes—a review. Chemosphere 174:665–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.019
Nasir N, Daud Z, Abd Kadir A et al (2019) Removal of ammonia nitrogen from rubber industry wastewater using zeolite as adsorbent. Malays J Fundam Appl Sci 15:862–866
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R, Velmathi S, Sanjini NS (2014) Magnetite as a heterogeneous electro Fenton catalyst for the removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 4:5698–5708. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA46969G
Petrucci E, Da Pozzo A, Di Palma L (2016) On the ability to electrogenerate hydrogen peroxide and to regenerate ferrous ions of three selected carbon-based cathodes for electro-Fenton processes. Chem Eng J 283:750–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.030
Poza-Nogueiras V, Rosales E, Pazos M, Sanromán MÁ (2018) Current advances and trends in electro-Fenton process using heterogeneous catalysts—a review. Chemosphere 201:399–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.002
Rezgui S, Amrane A, Fourcade F et al (2018) Electro-Fenton catalyzed with magnetic chitosan beads for the removal of Chlordimeform insecticide. Appl Catal b: Environ 226:346–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.12.061
Rizal S, Abdul Khalil HPS, Oyekanmi AA et al (2021) Cotton wastes functionalized biomaterials from micro to nano: a cleaner approach for a sustainable environmental application. Polymers 13:1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071006
Rosales E, Diaz S, Pazos M et al (2019) Comprehensive strategy for the degradation of anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac by different advanced oxidation processes. Sep Purif Technol 208:130–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.04.014
Saidi I, Fourcade F, Floner D et al (2017) Sulfamethazine removal by means of a combined process coupling an oxidation pretreatment and activated sludge culture—preliminary results. Environ Technol 38:2684–2690. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1273395
Sellers RM (1980) Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen peroxide using potassium titanium(IV) oxalate. Analyst 105:950. https://doi.org/10.1039/an9800500950
Sirés I, Brillas E, Oturan MA et al (2014) Electrochemical advanced oxidation processes: today and tomorrow. A review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:8336–8367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2783-1
Sklari SD, Plakas KV, Petsi PN et al (2015) Toward the development of a novel electro-fenton system for eliminating toxic organic substances from water. Part 2. preparation, characterization, and evaluation of iron-impregnated carbon felts as cathodic electrodes. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:2059–2073. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie5048779
Sopaj F, Oturan N, Pinson J et al (2016) Effect of the anode materials on the efficiency of the electro-Fenton process for the mineralization of the antibiotic sulfamethazine. Appl Catal B: Environ 199:331–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.035
Thor SH, Ho LN, Ong SA et al (2021) Discovering the roles of electrode distance and configuration in dye degradation and electricity generation in photocatalytic fuel cell integrated electro-Fenton process. Sep Purif Technol 278:119652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119652
Wang Q, Tian S, Ning P (2014) Degradation mechanism of methylene blue in a heterogeneous Fenton-like reaction catalyzed by ferrocene. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:643–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie403402q
Xiang Y, Yang X, Xu Z et al (2020) Fabrication of sustainable manganese ferrite modified biochar from vinasse for enhanced adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotics: effects and mechanisms. Sci Total Environ 709:136079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136079
Yahiaoui I, Aissani-Benissad F, Fourcade F, Amrane A (2013) Removal of tetracycline hydrochloride from water based on direct anodic oxidation (Pb/PbO2 electrode) coupled to activated sludge culture. Chem Eng J 221:418–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.091
Yahiaoui I, Aissani-Benissad F, Fourcade F, Amrane A (2015) Removal of a mixture tetracycline-tylosin from water based on anodic oxidation on a glassy carbon electrode coupled to activated sludge. Environ Technol 36:1837–1846. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1013571
Yahiaoui I, Yahia Cherif L, Madi K et al (2018) The feasibility of combining an electrochemical treatment on a carbon felt electrode and a biological treatment for the degradation of tetracycline and tylosin—application of the experimental design methodology. Sep Sci Technol 53:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1385626
Yao B, Luo Z, Yang J et al (2021a) FeIIFeIII layered double hydroxide modified carbon felt cathode for removal of ciprofloxacin in electro-Fenton process. Environ Res 197:111144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2021.111144
Yao Y, Chen Q, Huang Z, Zhou J (2021b) Catalytic activity comparison of typical iron-bearing particle electrodes in heterogeneous electro-Fenton oxidation processes. Environ Technol Innov 21:101321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101321
Yu X, Zhou M, Ren G, Ma L (2015) A novel dual gas diffusion electrodes system for efficient hydrogen peroxide generation used in electro-Fenton. Chem Eng J 263:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.053
Yu F, Li Y, Han S, Ma J (2016) Adsorptive removal of antibiotics from aqueous solution using carbon materials. Chemosphere 153:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.083
Zárate-Guzmán AI, González-Gutiérrez LV, Godínez LA et al (2019) Towards understanding of heterogeneous Fenton reaction using carbon-Fe catalysts coupled to in-situ H2O2 electro-generation as clean technology for wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 224:698–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.101
Zhao Z, Dong W, Wang H et al (2018) Simultaneous decomplexation in blended Cu(II)/Ni(II)-EDTA systems by electroFenton process using iron sacrificing electrodes. J Hazard Mater 350:128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.025
Zhou L, Hu Z, Zhang C et al (2013) Electrogeneration of hydrogen peroxide for electro-Fenton system by oxygen reduction using chemically modified graphite felt cathode. Sep Purif Technol 111:131–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.03.038
Acknowledgements
No financial support exists in this paper.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by IY, TA, FF, AA and FA-B. The first draft of the manuscript was written by TA and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical Standards
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aissani, T., Fourcade, F., Yahiaoui, I. et al. Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process Using a Cathode of Carbon Felt Impregnated with Iron for the Degradation and Biodegradability Enhancement of Sulfamethazine. Int J Environ Res 17, 61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-023-00550-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-023-00550-w