Abstract
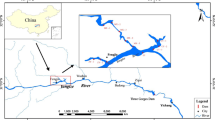
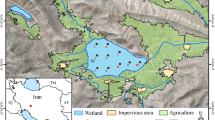
Heavy metals are a serious concern in terms of their pollution in aquatic ecosystems because of their persistence, environmental toxicity and bioaccumulation. Evaluating the total concentration and mobility of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in surficial sediments of Anzali wetland was taken into consideration in this study. Geo-accumulation index, ecological risk index and effects-range-median quotient were calculated to monitor the pollution risks. Additionally, four-step chemical partitioning analysis was performed on samples from eastern parts of the wetland. Index values categorized the whole area within the moderately to non-contaminated class. PTEs Cd > Pb > As > Zn showed remarkable percentages of total concentration in mobile phases (higher bioavailability risks). High values of LOI (loss on ignition) up to 15% and low values of Fe (1.6–2.62%) in sediment samples (higher shares of organics phase compared with Fe–Mn oxides) confirmed the eutrophic conditions. Findings of this research confirm the necessity of including PTEs index analysis and total concentration data accompanied by chemical partitioning results in mid- and long-term decision-making process within the framework of wetlands monitoring plan.
Highlights
-
A comprehensive scheme for integral interpretation of metals risk in wetland sediments
-
High LOI and low Fe content in sediments confirm eutrophic conditions
-
Higher shares of PTEs in oxidizable phase rather than reducibles were seen
-
Negligible share of Cd in residual phase confirms its anthropogenic source








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available in the manuscript.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abu El-Magd SA, Taha TH, Pienaar HH, Breil P, Amer RA, Namour P (2021) Assessing heavy metal pollution hazard in sediments of Lake Mariout. Egypt J African Earth Sci 176:104116
Aghsaei H, Dinan NM, Moridi A, Asadolahi Z, Delavar M, Fohrer N, Wagner PD (2020) Effects of dynamic land use/land cover change on water resources and sediment yield in the Anzali wetland catchment, Gilan. Iran Sci Total Environ 712:136449
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils, 2nd edn. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Amin HA, Saleh HN, Omar MY, Mostafa AR, Ebraham YE (2020) Spatial distribution and assessment of heavy metals pollution in sediments of Tobruk Bay (Libya). Adv Intell Syst Comput 1–55:618–629
Arisekar U, Shakila RJ, Shalini R, Jeyasekaran G (2020) Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in aquatic sediments and freshwater fish caught from Thamirabarani River, the Western Ghats of South Tamil Naduar. Pollut Bull 159(4):111496
Bai J, Cui B, Yang Z, Xu X, Ding Q, Gao H (2010) Heavy metal contamination of cultivated wetland soils along a typical plateau lake from southwest China. Environ Earth Sci 59:1781–1788
Bai J, Cui B, Chen B (2011) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from a typical plateau lake wetland. China Ecol Model 222(2):301–306
Bastami KD, Neyestani MR, Molamohyedin N, Shafeian E, Haghparast S, Shirzadi IA, Baniamam M (2018) Bioavailability, mobility, and origination of metals in sediments from Anzali Wetland, Caspian Sea. Marine pollution bulletin.136: 22–32.
Berenjkar P, Saeedi M, Yuan Q (2019) Assessment of heavy metal release from dredged materials for different disposal scenarios: Study of Anzali international wetland. Iran Process Saf Environ Prot 132:94–104
Boboria D, Maata M, Mani FS (2021) Metal pollution in sediments and bivalves in Marovo Lagoon. Solomon Islands Marine Pollution Bulletin 164:112026
Carr RS, Long ER, Windom HL, Chapman DC, Thursby G, Sloane GM, Wolfe DA (1996) Sediment quality assessment studies of Tampa Bay. Florida Environ Toxically Chem 15:1218–1231
Charkhabi A, Sakizadeh M (2006) Assessment of spatial variation of water quality parameters in the most polluted branch of the Anzali wetland, Northern Iran. Pol J Environ Stud 15:395–403
Charkhabi AH, Sakizadeh M, Bayat R (2008) Land use effects on heavy metal pollution of river sediments in Guilan, southwest of the Caspian Sea. Caspian J Environ Sci 6(2):133–140
Chester R, Hughes RM (1967) A chemical technique for the separation of ferro-manganese minerals, carbonate minerals and adsorbed trace elements from pelagic Sediment. Chem Geol 2:249–262
Darvish Bastami K, Neyestani MR, Molamohyedin N, Shafeian E, Haghparast S, Shirzadi IA, Baniamam M (2018) Bioavailability, mobility, and origination of metals in sediments from Anzali Wetland. Caspian Sea Marine Pollut Bull 136:22–32
Das AK, Chakraborty R, Cervera ML, De la Guardia M (1995) Metal speciation in solid matrices. Talanta 42(8):1007–1030
Davutluoglu OI, Seckın G, Kalat DG, Yılmaz T, Ersu CB (2010) Speciation and implications of heavy metal content in surface sediments of Akyatan Lagoon –Turkey. Desalination 260:199–210
De Caritat P, Cooper M, Jaireth S, Bastrakov E (2011) National Geochemical Survey of Australia: Preliminary implications for energy and mineral exploration. Geoscience Australia Record.
Eghbal N, Nasrabadi T, Karbassi AR, Taghavi L (2019) Evaluating the potential of plants (leaves) in removal of toxic metals from urban soils (case study of a district in Tehran city). Pollution 5(2):387–394
Esmaeilzadeh M, Karbassi A, Bastami KD (2017) Antioxidant response to metal pollution in Phragmites australis from Anzali wetland. Mar Pollut Bull 119(1):376–380
Fazeli G, Karbassi A, Khoramnejadian S, Nasrabadi T (2019) Evaluation of urban soil pollution: a combined approach of toxic metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Int J Environ Res 13(5):801–811
Foerstner U, Wittmann GTW (1981) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis part 1. Soil science society of america book series 5, p 383–411, Madison, Wisconsin, USA
Gibs RJ (1973) Mechanism of trace metal transport in rivers. Science 80:71–73
Canadian Interim Sediment Quality Guidelines (CISQG)(1995) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. Environment Canada, Ottawa. 9 pp.
Hakanson L (1980) An Ecological Risk Index for Aquatic Pollution Control–A Sedimentological Approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hargalani FZ, Karbassi A, Monavari SM, Azar PA (2014) A novel pollution index based on the bioavailability of elements: a study on Anzali wetland bed sediments. Environ Monit Assess 186(4):2329–2348
HosseiniAlhashemi A, Karbassi AR, Kiabi BH, Monavari SM, Nabavi MB (2011) Accumulation and bioaccessibility of trace elements in wetland sediments. Afr J Biotechnol 10(9):1625–1636
Huang L, Rad S, Xu L, Gui L, Song X, Li Y, Wu Z, Chen Z (2020) Heavy Metals Distribution, Sources, and Ecological Risk Assessment in Huixian Wetland. South China Water 12(2):431
Jamshidi S, Bastami KD (2016) Metal contamination and its ecological risk assessment in the surface sediments of Anzali wetland, Caspian Sea. Marine pollution bulletin.113(1–2):559–565.
Karbassi AR, Monavari SM, Bidhendi GRN, Nouri J, Nematpour K (2008) Metal pollution assessment of sediment and water in the Shur River. Environmental monitoring and assessment. 147(1–3):107–116.
Karbassi AR, Nasrabadi T, Rezai M, Modabberi S (2014) Pollution with metals (As, Sb, Hg, Zn) in agricultural soil located close to Zarshuran gold mine, Iran. Environ Eng Manage J (EEMJ).13(1): 115–122.
Khoshkam M, Marzuki A, Al-Mulali U (2016) Socio-demographic effects on Anzali wetland tourism development. Tourism Management.54:96–106.
Kumar V, Sharma A, Pandita S, Bhardwaj R, Thukral AK, Cerda A (2020) A review of ecological risk assessment and associated health risks with heavy metals in sediment from India. Int J Sedim Res 35:516–526
Liang J, Liu J, Yuan X, Zeng G, Lai X, Li X, Wu H, Yuan Y, Li F (2015) Spatial and temporal variation of heavy metal risk and source in sediments of Dongting Lake wetland, mid-south China. J Environ Sci Health Part a 50:100–108
Long ER, MacDonald DD (1998) Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 4(5):1019–1039
Lopez-Sanchez JF, Rubio R, Rauret G (1993) Comparison of two sequential extraction procedures for trace metal partitioning in sediments. Int J Environ Anal Chem 51(1–4):113–121
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Martin JM, Meybeck M (1979) Elemental mass-balance of mineral carried by major world rivers. Mar Chem 7:173–206
Miller WP, Mc Fee WW, Kelly JM (1983) Mobility and retention of heavy metals in sandy soils. J Environ Qual 12(4):579–584
Mohiuddin KM, Ogawa Y, Zakir HM, Otomo K, Shikazono N (2011) Trace elements contamination in water and sediments of an urban river in a developing country. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8:723–736
Muller G (1979) Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veranderungen Seit 1971. Umschau 79:778–783
Nasrabadi T, Ruegner H, Sirdari ZZ, Schwientek M, Grathwohl P (2016) Using total suspended solids (TSS) and turbidity as proxies for evaluation of metal transport in river water. Appl Geochem 68:1–9
Nasrabadi T, Ruegner H, Schwientek M, Bennett J, Fazel Valipour S, Grathwohl P (2018) Bulk metal concentrations versus total suspended solids in rivers: time-invariant & catchment-specific relationships. PLoS ONE 13(1):e0191314
Nasrabadi T, Soodarjani AE, Karbassi A, Baghdadi M (2022) Role of salinity and aeration on flocculation and remobilization of metals during estuarine mixing. Environ Earth Sci 81(10):1–8
Nasrabadi T, Bidhendi GN, Karbassi AR, Mehrdadi N(2010a) Evaluating the efficiency of sediment metal pollution indices in interpreting the pollution of Haraz River sediments, southern Caspian Sea basin. Environmental monitoring and assessment. 171(1–4): 395–410.
NasrabadiT BGN, Karbassi AR, Mehrdadi N (2010b) Partitioning of metals in sediments of the Haraz River (Southern Caspian Sea basin). Environ Earth Sci 59(5):1111–1117
Pertsemli E, Voutsa D (2007) Distribution of heavy metals in Lakes Doirani andKerkini. Northern Greece J Hazardous Material 148:529–537
Salomons W, Förstner U (1980) Trace metal analysis on polluted sediments: part II: evaluation of environmental impact. Environ Technol 1(11):506–517
Shaheen SM, El-Naggar A, Antoniadis V, Moghanm FS, Zhang Z, Tsang DCW, Ok YS, Rinklebe J (2020) Release of toxic elements in fishpond sediments under dynamic redox conditions: assessing the potential environmental risk for a safe management of fisheries systems and degraded waterlogged sediments. J Environ Manage 255:109778
Shariati S, Pourbabaee AA, Alikhani HA (2019) Investigation of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments of Anzali Wetland in North of Iran. Pollution 5(1):211–224
Talebi M, Tabatabaei BES, Akbarzadeh H (2019) Hyperaccumulation of Cu, Zn, Ni, and Cd in Azolla species inducing expression of methallothionein and phytochelatin synthase genes. Chemosphere 230:488–497
Tessier A, Campbell PG, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of Earth’s crust. Bull Geol Soc Am 72:175–192
Vatandoost M, Naghipour D, Omidi S, Ashrafi SD (2018) Survey and mapping of heavy metals in groundwater resources around the region of the Anzali International Wetland; a dataset. Data Brief 18:463–469
Vosoogh A, Saeedi M, Lak R (2016) Heavy metals relationship with water and size-fractionated sediments in rivers using canonical correlation analysis (CCA) case study, rivers of south western Caspian Sea. Environ Monitoring Assess 188:603
Vosoogh A, Saeedi M, Lak R (2017) Metal fractionation and pollution risk assessment of different sediment sizes in three major southwestern rivers of Caspian Sea. Environmental Earth Sciences 76:292
Xu F, Hu B, Dou Y, Song Z, Liu X, Yuan S, Sun Z, Li A, Yin X(2018)Prehistoric heavy metal pollution on the continental shelf off Hainan Island, South China Sea: from natural to anthropogenic impacts around 4.0 kyr BP. The Holocene.
Yancheshmeh RA, Bakhtiari AR, Mortazavi S(2014)Savabieasfahani, M., Sediment PAH: contrasting levels in the Caspian Sea and Anzali Wetland. Marine pollution bulletin.84(1–2):391–400.
Ye H, Zang S, Xiao H, Zhang L (2015) Speciation and ecological risk of heavy metals and metalloid in the sediments of Zhalong Wetland in China. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:115–124
Yong J, Jie Z, Liwei Z, Xiaoli L, DingdingW JL, Jing L (2017) Analysis of heavy metals in the surface sediments of shallow lakes in Nanjishan (Poyang Lake) NaturalWetland in China. J Environ Biol 38:561–570
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi R, Esmaili-Sari A, Mohammadi J, Bakhtiari AR, Savabieasfahani M (2013) Spatial distribution of cadmium and lead in the sediments of the western Anzali wetlands on the coast of the Caspian Sea (Iran). Mar Pollut Bull 74(1):464–470
Zamani-Ahmadmahmoodi R, Bakhtiari AR, Martín JAR (2014) Spatial relations of mercury contents in Pike (Esox lucius) and sediments concentration of the Anzali wetland, along the southern shores of the Caspian Sea. Iran Marine Pollut Bull 84(1–2):97–103
Zhang M, Chen G, Luo Z, Sun X, Xu J(2020)Spatiotemporal variation, seasonal variation, and potential risks of sedimentary heavy metals in a new artificial lagoon in eastern China, 2014–2019.Marine Pollution Bulletin. 157 : 111370
Zolfaghari G (2018) Risk assessment of mercury and lead in fish species from Iranian international wetlands. MethodsX 5:438–447
Funding
Authors would like to thank Department of Environment, Guilan Province for providing financial help (grant No. DOE14155).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nasrabadi, T., Vosoogh, A., Tajziehchi, S. et al. Comprehensive Scheme for Evaluation of Potentially Toxic Elements (PTEs) Pollution in Surface Sediments of Wetlands, Case Study: Anzali Wetland. Int J Environ Res 16, 96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00478-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00478-7