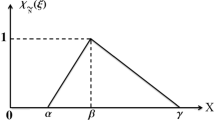
Abstract
This article considers the two-tier supply chain based on the single setup multiple delivery (SSMD) policy between a single vendor and a single buyer. The entire production process is performed in a single setup and the logarithmic reduction function is employed to reduce the expense of this setup. As the machine switches from the in-control stage to the out-of-control stage, the output of the manufactured item is found to be defective. Continuous investment has been made to reduce this imperfect production by improving the quality of the item. Furthermore, this model takes into account incomplete product restructuring. In some cases, due to certain issues, such as lead time, the order quantity may not be received on time. The buyer’s lead time duration is controlled by adding the crashing cost. The purpose of this research is to achieve optimum setup cost and defective item percentage with minimum total supply chain cost under a triangular fuzzy demand. Two numerical examples have been considered to evaluate this model. Moreover, sensitivity analysis, graphical representation, and managerial insights are given. Finally, the model obtains the minimum supply chain cost with decision variables as demonstrated by the numerical study.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björk K. M. (2009) An analytical solution to a fuzzy economic order quantity problem. Int J Approx Reason 50(3):485–493
Ben-Daya M, As’ ad R, Nabi KA (2019) A single-vendor multi-buyer production remanufacturing inventory system under a centralized consignment arrangement. Comput Ind Eng 135:10–27
Chang HC, Ouyang LY, Wu KS, Ho CH (2006) Integrated vendor-buyer cooperative inventory models with controllable lead time and ordering cost reduction. Eur J Oper Res 170(2):481–495
Chang HC, Yao JS, Ouyang LY (2006) Fuzzy mixture inventory model involving fuzzy random variable lead time demand and fuzzy total demand. Eur J Oper Res 169(1):65–80
Castellano D, Gallo M, Santillo LC, Song D (2017) A periodic review policy with quality improvement, setup cost reduction, backorder price discount, and controllable lead time. Prod Manuf Res 5(1):328–350
Dutta P, Chakraborty D, Roy AR (2005) A single-period inventory model with fuzzy random variable demand. Math Comput Model 41(8–9):915–922
Dey BK, Sarkar B, Sarkar M, Pareek S (2019) An integrated inventory model involving discrete setup cost reduction, variable safety factor, selling price dependent demand, and investment. RAIRO-Oper Res 53 (1):39–57
Goyal SK (1977) An integrated inventory model for a single supplier-single customer problem. The Int J Prod Res 15(1):107– 111
Gallego G, Moon I (1993) The distribution free newsboy problem: review and extensions. J Oper Res Soc 44(8):825–834
Giri BC, Roy B (2016) Modelling supply chain inventory system with controllable lead time under price-dependent demand. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 84(9–12):1861–1871
Guchhait R, Dey BK, Bhuniya S, Ganguly B, Mandal B, Bachar RK, Sarkar B, Wee H, Chaudhuri K (2020) Investment for process quality improvement and setup cost reduction in an imperfect production process with warranty policy and shortages. RAIRO-Oper Res 54(1):251–266
Heydari J, Zaabi-Ahmadi P, Choi TM (2018) Coordinating supply chains with stochastic demand by crashing lead times. Comput Oper Res 100:394–403
Jørgensen S, Kort PM (2002) Optimal pricing and inventory policies: Centralized and decentralized decision making. Eur J Oper Res 138(3):578–600
Jha JK, Shanker K (2009) Two-echelon supply chain inventory model with controllable lead time and service level constraint. Comput Ind Eng 57(3):1096–1104
Kazemi N, Ehsani E, Jaber MY (2010) An inventory model with backorders with fuzzy parameters and decision variables. Int J Approx Reason 51(8):964–972
Kumar RS, Tiwari MK, Goswami A (2016) Two-echelon fuzzy stochastic supply chain for the manufacturer-buyer integrated production-inventory system. J Intell Manuf 27(4):875– 888
Khara B, Dey JK, Mondal SK (2020) Sustainable recycling in an imperfect production system with acceptance quality level dependent development cost and demand. Comput Ind Eng 142:106300
Konur D, Yildirim G (2020) Cycle cost considerations in a continuous review inventory control model. J Oper Res Soc 1–22
Lu L (1995) A one-vendor multi-buyer integrated inventory model. Eur J Oper Res 81(2):312–323
Lo ST, Wee HM, Huang WC (2007) An integrated production-inventory model with imperfect production processes and Weibull distribution deterioration under inflation. Int J Prod Econ 106(1):248–260
Lin YJ (2008) Minimax distribution free procedure with backorder price discount. Int J Prod Econ 111(1):118–128
Lin YJ (2009) An integrated vendor-buyer inventory model with backorder price discount and effective investment to reduce ordering cost. Comput Ind Eng 56(4):1597–1606
Mandal P, Giri BC (2015) A single-vendor multi-buyer integrated model with controllable lead time and quality improvement through reduction in defective items. Int J Syst Sci Oper Logist 2(1):1–14
Malik AI, Sarkar B (2018) Optimizing a multi-product continuous-review inventory model with uncertain demand, quality improvement, setup cost reduction, and variation control in lead time. IEEE Access 6:36176–36187
Mukherjee A, Dey O, Giri BC (2019) An integrated imperfect production-inventory model with optimal vendor investment and backorder price discount. In: Information technology and applied mathematics. Springer, Singapore, pp 187–203
Mishra U, Wu JZ, Sarkar B (2020) A sustainable production-inventory model for a controllable carbon emissions rate under shortages. J Clean Prod 256:120268
Ouyang LY, Chang HC (2002) A minimax distribution free procedure for mixed inventory models involving variable lead time with fuzzy lost sales. Int J Prod Econ 76(1):1–12
Porteus EL (1986) Optimal lot sizing, process quality improvement and setup cost reduction. Oper Res 34(1):137–144
Pal B, Sana SS, Chaudhuri K (2014) Joint pricing and ordering policy for two echelon imperfect production inventory model with two cycles. Int J Prod Econ 155:229–238
Rached M, Bahroun Z, Campagne JP (2016) Decentralised decision-making with information sharing vs. centralised decision-making in supply chains. Int J Prod Res 54(24):7274–7295
Sana SS (2011) A production-inventory model of imperfect quality products in a three-layer supply chain. Decis Support Syst 50(2):539–547
Sarkar B, Moon I (2014) Improved quality, setup cost reduction, and variable backorder costs in an imperfect production process. Int J Prod Econ 155:204–213
Sarkar B, Chaudhuri K, Moon I (2015) Manufacturing setup cost reduction and quality improvement for the distribution free continuous-review inventory model with a service level constraint. Int Trans Oper Res 34:74–82
Sarkar B, Mandal B, Sarkar S (2015) Quality improvement and backorder price discount under controllable lead time in an inventory model. Int Trans Oper Res 35:26–36
Sarkar B, Mahapatra AS (2017) Periodic review fuzzy inventory model with variable lead time and fuzzy demand. Int Trans Oper Res 24(5):1197–1227
Sekar T, Uthayakumar R (2018) Optimization of an imperfect manufacturing system for deteriorating items with rework and shortage under inflation. Process Integr Optim Sustain 2(4):303–320
Sarkar M, Chung BD (2019) Flexible work-in-process production system in supply chain management under quality improvement. Int J Prod Res 1–18
Sarkar B, Omair M, Kim N (2020) A cooperative advertising collaboration policy in supply chain management under uncertain conditions. Appl Soft Comput 88:105948
Taleizadeh AA, Zamani-Dehkordi N (2017) Optimizing setup cost in (R, T) inventory system model with imperfect production process, quality improvement, and partial backordering. J Remanuf 7(2-3):199–215
Taleizadeh AA, Soleymanfar VR, Govindan K (2018) Sustainable economic production quantity models for inventory systems with shortage. J Clean Prod 174:1011–1020
Tayyab M, Sarkar B, Yahya B (2019) Imperfect multi-stage lean manufacturing system with rework under fuzzy demand. Mathematics 7(1):13
Yao JS, Chiang J (2003) Inventory without backorder with fuzzy total cost and fuzzy storing cost defuzzified by centroid and signed distance. Eur J Oper Res 148(2):401–409
Funding
The work of the authors are supported by UGC - SAP, Department of Mathematics, The Gandhigram Rural Institute (Deemed to be University) Gandhigram, Dindigul District, Tamil Nadu, India. Pincode: 624 302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karthick, B., Uthayakumar, R. Optimizing an Imperfect Production Model with Varying Setup Cost, Price Discount, and Lead Time Under Fuzzy Demand. Process Integr Optim Sustain 5, 13–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-020-00133-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41660-020-00133-8