Abstract
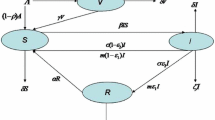
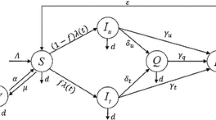
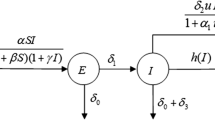
In this paper, we study a stochastic epidemic model with relapse, non linear incidence and a random transmission rate. The existence, uniqueness and boundedness of a positive solution are proved for any positive initial value. Using the Lyapunov analysis, we investigate the asymptotic behaviour of the solution. Mainly, we give sufficient conditions for extinction and persistence of the disease. Then, we propose an optimal control for both deterministic and stochastic models. Finally, we give some numerical illustrations to demonstrate our analytical results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrhazi, B., M. El Fatini, T. Caraballo, and R. Pettersson. 2018. A stochastic SIRI epidemic model with Lévy noise. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems 23 (6): 2415–2431.
Berrhazi, B., M. El Fatini, and A. Laaribi. 2018. A stochastic threshold for an epidemic model with Beddington-DeAngelis incidence, delayed loss of immunity and Lévy noise perturbation. Physica A 507: 312–320.
Berrhazi, B., M. El Fatini, R. Pettersson, and A. Laaribi. 2019. Media effects on the dynamics of a stochastic SIRI epidemic model with relapse and Levy noise perturbation. International Journal of Biomathematics 12: 1950037.
Capasso, V., and G. Serio. 1978. A generalization of the Kermack-McKendrick deterministic epidemic model. Mathematical Biosciences 42 (1): 43–61.
Caraballo, T., M. El Fatini, M. Khalifi, R. Gerlach, and R. Pettersson. 2020. Analysis of a stochastic distributed delay epidemic model with relapse and Gamma distribution kernel. Chaos Solitons Fractals 133: 109643.
Caraballo, T., M. El Fatini, R. Pettersson, and R. Taki. 2018. A stochastic SIRI epidemic model with relapse and media coverage. Discrete & Continuous Dynamical Systems-B 23 (8): 3483–3501.
Crowly, P.H., and E.K. Martin. 1989. Functional responses and interference within and between year classes of a dragonfly population. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 8: 211–221.
El Fatini, M., and B. Boukanjime. 2020. Stochastic analysis of a two delayed epidemic model incorporating Lévy processes with a general non-linear transmission. Stochastic Analysis and Applications 38 (3): 387–402.
El Fatini, M., A. Lahrouz, R. Pettersson, A. Settati, and R. Taki. 2018. Stochastic stability and instability of an epidemic model with relapse. Applied Mathematics and Computation 316: 326–341.
El Fatini, M., I. Sekkak, and A. Laaribi. 2019. A threshold of a delayed stochastic epidemic model with Crowly-Martin functional response and vaccination. Physica A 520: 151–160.
Gaff, H., and E. Schaefer. 2009. Optimal control applied to vaccination and treatment strategies for various epidemiological models. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 6: 469–492.
Georgescu, P., and H. Zhang. 2013. A Lyapunov functional for a SIRI model with nonlinear incidence of infection and relapse. Applied Mathematics and Computation 219 (16): 8496–8507.
Guo, P., X. Yang, and Z. Yang. 2014. Dynamical behaviors of an SIRI epidemic model with nonlinear incidence and latent period. Advances in Difference Equations 2014: 164. 18 pp.
Jiongmin, Y., and X.Y. Zhou. 1999. Stochastic Controls Hamiltonian Systems and HJB Equations, vol. 43. New York: Springer.
Kushner, H.J. 1975. Existence Results for Optimal Stochastic Controls. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications 15 (4): 347–359.
Lahrouz, A., L. Omari, and D. Kiouach. 2011. Global analysis of a deterministic and stochastic nonlinear SIRS epidemic model. Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control 16 (1): 59–76.
Lahrouz, A., and A. Settati. 2014. Necessary and sufficient condition for extinction and persistence of SIRS system with random perturbation. Applied Mathematics and Computation 233: 10–19.
Lahrouz, A., A. Settati, M. El Fatini, R. Pettersson, and R. Taki. 2018. Probability analysis of a perturbed epidemic system with relapse and cure. International Journal of Computational Methods 17: 1850140.
Liu, Q., D. Jiang, T. Hayat, and B. Ahmad. 2018. Stationary distribution and extinction of a stochastic SIRI epidemic model with relapse. Stochastic Analysis and Applications 36: 138–51.
Lukes, D.L. 1982. Differential equations classical to controlled, Mathematics in Science and Engineering, vol. 162. New York: Academic Press.
Mao, X. 2007. Stochastic Differential equations and applications, 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Martins, J., A. Pinto, and N. Stollenwerk. 2009. A scaling analysis in the SIRI epidemiological model. Journal of biological dynamics 3 (5): 479–496.
Michaelis, L., and M.L. Menten. 1913. Die Kinetik der Invertinwirkung. Biochemistry Z 49: 333–369.
Moreira, H.N., and Y. Wang. 1997. Global stability in an SIRI model. SIAM Review 39: 496–502.
Oksendal, B. 1998. Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications, Universitext, 5th ed. Berlin: Springer.
Pontryagin, L.S., V.G. Boltyanskii, R.V. Gamkrelidze, and E.F. Mishchenko. 1962. The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes, vol. 4. London: Gordon and Breach Science.
Lei, Q., and Z. Yang. 2016. Dynamical behaviours of a stochastic SIRI epidemic model. Applicable Analysis 96: 1–13.
Settati, A., A. Lahrouz, A. Assadouq, M. El Fatini, M. El Jarroudi, and K. Wang. 2020. The impact of nonlinear relapse and reinfection to derive a stochastic threshold for SIRI epidemic model. Chaos Solitons Fractals 137: 109897.
Van den Driessche P, P., and J. Watmough. 2002. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartments models of disease transmission. Mathematical biosciences 180: 29–48.
Witbooi, P.J., G.E. Muller, and G.J. Van Schalkwyk. 2015. Vaccination control in a stochastic SVIR epidemic model. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine 2015: 271654.
Xu, R. 2013. Global dynamics of a delayed epidemic model with latency and relapse. Nonlinear Analysis: Modelling and Control 18 (2): 250–263.
Zaman, G., Y. Kang, and I. Jung. 2008. Stability analysis and optimal vaccination of an SIR epidemic model. BioSystems 93: 240–249.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the Editor and the Reviewers for their helpful and constructive comments and suggestions. The authors are also thankful to the laboratory MAD (Management de l’agriculture Durable) of EST Sidi Bannour and the Faculty of sciences, Ibn Tofail University, Kenitra for their help and support.
Funding
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Fatini, M., Sekkak, I., Taki, R. et al. A control treatment for a stochastic epidemic model with relapse and Crowly–Martin incidence. J Anal 29, 713–729 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41478-020-00276-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41478-020-00276-4