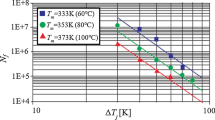
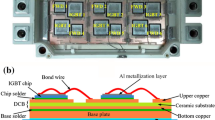
Abstract
A cooling technology roadmap is defined for power electronics modules such as insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT) and wideband gap semiconductor modules (SiC/GaN). These power modules are widely used for inverter and converter applications. Cooling technologies studied include natural air cooling, forced air cooling, forced liquid cooling, and thermal management technologies employing phase change. This work reviews the standard modes of failures of power electronics modules. The work helps to understand the thermal resistances at various interfaces in the module stack. The study highlights the importance of using electrothermal models for power loss estimation. Effective thermal management must ensure the power electronics components' junction (die) temperature is within the desired limits. The developed cooling technology roadmap suggests using heat flux at the module base and heat generation per temperature rise in the die as a metric for selecting cooling technology. Further, the review also stresses the importance of junction temperature swings experienced by the die during transient operation.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Area
- b :
-
Thickness of thermal interface material
- c :
-
Specific heat capacity
- d :
-
Diameter of copper tubes
- E :
-
Energy
- f :
-
Frequency
- g :
-
Acceleration due to gravity
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient
- \(h_{{fg}}\) :
-
Latent heat of vaporisation
- I :
-
Current
- \(K_{I}\) :
-
Exponents for current dependency of switching losses
- \(K_{I}\) :
-
Exponents for voltage dependency of switching losses
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- L :
-
Length of copper tubes
- m :
-
Modulation index
- \(\dot{m}\) :
-
Mass flow rate of the coolant
- N :
-
Number of IGBT modules
- n :
-
Number of transistor/diodes die
- \(n^{\prime }\) :
-
Exponent of Prandtl number
- Nu:
-
Nusselt number
- P :
-
Power
- p :
-
Power density
- \(\Pr\) :
-
Prandtl number
- Q :
-
Heat loss
- \(q_{s} ^{{\prime \prime }}\) :
-
Surface heat flux
- R :
-
Thermal resistance
- \(\text{Re}\) :
-
Reynolds number
- r :
-
Electrical resistance
- \(r_{{CE}}\) :
-
Temperature-dependent bulk resistance of the on-state characteristic for transistor
- \(r_{F}\) :
-
Temperature-dependent bulk resistance of the on-state characteristic for diode
- s :
-
Number of transistor/diode switches active in the circuit
- T :
-
Temperature
- \(TC\) :
-
Temperature coefficients for the switching losses
- \(\Delta T\) :
-
Temperature difference
- V :
-
Voltage
- \(V_{{ceo}}\) :
-
Temperature-dependent threshold voltage of the on-state characteristic for transistor
- \(V_{{Fo}}\) :
-
Temperature-dependent threshold voltage of the on-state characteristic for diode
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density
- \(\mu\) :
-
Viscosity
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Surface tension
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Effectiveness of cooling plate
- \(\lambda\) :
-
Parameter used in calculation of spreading resistance
- \(\cos \Phi\) :
-
Power factor
- \(\Delta T_{e}\) :
-
Degree of superheat
- cond:
-
Conduction
- cp:
-
Cooling plate
- D :
-
Diode
- E :
-
Energy
- j :
-
Junction
- l :
-
Liquid
- p :
-
Plate
- peak:
-
Peak
- ref:
-
Reference
- rms:
-
Root mean square
- s :
-
Source
- sp:
-
Spreading
- sw:
-
Switching
- th:
-
Thermal
- T :
-
Transistor
- v :
-
Vapor
References
Albatran S, Smadi IA, Ahmad HJ, Koran A (2017) Online optimal switching frequency selection for grid-connected voltage source inverters. Electronics (switzerland) 6(4):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics6040110
Andresen M, Liserre M (2014) Impact of active thermal management on power electronics design. Microelectron Reliab 54(9–10):1935–1939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2014.07.069
Bahman AS, Ma K, Blaabjerg F (2018) Coupling and thermal boundary conditions for. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(3):2518–2530
Bennion K, Thornton M (2010) Integrated vehicle thermal management for advanced vehicle propulsion technologies. SAE Technical Papers, no. February. https://doi.org/10.4271/2010-01-0836
Biswal L, Chakraborty S, Som SK (2009) Design and optimization of single-phase liquid cooled microchannel heat sink. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 32(4):876–886
Cougo B, Morais LM, Segond G, Riva R, Tran Duc H (2020) Influence of PWM methods on semiconductor losses and thermal cycling of 15-KVA three-phase SiC inverter for aircraft applications. Electronics (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040620
Ghaisas G, Krishnan S (2019) IHMTC2019-POS-141 analysis of thermal interactions among multiple discrete sources in air-cooled power electronics for vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 25th National and 3rd International ISHMT-ASTFE Heat and Mass Transfer Conference (IHMTC-2019), December 28–21, 2019. IIT Roorkee, Roorkee
Ghaisas G, Krishnan S (2021) Thermal influence coefficients-based electrothermal modeling approach for power electronics. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Manuf Technol 11(8):1187–1196. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcpmt.2021.3096073
Gillot C, Schaeffer C, Massit C, Meysenc L (2001) Double-sided cooling for high power IGBT modules using flip chip technology. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 24(4):698–704
Gu X, Wei B, Zhang G, Wang Z, Chen W (2019) Improved synchronized space vector PWM strategy for three-level inverter at low modulation Index. Electronics (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121400
Hafezi H, Faranda R (2021) A new approach for power losses evaluation of IGBT/diode module. Electronics (switzerland) 10(3):1–21. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10030280
Hu Z, Zhang W, Wu J (2019) An improved electrothermal model to estimate the junction temperature of IGBT module. Electronics (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8101066
Jankowski NR, Mccluskey FP (2009) Modeling transient thermal response of pulsed power electronic packages. In: 2009 IEEE Pulsed Power Conference, pp 820–825. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/PPC.2009.5386368
Jordà X, Perpiñà X, Vellvehi M, Fernández M, Llorente S, Aranda S (2016) Characterization of thermal interface materials for IGBT inverter applications. In: THERMINIC 2016—22nd International Workshop on Thermal Investigations of ICs and Systems, pp 136–140. https://doi.org/10.1109/THERMINIC.2016.7749041
Kandlikar SG, Hayner CN (2009) Liquid cooled cold plates for industrial high- power electronic devices—thermal design and manufacturing considerations. Heat Transfer Eng 30(12):918–930. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457630902837343
Lin SC, Chrysler G, Mahajan R, De VK, Banerjee K (2007) A self-consistent substrate thermal profile estimation technique for nanoscale ICs—Part I: electrothermal couplings and full-chip package thermal model. IEEE Trans Electron Dev 54(12):3342–3350. https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2007.909039
Mathew J, Bhagat A, Ghaisas G, Krishnan S (2021) Control of boiling instabilities in a two-phase pumpless loop using water-alcohol mixtures. J Thermal Sci Eng Appl 13(April):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4049755
Mathew J, Krishnan S (2021) A review on transient thermal management of electronic devices. J Electron Packag 144(1)
Morris GK, Polakowski M, Wei L, Ball MD, Mark G Phillips, Mosey C, Lukaszewski RA (2015) Thermal interface material evaluation for igbt modules under realistic power cycling conditions. In: 2015 IEEE International Workshop on integrated power packaging (IWIPP), pp 111–114. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWIPP.2015.7295991
Mudawar I, Bharathan D, Kelly K, Narumanchi S (2009) Two-phase spray cooling of hybrid vehicle electronics. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 32(2):501–512. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCAPT.2008.2006907
Okumura H (2018) A roadmap for future wide bandgap semiconductor power electronics. MRS Bull 40(5):439–444. https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs.2015.97
Pou J, Osorno D, Zaragoza J, Ceballos S, Jaen C (2011) Power losses calculation methodology to evaluate inverter efficiency in electrical vehicles. In: 2011 7th International Conference-Workshop compatibility and power electronics, CPE 2011—conference proceedings, pp 404–409. https://doi.org/10.1109/CPE.2011.5942269
Qian C, Gheitaghy AM, Fan J, Tang H, Sun B, Ye H, Zhang G (2018) Thermal management on IGBT power electronic devices and modules. IEEE Access 6:12868–12884. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2793300
Rama Raju VSV, Krishnan S (2020) Experimental investigation of two-phase pumpless loop with aqueous anionic surfactant as working fluid. Int J Therm Sci 154(March):106400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106400
Rohsenow WM (1952) MITLibraries. Trans ASME 74:969
Semenic T, Bhunia A, Gollhardt N, Morris G, Lukaszewski R (2017) Low thermal resistance thermal pad for power converter modules. In: 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on power electronics and drive systems (PEDS), pp 453–55. https://doi.org/10.1109/PEDS.2017.8289121
Tuckerman DB, Pease RFW (1981) High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett 2(5):126–129
Valentine N, Das D, Pecht M (2015) Failure mechanisms of insulated gate bipolar transistors ( IGBTs ). In: 2015 NREL Photovoltaic Reliability Workshop, CALCE, Univeristy of Maryland, pp 1–30. http://www.nrel.gov/pv/performance_reliability/pdfs/2015_pvmrw_131_das.pdf
Wang P, Mccluskey P, Bar-Cohen A (2013) Two-phase liquid cooling for thermal management of IGBT power electronic module. J Electron Packag Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4023215
Wang B, Wang L, Yang F, Mu W, Qin M et al (2021) Air-cooling system optimization for IGBT modules in MMC using embedded o-shaped heat pipes”. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron. https://doi.org/10.1109/JESTPE.2021.3054918
Wang Y, Dai X, Liu G, Wu Y, Li D, Jones S (2015) Integrated liquid cooling automotive igbt module for high temperatures coolant application abstract. In: Proceedings of PCIM Europe 2015; International Exhibition and Conference for power electronics, intelligent motion, renewable energy and energy management, pp 19–21
Wintrich A, Ulrich N, Werner T, Reimann T (2015) Application manual power semiconductors. Semikron. https://doi.org/10.1109/50.762905
Xu D, Lu H, Huang L, Azuma S, Kimata M, Uchida R (2002) Power loss and junction temperature analysis of power semiconductor devices. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 38(5):1426–1431. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2002.802995
Yun CS, Malberti P, Ciappa M, Fichtner W (2001) Thermal component model for electrothermal analysis of IGBT module systems. IEEE Trans Adv Packag 24(3):401–406. https://doi.org/10.1109/6040.938309
Zhihong W, Xiezu S, Yuan Z (2018) IGBT junction and coolant temperature estimation by thermal model. Microelectron Reliab 87(June):168–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2018.06.018
Zhu Y, Xiao M, Su X, Yang G, Lu K, Wu Z, Hu Z et al (2007) Power loss and junction temperature analysis in the modular multilevel converters for HVDC transmission systems. J Power Electron 10(3):1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1109/CPE.2011.5942269
Funding
This work was partially funded by Cummins India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaisas, G., Krishnan, S. A Critical Review and Perspective on Thermal Management of Power Electronics Modules for Inverters and Converters. Trans Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 7, 47–60 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-021-00268-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-021-00268-1