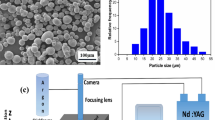
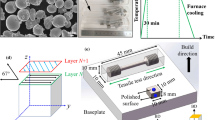
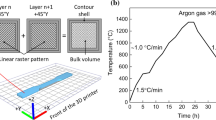
Abstract
Metallic components prepared by additive manufacturing are expected to exhibit microstructural anisotropy due to their layer-by-layer architecture. This in-homogeneity in microstructure can result in variations in the deformation behaviour of materials in different directions, which may lead to premature failure of a component loaded in a particular orientation. Therefore, in the present study, an attempt has been made to investigate the microstructural characteristics and ensuing mechanical properties, in three different orientations with respect to the build direction in a 316L stainless steel, printed using selective laser melting technique. Tensile tests were performed on micro-tensile specimens using a straining stage attached to scanning electron microscope (SEM) while observing crack initiation and propagation. The results were compared with that of conventionally processed AISI 316L stainless steel. Microstructural analysis of the SLM printed component revealed the presence of fine cellular structure within the clearly defined prior melt-pool boundaries. Furthermore, EBSD analysis revealed the presence of columnar grains, which were mostly oriented along the <001> to <101> direction in the build plane and along the <111> direction in the long transverse plane. The favourable grain orientation for twinning in the samples drawn along the build plane led to a better accommodation of plastic strain during tensile deformation. Hence, the sample drawn from build plane showed an improved combination of strength and ductility, in comparison to the transverse orientations. When compared with conventionally processed 316L stainless steel, the SLM printed samples showed a significant increase in the strength in all the three orientations with a concurrent decrease in the ductility.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Experimental data are available in soft copy format wherever such data are acquired from the source equipment/test facility.
References
Akbari M, Kovacevic R (2018) An investigation on mechanical and microstructural properties of 316LSi parts fabricated by a robotized laser/wire direct metal deposition system. Add Manuf 23:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.08.031
Alsalla HH, Smith C, Hao L (2018) Effect of build orientation on the surface quality, microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melting 316L stainless steel. Rapid Prototyp J 24:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-04-2016-0068
ASM International (1992) ASM Handbook, vol 12: Fractography, 9th edn. ASM International, Ohio (ISBN: 978-0-87170-018-6)
Bahl S, Mishra S, Yazar KU, Raju I, Chatterjee KK, Suwas S (2019) Non-equilibrium microstructure, crystallographic texture and morphological texture synergistically result in unusual mechanical properties of 3D printed 316L stainless steel. Add Manuf 28:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.04.016
Bajaj P, Hariharan A, Kini A, Kürnsteiner P, Raabe D, Jägle EA (2020) Steels in additive manufacturing: a review of their microstructure and properties. Mater Sci Eng A 772:138633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2019.138633
Bartolomeu F, Buciumeanu M, Pinto E, Alves N, Carvalho O, Silva FS, Miranda G (2017) 316L stainless steel mechanical and tribological behavior—a comparison between selective laser melting, hot pressing and conventional casting. Add Manuf 16:81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2017.05.007
Chandan AK, Mishra G, Mahato B, Chowdhury SG, Kundu S, Chakraborty J (2019) Stacking fault energy of austenite phase in medium manganese steel. Metall Mater Trans A 50:4851–4866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05367-x
Christian JW, Mahajan S (1995) Deformation twinning. Prog Mater Sci 39:1–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/0079-6425(94)00007-7
Gutierrez-Urrutia I, Zaefferer S, Raabe D (2010) The effect of grain size and grain orientation on deformation twinning in a Fe-22 wt.% Mn-0.6 wt.% C TWIP steel. Mater Sci Eng A 527:3552–3560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.041
Hitzler L, Hirsch J, Heine B, Merkel M, Hall W, Öchsner A (2017) On the anisotropic mechanical properties of selective laser-melted stainless steel. Materials 10:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10101136
Hong Y, Zhou C, Zheng Y, Zhang L, Zheng J, Chen X, An B (2019) Formation of strain-induced martensite in selective laser melting austenitic stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 740–741:420–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.10.121
Im YD, Kim KH, Jung KH, Lee YK, Song KH (2019) Anisotropic mechanical behavior of additive manufactured AISI 316L steel. Metall Mater Trans A 50:2014–2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05139-7
Kruth JP, Mercelis P, Vaerenbergh JV, Froyen L, Rombouts M (2005) Binding mechanisms in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp J 11:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1108/13552540510573365
Kunze K, Etter T, Grässlin J, Shklover V (2015) Texture, anisotropy in microstructure and mechanical properties of IN738LC alloy processed by selective laser melting (SLM). Mater Sci Eng A 620:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.003
Lee YK (2012) Microstructural evolution during plastic deformation of twinning-induced plasticity steels. Scr Mater 66:1002–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.12.016
Lee TH, Oh CS, Kim SJ, Takaki S (2007) Deformation twinning in high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel. Acta Mater 55:3649–3662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.02.023
Marya M, Singh V, Marya S, Hascoet JY (2015) Microstructural development and technical challenges in laser additive manufacturing: case study with a 316L industrial part. Metall Mater Trans B 46:1654–1665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0310-5
Montero-Sistiaga ML, Godino-Martinez M, Boschmans K, Kruth JP, Humbeeck JV, Vanmeensel K (2018) Microstructure evolution of 316L produced by HP-SLM (high power selective laser melting). Add Manuf 23:402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.08.028
Mukherjee M (2019) Effect of build geometry and orientation on microstructure and properties of additively manufactured 316L stainless steel by laser metal deposition. Materialia 7:100359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2019.100359
Pacchioni G (2017) 3D printing: May the strength be with you. Nat Rev Mater 2:17081. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2017.81
Pinomaa T, Lindroos M, Walbrühl M, Provatas N, Laukkanen A (2020) The significance of spatial length scales and solute segregation in strengthening rapid solidification microstructures of 316L stainless steel. Acta Mater 184:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2019.10.044
Pozuelo M, Wittig JE, Jiménez JA, Frommeyer G (2009) Enhanced mechanical properties of a novel high-nitrogen Cr–Mn–Ni–Si austenitic stainless steel via TWIP/TRIP effects. Metall Mater Trans A 40:1826–1834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-9863-8
Song B, Zhao X, Li S, Han C, Wei Q, Wen S, Liu J, Shi Y (2015) Differences in microstructure and properties between selective laser melting and traditional manufacturing for fabrication of metal parts: a review. Front Mech Eng 10:111–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11465-015-0341-2
Spierings AB, Starr TL, Wegener K (2013) Fatigue performance of additive manufactured metallic parts. Rapid Prototyp J 19:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1108/13552541311302932
Sun Z, Tan X, Tor SB, Chua CK (2018) Simultaneously enhanced strength and ductility for 3D-printed stainless steel 316L by selective laser melting. NPG Asia Mater 10:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41427-018-0018-5
Wang YM, Voisin T, McKeown JT, Ye J, Calta NP, Li Z, Zeng Z, Zhang Y, Chen W, Roehling TT, Ott RT, Santala MK, Depond PJ, Matthews MJ, Hamza AV, Zhu T (2018) Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility. Nat Mater 17:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat5021
Yang P, Xie Q, Meng L, Ding H, Tang Z (2006) Dependence of deformation twinning on grain orientation in a high manganese steel. Scr Mater 55:629–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2006.06.004
Zhong Y, Liu L, Wikman S, Cui D, Shen Z (2016) Intragranular cellular segregation network structure strengthening 316L stainless steel prepared by selective laser melting. J Nuclear Mater 470:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2015.12.034
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Director, CSIR-NML Jamshedpur, for his permission to publish this work and providing financial assistance under the i-PSG initiative with Project No. OLP-0341. The authors are grateful to the Advanced Research School for Technology and Product Simulation (ARSTPS) division of CIPET, Chennai, for the help in printing the test block.
Funding
Director, CSIR-National Metallurgical Laboratory Jamshedpur.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, G.K., Chandan, A.K., Srivastava, V.C. et al. Studies on Tensile Behaviour of Selective Laser Melted 316L Stainless Steel Using SEM Straining Stage. Trans Indian Natl. Acad. Eng. 6, 1005–1015 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-021-00214-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-021-00214-1