Abstract
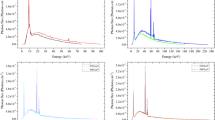
In this study, the gamma radiation shielding features of several environmentally friendly materials were investigated. For this purpose, several attenuation parameters, such as the mass attenuation coefficient (\(\mu /\rho\)), radiation protection efficiency (RPE), and effective atomic number (Zeff) were determined experimentally and compared with numerical data obtained using WinXCom software. In the measurements, the emitted gamma photons were counted by a gamma spectrometer equipped with an HPGe detector using 22Na, 54Mn, 57Co, 60Co, 133Ba, and 137Cs radioactive point sources in the energy region of 81–1333 keV. The obtained results indicate that the \(\mu /\rho\) and RPE values of the samples decrease with an increase in photon energy. The experimental values are in good agreement with those obtained using WinXCom software. The RPE and Zeff results show that among the studied materials, the NaY0.77Yb0.20Er0.03F4 sample has the best gamma radiation shielding effectiveness.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Humphries, Rare Earth Elements: The Global Supply Chain. https://fas.org/sgp/crs/natsec/R41347.pdf. Accessed 15 Sept 2018
K. Binnemans, P.T. Jones, B. Blanpain et al., Recycling of rare earths: a critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 51(1–22), 2013 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.12.037
T. Hirajima, K. Sasaki, A. Bissombolo et al., Feasibility of an efficient recovery of rare earth-activated phosphors from waste fluorescent lamps through dense-medium centrifugation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 44(3), 197–204 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2004.12.014
R. Shanker, A.F. Khan, R. Kumar et al., Understanding and arresting degradation in highly efficient blue emitting BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ phosphor—a longstanding technological problem. J. Lumin. 143, 173–180 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2013.04.021
V. Singh, R.P.S. Chakradhar, J.L. Rao et al., EPR and photoluminescence properties of combustion-synthesized ZnAl2O4:Cr3+ phosphors. J. Mater. Sci. 46(7), 2331–2337 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5078-z
C.W. Won, H.H. Nersisyan, H.I. Won et al., Synthesis of nano-size BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ blue phosphor by a rapid exothermic reaction. J. Lumin. 130(4), 678–681 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2009.11.017
B.M.J. Smets, Phosphors based on rare-earths, a new era in fluorescent lighting. Mater. Chem. Phys. 16(3–4), 283–299 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0254-0584(87)90103-9
J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, Z. Tang et al., Mn2+ luminescence in (Ce, Tb)MgAl11O19 phosphor. Mater. Chem. Phys. 72(1), 81–84 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0254-0584(01)00301-7
B. Park, S. Lee, J. Kang et al., Single-step solid-state synthesis of CeMgAl11O19:Tb phosphor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 28(9), 1467–1471 (2007). https://doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2007.28.9.1467
Q. Liu, W. Feng, T. Yang et al., Upconversion luminescence imaging of cells and small animals. Nat. Protoc. 8(10), 2033–2044 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.114
J.C. Zhou, Z.L. Yang, W. Dong et al., Bioimaging and toxicity assessments of near-infrared upconversion luminescent NaYF4:Yb, Tm nanocrystals. Biomaterials 32(34), 9059–9067 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.038
J. Shan, J. Chen, J. Meng et al., Biofunctionalization, cytotoxicity, and cell uptake of lanthanide doped hydrophobically ligated NaYF4 upconversion nanophosphors. J. Appl. Phys. 104(9), 094308 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3008028
D. Dacyl, D. Uhlich, T. Jüstel, The effect of calcium substitution on the afterglow of Eu2+/Dy3+doped Sr4Al14O25. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 7(2), 164–167 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11532-009-0017-z
L.B.T. La, C. Leatherday, Y.K. Leong et al., Green lightweight lead-free Gd2O3/epoxy nanocomposites with outstanding X-ray attenuation performance. Compos. Sci. Technol. 163, 89–95 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.05.018
J.P. McCaffrey, F. Tessier, H. Shen, Radiation shielding materials and radiation scatter effects for interventional radiology (IR) physicians. Med. Phys. 39(7), 4537–4546 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4730504
G.J. Scuderi, G.V. Brusovanik, D.R. Campbell et al., Evaluation of on-lead-based protective radiological material in spinal surgery. Spine J. 6(5), 577–582 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2005.09.010
Maestro. https://www.ortec-online.com/products/application-software/maestro-mca. Accessed 15 Sept 2018
O. Agar, I. Boztosun, C. Segebade, Multielemental analysis of some soils in Karaman by PAA using a cLINAC. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 122, 57–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.01.011
F. Akman, I.H. Geçibesler, M.I. Sayyed et al., Determination of some useful radiation interaction parameters for waste foods. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 50(6), 944–949 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2018.05.007
H.S. Mann, G.S. Brar, K.S. Mann et al., Experimental investigation of clay fly ash bricks for gamma-ray shielding. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 48(5), 1230–1236 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2016.04.001
J.H. Hubbell, Photon mass attenuation and energy-absorption coefficients. Int. J. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 33(11), 1269–1290 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-708X(82)90248-4
L. Gerward, N. Guilbert, K.B. Jensen et al., WinXCom—a program for calculating X-ray attenuation coefficients. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 71(3), 653–654 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2004.04.040
M.I. Sayyed, Bismuth modified shielding properties of zinc boro-tellurite glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 688, 111–117 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.07.153
F. Akman, R. Durak, M.F. Turhan et al., Studies on effective atomic numbers, electron densities from mass attenuation coefficients near the K edge in some samarium compounds. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 101, 107–113 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2015.04.001
F. Akman, M.R. Kaçal, F. Akman et al., Determination of effective atomic numbers and electron densities from mass attenuation coefficients for some selected complexes containing lanthanides. Can. J. Phys. 95, 1005–1011 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1139/cjp-2016-0811
M.I. Sayyed, H.O. Tekin, O. Kılıcoglu et al., Shielding features of concrete types containing sepiolite mineral: comprehensive study on experimental, XCOM and MCNPX results. Results Phys. 11, 40–45 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2018.08.029
C. Eke, O. Agar, C. Segebade et al., Attenuation properties of radiation shielding materials such as granite and marble against γ-ray energies between 80 and 1350 keV. Radiochim. Acta 105(10), 851–863 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2016-2690
F. Akman, R. Durak, M.R. Kacal et al., Study of absorption parameters around the K edge for selected compunds of Gd. X-Ray Spectrom. 45(2), 103–110 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/xrs.2676
O. Agar, M.I. Sayyed, F. Akman et al., An extensive investigation on gamma ray shielding features of Pd/Ag-based alloys. Nucl. Eng. Technol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.net.2018.12.014
M.I. Sayyed, Y. Elmahroug, B.O. Elbashir et al., Gamma-ray shielding properties of zinc oxide soda lime silica glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(5), 4064–4074 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-6022-z
L. Shamshad, G. Rooh, P. Limkitjaroenporn et al., A comparative study of gadolinium based oxide and oxyfluoride glasses as low energy radiation shielding materials. Prog. Nucl. Energy 97, 53–59 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2016.12.014
I.I. Bashter, Calculation of radiation attenuation coefficients for shielding concretes. Ann. Nucl. Energy 24(17), 1389–1401 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0306-4549(97)00003-0
M.L. Taylor, R.L. Smith, F. Dossing et al., Robust calculation of effective atomic numbers: the Auto-Z eff software. Med. Phys. 39(4), 1769–1778 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3689810
R. El-Mallawany, M.I. Sayyed, M.G. Dong, Comparative shielding properties of some tellurite glasses: part 2. J. Non Cryst. Solids 474, 16–23 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.08.011
P. Kaur, D. Singh, T. Singh, Heavy metal oxide glasses as gamma rays shielding material. Nucl. Eng. Des. 307, 364–376 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2016.07.029
N. Chanthima, J. Kaewkhao, Investigation on radiation shielding parameters of bismuth borosilicate glass from 1 keV to 100 GeV. Ann. Nucl. Energy 55, 23–28 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anucene.2012.12.011
M.I. Sayyed, Investigation of shielding parameters for smart polymers. Chin. J. Phys. 54(3), 408–415 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2016.05.002
O. Agar, Study on gamma ray shielding performance of concretes doped with natural sepiolite mineral. Radiochim. Acta 106(12), 1009–1016 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2018-2981
http://skuld.bmsc.washington.edu/scatter/AS_periodic.html. X-ray Absorption Edges (2018). Accessed 15 Sept 2018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akman, F., Agar, O., Kaçal, M.R. et al. Comparison of experimental and theoretical radiation shielding parameters of several environmentally friendly materials. NUCL SCI TECH 30, 110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-019-0631-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-019-0631-1