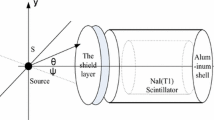
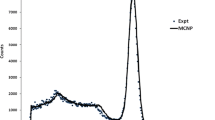
Abstract
NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors have been widely applied for gamma-ray spectrum measurements owing to advantages such as high detection efficiency and low price. However, the mitigation of the limited energy resolution of these detectors, which detracts from an accurate analysis of the instrument spectra obtained, remains a crucial need. Based on the physical properties and spectrum formation processes of NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors, the detector response to gamma photons with different energies is represented by photopeaks that are approximately Gaussian in shape with unique full-width-at-half-maximum (FWHM) values. The FWHM is established as a detector parameter based on resolution calibrations and is used in the construction of a general Gaussian response matrix, which is employed for the inverse decomposition of gamma spectra obtained from the detector. The Gold and Boosted Gold iterative algorithms are employed to accelerate the decomposition of the measured spectrum. Tests of the inverse decomposition method on multiple simulated overlapping peaks and on experimentally obtained U and Th radionuclide series spectra verify the practicability of the method, particularly in the low-energy region of the spectrum, providing for the accurate qualitative and quantitative analysis of radionuclides.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.D. Milbrath, B.J. Choate, J.E. Fast et al., Comparison of LaBr 3: Ce and NAI(Tl) scintillators for radio-isotope identification devices. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 572, 774–784 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2006.12.003
X.M. Fang, L.I. Xin-Nian, Comparison of performances of NaI and HPGe detectors. J. Shanghai Univ Nat. Sci. Ed. 10, 389–392 (2004). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2861.2004.04.013
A. Likar, T. Vidmar, A peak-search method based on spectrum convolution. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36, 1903–1909 (2003). doi:10.1088/0022-3727/36/15/323
M.H. Zhu, L.G. Liu, Q.I. Dong-Xu et al., Least square fitting of low resolution gamma ray spectra with cubic B-spline basis functions. Chin. Phys. C 33, 24–30 (2009). doi:10.1088/1674-1137/33/1/006
M. Morhác, An algorithm for determination of peak regions and baseline elimination in spectroscopic data. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 600, 478–487 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2008.11.132
J.F. Pang, Gamma Energy Spectrum Analysis (Shanxi Science and Technology Press, Xi’an, 1993), pp. 350–716
J.F. He, Q.F. Wu, J.P. Cheng et al., An Inversion Decomposition Test Based on Monte Carlo Response Matrix on the Gamma Ray Spectra from NaI(Tl) Scintillation Detector, in Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, ed. by L.H. Sun (Springer, Singapore, 2016)
B. Tang, L.Q. Ge, F. Fang et al., The Principle of Measurement on Nuclear Radiation (Harbin Engineering University Press, Harbin, 2010), pp. 161–215
Gordon R. Gilmore, Practical Gamma-ray Spectrometry, 2nd edn. (Nuclear Training Services Ltd, Warrington, 2008). doi:10.1002/9780470861981
R.P. Gardner, X. Ai, C.R. Peeples et al., Use of an iterative convolution approach for qualitative and quantitative peak analysis in low resolution gamma-ray spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 652, 544–549 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2010.12.224
M.S. Rahman, G. Cho, Unfolding low-energy gamma-ray spectrum obtained with NaI(Tl) in air using matrix inversion method. J. Sci. Res. 2, 221–226 (2010). doi:10.3329/jsr.v2i2.4372
M. Morhác, V. Matoušek, Complete positive deconvolution of spectrometric data. Digit. Signal Process. 19, 372–392 (2009). doi:10.1016/j.dsp.2008.06.002
J.L. Zheng, Q.X. Ying, W.L. Yang, Signals and Systems (Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2011), pp. 28–130
M.S. Rahman, G. Cho, B.S. Kang, Deconvolution of gamma-ray spectra obtained with NaI(Tl) detector in a water tank. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 135, 203–210 (2009). doi:10.1093/rpd/ncp102
R.L. Heath, Scintillation Spectrometry Gamma-Ray Spectrum Catalogue, vol. 1(Rev), 2nd edn. (γ-Ray Spectrometry Center Idaho National Engineering and Environmental Laboratory, Idaho, 1997). doi:10.2172/4033555
Y. Wang, Y. Wei, Implicit FWHM calibration for gamma-ray spectra. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 24(020403–297), 2013 (2013). doi:10.13538/j.1001-8042/nst.02.005
R. Gold, in An Iterative Unfolding Method for Response Matrices, vol. III. AEC Research and Development Report ANL-6984. Argonne National Laboratories, Argo. (1964). doi: 10.2172/4634295
S. Wachtmeister, S. Csillag, Implementation of gold deconvolution for enhanced energy resolution in EEL spectra. Ultramicroscopy 111, 79–89 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2010.10.006
P. Bandzuch, M. Morhac, J. Kristiak, Study of the Van Cittert and Gold iterative methods of deconvolution and their application in the deconvolution of experimental spectra of positron annihilation. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 384, 506–515 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(96)00874-1
M. Guttormsen, T.S. Tveter, L. Bergholt et al., The unfolding of continuum γ-ray spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 374, 371–376 (1996). doi:10.1016/0168-9002(96)00197-0
M. Miroslav, J. Klimanb, V. Matousek et al., Background elimination methods for multidimensional coincidence γ-ray spectra. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 401, 113–132 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(97)01023-1
C. Xu, I. Aissaoui, S. Jacquey, Algebraic analysis of the Van Cittert iterative method of deconvolution with a general relaxation factor. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 11, 2804–2808 (1994). doi:10.1364/JOSAA.11.002804
M. Jandel, M. Morhac, J. Kliman et al., Decomposition of continuum γ-ray spectra using synthesized response matrix. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 516, 172–183 (2004). doi:10.1016/j.nima.2003.07.047
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11365001), National Major Scientific Equipment Development Projects (Grant No. 041514065), the Educational Commission of Jiangxi Province of China (Grant No. GJJ13464), Plan of Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20141BBE50024), and the Fundamental Science on Radioactive Geology and Exploration Technology Laboratory, East China Institute of Technology (Grant No. RGET1316).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, JF., Yang, YZ., Qu, JH. et al. An inversion decomposition method for better energy resolution of NaI(Tl) scintillation detectors based on a Gaussian response matrix. NUCL SCI TECH 27, 58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0062-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41365-016-0062-1