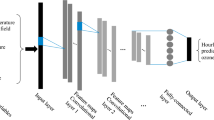
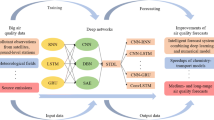
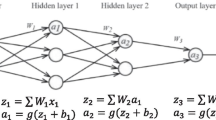
Abstract
Nowadays, accurate time series predictions rely greatly on deep learning models, as they have excellent predictive abilities and do not necessitate complex feature engineering tasks. Nevertheless, current state-of-the-art deep learning models still demonstrate shortcomings in coping with long-term-dependent sequences and periodic data. In this research paper, we shine a light on the models Prophet and Neural Prophet, presenting a comprehensive comparison of their abilities to predict ozone pollution levels based on data from a fixed station of the National Air Quality Monitoring Network (RSNQA) in Tunisia. Although both models produced results that showed >90% correlation with the test sample measures, they also showed that Neural Prophet provides a 70% improvement in accuracy over the Prophet model for the performance indicators MAE, MAPE, and MASE. This is due to the contribution of deep learning in the Neural Prophet model, and reveals the weaknesses of the Prophet model compared to its successor.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Athira V, Geetha P, Vinayakumar R, Soman KP (2018) DeepAirNet: applying recurrent networks for air quality prediction. Procedia Comput Sci 132:1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PROCS.2018.05.068
Carslaw DC, Ropkins K (2012) openair—an R package for air quality data analysis. Environ Model Softw. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2011.09.008
Dahech S, Daoud A, Beltrando G (2011) Les inégalités spatiales de la qualité de l’air dans l’agglomération de Sfax et ses environs: Le cas Des températures, de la brise, du CO et SO2. Cybergeo. https://doi.org/10.4000/CYBERGEO.24701
Du S, Li T, Yang Y, Horng SJ (2021) Deep air quality forecasting using hybrid deep learning framework. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 33:2412–2424. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2019.2954510
Du J, Qiao F, Lu P, Yu L (2022) Forecasting ground-level ozone concentration levels using machine learning. Resour Conserv Recycl 184:106380. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2022.106380
Eslami E, Choi Y, Lops Y, Sayeed A (2019) A real-time hourly ozone prediction system using deep convolutional neural network. Neural Comput Appl 3213(32):8783–8797. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-019-04282-X
Ghoneim OA, Doreswamy, Manjunatha BR (2017) Forecasting of ozone concentration in smart city using deep learning. In: 2017 Int Conf on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI), Udupi, India, 13–16 Sept 2017, pp 1320–1326. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCI.2017.8126024
Harrou F, Dairi A, Sun Y, Kadri F (2018) Detecting abnormal ozone measurements with a deep learning-based strategy. IEEE Sens J 18:7222–7232. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2018.2852001
Hsieh H-P, Wu S, Ko C-C et al (2022) Forecasting fine-grained air quality for locations without monitoring stations based on a hybrid predictor with spatial-temporal attention based network. Appl Sci 12:4268. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP12094268
Huang B, Zheng H, Guo X et al (2021) A novel model based on DA-RNN network and skip gated recurrent neural network for periodic time series forecasting. Sustainability 14:326. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU14010326
Jin XB, Gong WT, Kong JL et al (2022) A variational Bayesian deep network with data self-screening layer for massive time-series data forecasting. Entropy 24:335. https://doi.org/10.3390/E24030335
Kleinert F, Leufen LH, Lupascu A, Butler T, Schultz MG (2022) Representing chemical history in ozone time-series predictions—a model experiment study building on the MLAir (v1.5) deep learning framework. Geosci Model Dev 15:8913–8930. https://gmd.copernicus.org/preprints/gmd-2022-122/. Accessed 25 May 2022
Kristiani E, Lin H, Lin JR et al (2022) Short-term prediction of PM2.5 using LSTM deep learning methods. Sustainability 14:2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU14042068
Lara-Benítez P, Carranza-García M, Martínez-Álvarez F, Riquelme JC (2020) On the performance of deep learning models for time series classification in streaming. Adv Intell Syst Comput 1268:144–154 (arxiv.2003.02544)
Liu H, Yan G, Duan Z, Chen C (2021) Intelligent modeling strategies for forecasting air quality time series: a review. Appl Soft Comput 102:106957. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2020.106957
Ma J, Cheng JCP, Lin C et al (2019) Improving air quality prediction accuracy at larger temporal resolutions using deep learning and transfer learning techniques. Atmos Environ 214:116885. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2019.116885
Mao W, Jiao L, Wang W (2022) Long time series ozone prediction in China: A novel dynamic spatiotemporal deep learning approach. Build Environ 218:109087. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BUILDENV.2022.109087
Masmoudi S, Elghazel H, Taieb D et al (2020) A machine-learning framework for predicting multiple air pollutants’ concentrations via multi-target regression and feature selection. Sci Total Environ 715:136991. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.136991
MengaraMengara AG, Park E, Jang J, Yoo Y (2022) Attention-based distributed deep learning model for air quality forecasting. Sustainability 14:3269. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU14063269
Nath P, Saha P, Middya AI, Roy S (2021) Long-term time-series pollution forecast using statistical and deep learning methods. Neural Comput Appl 33:12551–12570. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00521-021-05901-2/FIGURES/13
Navares R, Aznarte JL (2020) Predicting air quality with deep learning LSTM: towards comprehensive models. Ecol Inform 55:101019. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOINF.2019.101019
Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, Killeen T (2019) PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv Neural Inf Proc Syst 32
Qin Y, Song D, Cheng H, et al (2017) A dual-stage attention-based recurrent neural network for time series prediction. In: Proc 26th Int J Conf on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-17), Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 Aug 2017 (arxiv.1704.02971)
Ren X, Mi Z, Georgopoulos PG (2020) Comparison of machine learning and land use regression for fine scale spatiotemporal estimation of ambient air pollution: modeling ozone concentrations across the contiguous United States. Environ Int 142:105827. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2020.105827
Ren X, Mi Z, Cai T et al (2022) Flexible Bayesian ensemble machine learning framework for predicting local ozone concentrations. Environ Sci Technol 56:3871–3883. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACS.EST.1C04076/SUPPL_FILE/ES1C04076_SI_001.PDF
Samal K, Babu K, Das S (2018) Spatio-temporal prediction of air quality using distance based interpolation and deep learning techniques. EAI Endorsed Trans Smart Cities. https://doi.org/10.4108/EAI.15-1-2021.168139
Snoun H, Bellakhal G, Kanfoudi H et al (2019a) One-way coupling of WRF with a Gaussian dispersion model: a focused fine-scale air pollution assessment on southern Mediterranean. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22892–22906. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-019-05486-3
Snoun H, Kanfoudi H, Bellakhal G, Chahed J (2019b) Validation and sensitivity analysis of the WRF mesoscale model PBL schemes over Tunisia using dynamical downscaling approach. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-019-0103-3
Snoun H, Kanfoudi H, Bellakhal G, Chahed J (2021) Hazardous materials prediction using an artificial neural network and meteorological FASDAS data assimilation. Environ Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_320
Soh PW, Chang JW, Huang JW (2018) Adaptive deep learning-based air quality prediction model using the most relevant spatial-temporal relations. IEEE Access 6:38186–38199. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2849820
Zhang Z, Zeng Y, Yan K (2021) A hybrid deep learning technology for PM2.5 air quality forecasting. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:39409–39422. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-021-12657-8
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Facebook data science team for the provision of the Neural Prophet model website (https://neuralprophet.com/) used in this publication. We also thank the Tunisian National Agency for Environment Protection (ANPE) for providing the air quality monitoring data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author’s contributions
Hatem Cherif conceived, designed and drafted the manuscript. Hosni Snoun conceived and coordinated the study and contributed to the acquisition of resources. Ghazi Belkakhal and Hatem Kanfoudi carried out the literature review and supervised the research study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed Ksibi.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chérif, H., Snoun, H., Bellakhal, G. et al. Forecasting of ozone concentrations using the Neural Prophet model: application to the Tunisian case. Euro-Mediterr J Environ Integr 8, 987–998 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00414-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41207-023-00414-x