Abstract
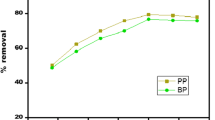
The removal of methylene blue dye from wastewater using Ailanthus excelsa Roxb was investigated via batch mode in this study. The following parameters were used: pH 2–12, contact time 0–240 min, adsorbent dose 0.1–1 g and dye concentration 12.5, 25, 50, 75 and 100 ppm. Various isotherms including Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) models and kinetics study including first-order, second-order, Lagergren equation and pseudo-second-order were carried out. The removal efficiency was found to be 68% at pH of 10, contact time of 180 min, initial concentration 100 ppm and 0.5 g/100 mL adsorbent dose at 300 K. Based on the coefficient of correlation, pseudo-second-order kinetics and the Freundlich isotherm model were found to best represent the dye removal. The experimental adsorption capacity was found to be 18.867 mg g−1. Thermodynamics study showed that the experiment performed was endothermic and spontaneous.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Color index
- MB:
-
Methylene blue
- ALP:
-
Ardu leaf powder
- SSE:
-
Squares of the errors
- RMSE:
-
Residual root mean square error
- χ2:
-
Chi-square test
- R2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
References
Khamparia, S., Jaspal, D., & Malviya, A. (2018). 10 green and eco-friendly materials for the removal of phosphorus from wastewater. Life Cycle Assessment of Wastewater Treatment
Willmott N, Guthrie J, Nelson G (1998) The biotechnology approach to colour removal from textile effluent. J Soc Dye Colour 114:38–41
Isah UA, Lawal M (2012) Acid activated tea bag waste as an adsorbent for the removal of chromium ions from tannery waste water. Pelagia Res Library 3:4033–4035
Bansal S, Kushwaha JP, Sangal VK (2013) Electrochemical treatment of reactive black 5 textile wastewater: optimization, kinetics, and disposal study. Water Environ Res 85(12):2294–2306
Ahmad R (2009) Studies on adsorption of crystal violet dye from aqueous solution onto coniferous pinus bark powder (CPBP). J Hazard Mater 171:767–773
Srivastava R (2016) Dye removal through eco-friendly and economic viable adsorbent. Int j Sci Innov Res 4(1)
Hameed BH (2009) Spent tea leaves: a new non-conventional and low-cost adsorbent for removal of basic dye from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 161(2-3):753–759
Gupta VK (2009) Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review. J Environ Manag 90(8):2313–2342
Sud D, Mahajan G, Kaur MP (2008) Agricultural waste material as potential adsorbent for sequestering heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions–a review. Bioresour Technol 99(14):6017–6027
Foo KY (2012) Preparation, characterization and evaluation of adsorptive properties of orange peel based activated carbon via microwave induced K2CO3 activation. Bioresour Technol 104:679–686
Jat HS, Singh RK, Mann JS (2011) Ardu (Ailanthus sp) in arid ecosystem: a compatible species for combating with drought and securing livelihood security of resource poor people
Basha S, Murthy ZVP, Jha B (2009) Sorption of hg (II) onto Carica papaya: experimental studies and design of batch sorber. Chem Eng J 147(2-3):226–234
Wong S, Ngadi N, Inuwa IM, Hassan O (2018) Recent advances in applications of activated carbon from biowaste for wastewater treatment: a short review. J Clean Prod 175:361–375
Zamri TKATM, Munaim MSA, Abdul Z (2017) Regression analysis for the adsorption isotherms of natural dyes onto bamboo yarn. Int Res J Eng Technol 4(6):1699–1703
Pathania D, Sharma S, Singh P (2017) Removal of methylene blue by adsorption onto activated carbon developed from Ficus carica bast. Arab J Chem 10:S1445–S1451
Garg VK, Amita M, Kumar R, Gupta R (2004) Basic dye (methylene blue) removal from simulated wastewater by adsorption using Indian rosewood sawdust: a timber industry waste. Dyes Pigments 63(3):243–250
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Abdelwahab O (2009) Treatment of artificial textile dye effluent containing direct yellow 12 by orange peel carbon. Desalination 238(1-3):210–232
Ramaraju B, Manoj Kumar Reddy P, Subrahmanyam C (2014) Low cost adsorbents from agricultural waste for removal of dyes. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 33(1):38–46
Pandey PK, Sharma SK, Sambi SS (2015) Removal of lead (II) from waste water on zeolite-nax. J Environ Chem Eng 3(4):2604–2610
Banerjee K, Ramesh ST, Gandhimathi R, Nidheesh PV, Bharathi KS (2012) A novel agricultural waste adsorbent, watermelon shell for the removal of copper from aqueous solutions. Iranica J Energy Environ 3(2):143–156
Han R, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang Y, Xie F, Cheng J, Tang M (2009) Adsorption of methylene blue by phoenix tree leaf powder in a fixed-bed column: experiments and prediction of breakthrough curves. Desalination 245(1-3):284–297
Faust SD, Aly OM (1987) Burterworth publishers. Stoneham, M.A, USA
Langmuir I (1918) J Am Chem Soc 40:1361
Ho YS, Thesis PD (1995) Univ. Birmingham, Birmingham. In: U.K
Lagergren S(1898) Kungliga Suenska Vetens kapsakademiens Handlingar, 24:
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivers A, Vermenlem T (1966) Ind Eng Chem Res 5:212
Ghogomu JN, Noufame TD, Ketcha MJ, Ndi NJ (2013) Removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by kaolinite and Metakaolinite materials. Current J App Sci Techn:942–961
Zuo R, Chen M, Lin Y, Yang J, Jin S, Yue W, Teng Y (2019) Effect of a humic acid colloid on the sorption behaviour of Sr onto soil in a candidate high-level radioactive waste geological disposal site. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):25235–25246
Nasuha N, Hameed BH, Din ATM (2010) Rejected tea as a potential low-cost adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue. J Hazard Mater 175(1-3):126–132
Tang, R., Dai, C., Li, C., Liu, W., Gao, S., & Wang, C. (2017). Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using agricultural residue walnut shell: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. J Chem
Annadurai G, Juang RS, Lee DJ (2002) Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 92(3):263–274
Pavan FA, Mazzocato AC, Gushikem Y (2008) Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by adsorption using yellow passion fruit peel as adsorbent. Bioresour Technol 99(8):3162–3165
Banerjee S, Dastidar MG (2005) Use of jute processing wastes for treatment of wastewater contaminated with dye and other organics. Bioresour Technol 96(17):1919–1928
Sharma, A., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2005) Utilization of a biosorbent based on Azadirachta indica (neem) leaves for removal of water-soluble dyes
Gupta N, Kushwaha AK, Chattopadhyaya MC (2012) Adsorption studies of cationic dyes onto Ashoka (Saraca asoca) leaf powder. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(4):604–613
Sogbochi E, Balogoun CK, Dossa CPA, Sohounhloue DCK (2017) Evaluation of adsorption capacity of methylene blue in aqueous medium by two adsorbents: the raw hull of Lophira lanceolata and its activated carbon. Am J Phys Chem 6:76–87
Kong L, Gong L, Wang J (2015) Removal of methylene blue from wastewater using fallen leaves as an adsorbent. Desalin Water Treat 53(9):2489–2500
Ansari, S. A., Khan, F., & Ahmad, A. (2016) Cauliflower leave, an agricultural waste biomass adsorbent, and its application for the removal of MB dye from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Int J Anal Chem
Patriota SN, Francisco W, Araújo DF, Mulholland DS (2020) Adsorption of copper and methylene blue on an agrowaste of Mauritia Flexuosa. J Environ Eng 146(6):04020039
Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS (2020) Mesoporous Iraqi red kaolin clay as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue dye: adsorption kinetic, isotherm and mechanism study. Surf Int 18:100422
Rangabhashiyam S, Lata S, Balasubramanian P (2018) Biosorption characteristics of methylene blue and malachite green from simulated wastewater onto Carica papaya wood biosorbent. Surf Int 10:197–215
Etim UJ, Umoren SA, Eduok UM (2016) Coconut coir dust as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of cationic dye from aqueous solution. J Saudi Chem Soc 20:S67–S76
Kumar PS, Abhinaya RV, Lashmi KG, Arthi V, Pavithra R, Sathyaselvabala V, Sivanesan S (2011) Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution by agricultural waste: equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Colloid J 73(5):651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bansal, S., Pandey, P.K. & Upadhayay, S. Methylene Blue Dye Removal from Wastewater Using Ailanthus Excelsa Roxb as Adsorbent. Water Conserv Sci Eng 6, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-020-00097-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-020-00097-3