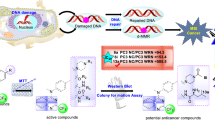
Abstract
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused a worldwide pandemic since 2019, spreading rapidly and posing a significant threat to human health and life. With over 6 billion confirmed cases of the virus, the need for effective therapeutic drugs has become more urgent than ever before. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) is crucial in viral replication and transcription, catalysing viral RNA synthesis and serving as a promising therapeutic target for developing antiviral drugs. In this article, we explore the inhibition of RdRp as a potential treatment for viral diseases, analysing the structural information of RdRp in virus proliferation and summarizing the reported inhibitors’ pharmacophore features and structure–activity relationship profiles. We hope that the information provided by this review will aid in structure-based drug design and aid in the global fight against SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
Exploring the potential clinical targets for attenuating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by structure-based drug designing of RdRp inhibitors.
-
RdRp catalytic site and druggable cavities predictions of SARS-CoV-2.
-
Pharmacophoric features and structure–activity relationship analysis of different repurposed therapeutic drugs for COVID-19 against RdRp of SARS-CoV-2.
-
Current treatments are logistically challenging, increasing the need for safe and effective oral therapies.
-
Ongoing global efforts to prevent the spread of COVID-19 disease and the current status of SARS-CoV-2.



























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data supporting this work is available in this paper, and all other details are present in the supporting information. Furthermore, the data supporting this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- EUA:
-
Emergency Use Authorization
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- ACE2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- NHC:
-
N4-hydroxycytidine
- RSV:
-
Respiratory syncytial virus
- TNF-α:
-
Tumour necrosis factor α
- ExoN:
-
Exoribonuclease
- CTP:
-
Cytidine triphosphate
- HBD:
-
Hydrogen-bond donors
- HBA:
-
Hydrogen-bond acceptors
- NiRAN:
-
Nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyl transferase
References
Park SE (2020) Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus disease-19). Pediatr Infect Vaccine 27(1):1–10
Ilyas M, Muhammad S, Iqbal J, Amin S, Al-Sehemi AG, Algarni H, Alarfaji SS, Alshahrani MY, Ayub K (2022) Insighting isatin derivatives as potential antiviral agents against NSP3 of COVID-19. Chem Pap 76(10):6271–6285
Wu W, Wang A, Liu M (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395(10223):497–506
Dyall J, Gross R, Kindrachuk J, Johnson RF, Olinger GG Jr, Hensley LE, Frieman MB, Jahrling PB (2017) Middle East respiratory syndrome and severe acute respiratory syndrome: current therapeutic options and potential targets for novel therapies. Drugs 77(18):1935–1966
Deng S-Q, Peng H-J (2020) Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China. J Clin Med 9(2):575
Allan M, Lièvre M, Laurenson-Schaefer H, de Barros S, Jinnai Y, Andrews S, Stricker T, Formigo JP, Schultz C, Perrocheau A (2022) The World Health Organization COVID-19 surveillance database. Int J Equity Health 21(Suppl 3):167
Agostini ML, Andres EL, Sims AC, Graham RL, Sheahan TP, Lu X, Smith EC, Case JB, Feng JY, Jordan R (2018) Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. MBio 9(2):e00221-18
Harrison AG, Lin T, Wang P (2020) Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and pathogenesis. Trends Immunol 41(12):1100–1115
Gordon CJ, Tchesnokov EP, Feng JY, Porter DP, Götte M (2020) The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J Biol Chem 295(15):4773–4779
Yin W, Mao C, Luan X, Shen D-D, Shen Q, Su H, Wang X, Zhou F, Zhao W, Gao M (2020) Structural basis for inhibition of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir. Science 368(6498):1499–1504
Parvez MSA, Karim MA, Hasan M, Jaman J, Karim Z, Tahsin T, Hasan MN, Hosen MJ (2020) Prediction of potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 using comprehensive drug repurposing and molecular docking approach. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1787–1797
Jordheim LP, Durantel D, Zoulim F, Dumontet C (2013) Advances in the development of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues for cancer and viral diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12(6):447–464
Schuler J, Falls Z, Mangione W, Hudson ML, Bruggemann L, Samudrala R (2022) Evaluating the performance of drug-repurposing technologies. Drug Discov Today 27(1):49–64
Zhang J, Xiao T, Cai Y, Chen B (2021) Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Curr Opin Virol 50:173–182
Li G, De Clercq E (2020) Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat Rev Drug Discov 19(3):149–150
Aronskyy I, Masoudi-Sobhanzadeh Y, Cappuccio A, Zaslavsky E (2021) Advances in the computational landscape for repurposed drugs against COVID-19. Drug Discov Today 26(12):2800–2815
Muhammad S, Amin S, Iqbal J, Al-Sehemi AG, Alarfaji SS, Ilyas M, Atif M, Ullah S (2022) Insighting the therapeutic potential of fifty (50) shogaol derivatives against mpro of SARS-CoV-2. J Comput Biophys Chem 21(05):555–568
McBride R, Van Zyl M, Fielding BC (2014) The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein. Viruses 6(8):2991–3018
Hilgenfeld R (2014) From SARS to MERS: crystallographic studies on coronaviral proteases enable antiviral drug design. FEBS J 281(18):4085–4096
Li F (2016) Structure, function, and evolution of coronavirus spike proteins. Annu Rev Virol 3:237–261
Morse JS, Lalonde T, Xu S, Liu WR (2020) Learning from the past: possible urgent prevention and treatment options for severe acute respiratory infections caused by 2019-nCoV. Chembiochem 21(5):730–738
Hillen HS (2021) Structure and function of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Curr Opin Virol 48:82–90
Te Velthuis AJ, Van Den Worm SH, Snijder EJ (2012) The SARS-coronavirus nsp7+ nsp8 complex is a unique multimeric RNA polymerase capable of both de novo initiation and primer extension. Nucleic Acids Res 40(4):1737–1747
Muhammad S, Qaisar M, Iqbal J, Khera RA, Al-Sehemi AG, Alarfaji SS, Adnan M (2022) Exploring the inhibitory potential of novel bioactive compounds from mangrove actinomycetes against nsp10 the major activator of SARS-CoV-2 replication. Chem Pap 76(5):3051–3064
Kaushik D, Bhandari R, Kuhad A (2021) TLR4 as a therapeutic target for respiratory and neurological complications of SARS-CoV-2. Expert Opin Ther Targets 25(6):491–508
Li X, Yang Y, Liu L, Yang X, Zhao X, Li Y, Ge Y, Shi Y, Lv P, Zhang J (2020) Effect of combination antiviral therapy on hematological profiles in 151 adults hospitalized with severe coronavirus disease 2019. Pharmacol Res 160:105036
Tompa DR, Immanuel A, Srikanth S, Kadhirvel S (2021) Trends and strategies to combat viral infections: a review on FDA approved antiviral drugs. Int J Biol Macromol 172:524–541
Singhal T (2020) A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). Indian J Pediatr 87(4):281–286
Bobrowski T, Melo-Filho CC, Korn D, Alves VM, Popov KI, Auerbach S, Schmitt C, Moorman NJ, Muratov EN, Tropsha A (2020) Learning from history: do not flatten the curve of antiviral research! Drug Discov Today 25(9):1604–1613
Bank PD (2021) RCSB protein data bank: integrated searching and efficient access to macromolecular structure data from the PDB archive. Found Crystallogr 77:a253
Kouranov A, Xie L, de la Cruz J, Chen L, Westbrook J, Bourne PE, Berman HM (2006) The RCSB PDB information portal for structural genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Suppl 1):D302–D305
Tian W, Chen C, Liang J (2018) CASTp 30: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins and beyond. Biophys J 114(3):50a
Chan JF-W, Kok K-H, Zhu Z, Chu H, To KK-W, Yuan S, Yuen K-Y (2020) Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg Microbes Infect 9(1):221–236
Grellet E, Goulet A, Imbert I (2022) Replication of the coronavirus genome: a paradox among positive-strand RNA viruses. J Biol Chem 298:101923
Gao Y, Yan L, Huang Y, Liu F, Zhao Y, Cao L, Wang T, Sun Q, Ming Z, Zhang L (2020) Structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from COVID-19 virus. Science 368(6492):779–782
Shu B, Gong P (2016) Structural basis of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalysis and translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(28):E4005–E4014
Kirchdoerfer RN, Ward AB (2019) Structure of the SARS-CoV nsp12 polymerase bound to nsp7 and nsp8 co-factors. Nat Commun 10(1):2342
Furuta Y, Takahashi K, Kuno-Maekawa M, Sangawa H, Uehara S, Kozaki K, Nomura N, Egawa H, Shiraki K (2005) Mechanism of action of T-705 against influenza virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(3):981–986
Furuta Y, Komeno T, Nakamura T (2017) Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B 93(7):449–463
Furuta Y, Gowen BB, Takahashi K, Shiraki K, Smee DF, Barnard DL (2013) Favipiravir (T-705), a novel viral RNA polymerase inhibitor. Antivir Res 100(2):446–454
Abdelnabi R, de Morais ATS, Leyssen P, Imbert I, Beaucourt S, Blanc H, Froeyen M, Vignuzzi M, Canard B, Neyts J (2017) Understanding the mechanism of the broad-spectrum antiviral activity of favipiravir (T-705): key role of the F1 motif of the viral polymerase. J Virol 91(12):e00487-17
Graci JD, Cameron CE (2006) Mechanisms of action of ribavirin against distinct viruses. Rev Med Virol 16(1):37–48
Deval J, Fung A, Stevens SK, Jordan PC, Gromova T, Taylor JS, Hong J, Meng J, Wang G, Dyatkina N (2016) Biochemical effect of resistance mutations against synergistic inhibitors of RSV RNA polymerase. PLoS One 11(5):e0154097
Deval J, Hong J, Wang G, Taylor J, Smith LK, Fung A, Stevens SK, Liu H, Jin Z, Dyatkina N (2015) Molecular basis for the selective inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus RNA polymerase by 2′-fluoro-4′-chloromethyl-cytidine triphosphate. PLoS Pathog 11(6):e1004995
Wang G, Deval J, Hong J, Dyatkina N, Prhavc M, Taylor J, Fung A, Jin Z, Stevens SK, Serebryany V (2015) Discovery of 4′-chloromethyl-2′-deoxy-3′, 5′-di-O-isobutyryl-2′-fluorocytidine (ALS-8176), a first-in-class RSV polymerase inhibitor for treatment of human respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Med Chem 58(4):1862–1878
Nilsson M, Kalayanov G, Winqvist A, Pinho P, Sund C, Zhou X-X, Wähling H, Belfrage A-K, Pelcman M, Agback T (2012) Discovery of 4′-azido-2′-deoxy-2′-C-methyl cytidine and prodrugs thereof: a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(9):3265–3268
Rondla R, Coats SJ, McBrayer TR, Grier J, Johns M, Tharnish PM, Whitaker T, Zhou L, Schinazi RF (2009) Anti-hepatitis C virus activity of novel β-d-2′-C-methyl-4′-azido pyrimidine nucleoside phosphoramidate prodrugs. Antivir Chem Chemother 20(2):99–106
Deutsch M, Hadziyannis S (2008) Old and emerging therapies in chronic hepatitis C: an update. J Viral Hepat 15(1):2–11
Gerber L, Welzel TM, Zeuzem S (2013) New therapeutic strategies in HCV: polymerase inhibitors. Liver Int 33:85–92
Andreou A, Trantza S, Filippou D, Sipsas N, Tsiodras S (2020) COVID-19: the potential role of copper and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in a combination of candidate antiviral treatments against SARS-CoV-2. In Vivo 34(3 suppl):1567–1588
Painter WP, Holman W, Bush JA, Almazedi F, Malik H, Eraut NC, Morin MJ, Szewczyk LJ, Painter GR (2021) Human safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of molnupiravir, a novel broad-spectrum oral antiviral agent with activity against SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65(5):e02428-20
Cox RM, Wolf JD, Plemper RK (2021) Therapeutically administered ribonucleoside analogue MK-4482/EIDD-2801 blocks SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Nat Microbiol 6(1):11–18
Celik I, Tallei TE (2022) A computational comparative analysis of the binding mechanism of molnupiravir’s active metabolite to RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of wild-type and Delta subvariant AY 4 of SARS-CoV-2. J Cell Biochem 123(4):807–818
Painter GR, Bowen RA, Bluemling GR, DeBergh J, Edpuganti V, Gruddanti PR, Guthrie DB, Hager M, Kuiper DL, Lockwood MA (2019) The prophylactic and therapeutic activity of a broadly active ribonucleoside analog in a murine model of intranasal Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus infection. Antivir Res 171:104597
Agostini ML, Pruijssers AJ, Chappell JD, Gribble J, Lu X, Andres EL, Bluemling GR, Lockwood MA, Sheahan TP, Sims AC (2019) Small-molecule antiviral β-d-N 4-hydroxycytidine inhibits a proofreading-intact coronavirus with a high genetic barrier to resistance. J Virol 93(24):e01348-19
Julander JG, Demarest JF, Taylor R, Gowen BB, Walling DM, Mathis A, Babu Y (2021) An update on the progress of galidesivir (BCX4430), a broad-spectrum antiviral. Antivir Res 195:105180
Aschenbrenner DS (2021) Remdesivir approved to treat COVID-19 amid controversy. Am J Nurs 121(1):22–24
Young B, Tan TT, Leo YS (2021) The place for remdesivir in COVID-19 treatment. Lancet Infect Dis 21(1):20–21
Hendaus MA (2021) Remdesivir in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a simplified summary. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(10):3787–3792
Shannon A, Fattorini V, Sama B, Selisko B, Feracci M, Falcou C, Gauffre P, El Kazzi P, Delpal A, Decroly E (2022) A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase. Nat Commun 13(1):621
Good SS, Westover J, Jung KH, La Colla P, Collu G, Moussa A, Canard B, Sommadossi J-P (2020) AT-527 is a potent in vitro replication inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. Biorxiv 2020:242834
Elfiky AA, Elshemey WM, Gawad WA (2015) 2′-Methylguanosine prodrug (IDX-184), phosphoramidate prodrug (sofosbuvir), diisobutyryl prodrug (R7128) are better than their parent nucleotides and ribavirin in hepatitis C virus inhibition: a molecular modeling study. J Comput Theor Nanosci 12(3):376–386
Elfiky AA (2016) Zika viral polymerase inhibition using anti-HCV drugs both in market and under clinical trials. J Med Virol 88(12):2044–2051
Sadeghi A, Ali Asgari A, Norouzi A, Kheiri Z, Anushirvani A, Montazeri M, Hosamirudsai H, Afhami S, Akbarpour E, Aliannejad R (2020) Sofosbuvir and daclatasvir compared with standard of care in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with moderate or severe coronavirus infection (COVID-19): a randomized controlled trial. J Antimicrob Chemother 75(11):3379–3385
Vicenti I, Zazzi M, Saladini F (2021) SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a therapeutic target for COVID-19. Expert Opin Ther Patents 31(4):325–337
Shannon A, Canard B (2023) Kill or corrupt: mechanisms of action and drug-resistance of nucleotide analogues against SARS-CoV-2. Antivir Res 210:105501
Moeller NH, Shi K, Demir Ö, Belica C, Banerjee S, Yin L, Durfee C, Amaro RE, Aihara H (2022) Structure and dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 proofreading exoribonuclease ExoN. Proc Natl Acad Sci 119(9):e2106379119
Jia X, Schols D, Meier C (2020) Lipophilic triphosphate prodrugs of various nucleoside analogues. J Med Chem 63(13):6991–7007
Mackman RL (2022) Phosphoramidate prodrugs continue to deliver, the journey of remdesivir (GS-5734) from RSV to SARS-CoV-2. ACS Med Chem Lett 13(3):338–347
Elfiky AA (2020) Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19. Life Sci 248:117477
Wang Z, Yang L, Zhao X-E (2021) Co-crystallization and structure determination: an effective direction for anti-SARS-CoV-2 drug discovery. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:4684–4701
Zhang W-F, Stephen P, Theriault J-F, Wang R, Lin S-X (2020) Novel coronavirus polymerase and nucleotidyl-transferase structures: potential to target new outbreaks. J Phys Chem Lett 11(11):4430–4435
Celik I, Erol M, Duzgun Z (2021) In silico evaluation of potential inhibitory activity of remdesivir, favipiravir, ribavirin and galidesivir active forms on SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase. Mol Divers 26:279–292
Du YX, Chen XP (2020) Favipiravir: pharmacokinetics and concerns about clinical trials for 2019-nCoV infection. Clin Pharmacol Ther 108(2):242–247
Naydenova K, Muir KW, Wu L-F, Zhang Z, Coscia F, Peet MJ, Castro-Hartmann P, Qian P, Sader K, Dent K (2021) Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in the presence of favipiravir-RTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci 118(7):e2021946118
Pilkington V, Pepperrell T, Hill A (2020) A review of the safety of favipiravir – a potential treatment in the COVID-19 pandemic? J Virus Erad 6(2):45–51
Chen C, Huang J, Yin P, Zhang Y, Cheng Z, Wu J, Chen S, Zhang Y, Chen B, Lu M (2020) Favipiravir versus arbidol for COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. MedRxiv 2020:20037432
Blattman N (2015) Management of hepatitis C in patients with HIV care for patients with HIV-HCV co-infection is evolving as new medications are introduced that will provide simpler, more accessible treatment regimens. Fed Pract 32(Suppl 2):15S
Arabi YM, Shalhoub S, Mandourah Y, Al-Hameed F, Al-Omari A, Al Qasim E, Jose J, Alraddadi B, Almotairi A, Al Khatib K (2020) Ribavirin and interferon therapy for critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome: a multicenter observational study. Clin Infect Dis 70(9):1837–1844
Parker WB (2005) Metabolism and antiviral activity of ribavirin. Virus Res 107(2):165–171
Unal MA, Bitirim CV, Summak GY, Bereketoglu S, CevherZeytin I, Besbinar O, Gurcan C, Aydos D, Goksoy E, Kocakaya E (2021) Ribavirin shows antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and downregulates the activity of TMPRSS2 and the expression of ACE2 in vitro. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 99(5):449–460
Bylehn F, Menendez CA, Perez-Lemus GR, Alvarado W, De Pablo JJ (2021) Modeling the binding mechanism of remdesivir, favilavir, and ribavirin to SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. ACS Cent Sci 7(1):164–174
Uddin R, Jalal K, Khan K (2022) Re-purposing of hepatitis C virus FDA approved direct acting antivirals as potential SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors. J Mol Struct 1250:131920
Elfiky AA (2020) Ribavirin, remdesivir, sofosbuvir, galidesivir, and tenofovir against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp): a molecular docking study. Life Sci 253:117592
Crotty S, Andino R (2002) Implications of high RNA virus mutation rates: lethal mutagenesis and the antiviral drug ribavirin. Microbes Infect 4(13):1301–1307
Leong HN, Ang B, Earnest A, Teoh C, Xu W, Leo YS (2004) Investigational use of ribavirin in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Singapore, 2003. Trop Med Int Health 9(8):923–927
Booth CM, Matukas LM, Tomlinson GA, Rachlis AR, Rose DB, Dwosh HA, Walmsley SL, Mazzulli T, Avendano M, Derkach P (2003) Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. JAMA 289(21):2801–2809
Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, Ahuja A, Yung MY, Leung C, To K (2003) A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med 348(20):1986–1994
Tan EL, Ooi EE, Lin C-Y, Tan HC, Ling AE, Lim B, Stanton LW (2004) Inhibition of SARS coronavirus infection in vitro with clinically approved antiviral drugs. Emerg Infect Dis 10(4):581
Muller MP, Dresser L, Raboud J, McGeer A, Rea E, Richardson SE, Mazzulli T, Loeb M, Louie M (2007) Adverse events associated with high-dose ribavirin: evidence from the Toronto outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Pharmacotherapy 27(4):494–503
Barlow A, Landolf KM, Barlow B, Yeung SYA, Heavner JJ, Claassen CW, Heavner MS (2020) Review of emerging pharmacotherapy for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019. Pharmacotherapy 40(5):416–437
Chang C-H, Chen K, Lai M-Y, Chan K (2002) Meta-analysis: ribavirin-induced haemolytic anaemia in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 16(9):1623–1632
Knowles SR, Phillips EJ, Dresser L, Matukas L (2003) Common adverse events associated with the use of ribavirin for severe acute respiratory syndrome in Canada. Clin Infect Dis 37(8):1139–1142
Kaur K, Gandhi MA, Slish J (2015) Drug-drug interactions among hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) medications. Infect Dis Ther 4:159–172
Zandi K, Amblard F, Musall K, Downs-Bowen J, Kleinbard R, Oo A, Cao D, Liang B, Russell OO, McBrayer T (2020) Repurposing nucleoside analogs for human coronaviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65(1):e01652-20
Goswami D (2021) Comparative assessment of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors under clinical trials to control SARS-CoV2 using rigorous computational workflow. RSC Adv 11(46):29015–29028
Mandal M, Chowdhury SK, Khan AA, Baildya N, Dutta T, Misra D, Ghosh NN (2021) Inhibitory efficacy of RNA virus drugs against SARS-CoV-2 proteins: an extensive study. J Mol Struct 1234:130152
Chang J (2022) 4′-Modified nucleosides for antiviral drug discovery: achievements and perspectives. Acc Chem Res 55(4):565–578
Clark JL, Hollecker L, Mason JC, Stuyver LJ, Tharnish PM, Lostia S, McBrayer TR, Schinazi RF, Watanabe KA, Otto MJ (2005) Design, synthesis, and antiviral activity of 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methylcytidine, a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication. J Med Chem 48(17):5504–5508
Fung A, Jin Z, Dyatkina N, Wang G, Beigelman L, Deval J (2014) Efficiency of incorporation and chain termination determines the inhibition potency of 2′-modified nucleotide analogs against hepatitis C virus polymerase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(7):3636–3645
Deore R, Chern JW (2010) NS5B RNA dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors: the promising approach to treat hepatitis C virus infections. Curr Med Chem 17(32):3806–3826
Nishiyama T, Kobayashi T, Jirintai S, Nagashima S, Primadharsini PP, Nishizawa T, Okamoto H (2019) Antiviral candidates against the hepatitis E virus (HEV) and their combinations inhibit HEV growth in in vitro. Antivir Res 170:104570
Qu C, Xu L, Yin Y, Peppelenbosch MP, Pan Q, Wang W (2017) Nucleoside analogue 2′-C-methylcytidine inhibits hepatitis E virus replication but antagonizes ribavirin. Adv Virol 162:2989–2996
Lee J-C, Tseng C-K, Wu Y-H, Kaushik-Basu N, Lin C-K, Chen W-C, Wu H-N (2015) Characterization of the activity of 2′-C-methylcytidine against dengue virus replication. Antivir Res 116:1–9
Rocha-Pereira J, Jochmans D, Dallmeier K, Leyssen P, Cunha R, Costa I, Nascimento M, Neyts J (2012) Inhibition of norovirus replication by the nucleoside analogue 2′-C-methylcytidine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427(4):796–800
Elfiky AA (2021) SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) targeting: an in silico perspective. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(9):3204–3212
Jena N (2020) Identification of potent drugs and antiviral agents for the treatment of the SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Biol Med Chem
Pierra C, Amador A, Benzaria S, Cretton-Scott E, d’Amours M, Mao J, Mathieu S, Moussa A, Bridges EG, Standring DN (2006) Synthesis and pharmacokinetics of valopicitabine (NM283), an efficient prodrug of the potent anti-HCV agent 2′-C-methylcytidine. J Med Chem 49(22):6614–6620
Kuntzen T, Timm J, Berical A, Lennon N, Berlin AM, Young SK, Lee B, Heckerman D, Carlson J, Reyor LL (2008) Naturally occurring dominant resistance mutations to hepatitis C virus protease and polymerase inhibitors in treatment-naive patients. Hepatology 48(6):1769–1778
Kumar R, Mishra S, Maurya SK (2021) Recent advances in the discovery of potent RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors targeting viruses. RSC Med Chem 12(3):306–320
Tian L, Qiang T, Liang C, Ren X, Jia M, Zhang J, Li J, Wan M, YuWen X, Li H (2021) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors: the current landscape and repurposing for the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur J Med Chem 213:113201
Gordon CJ, Tchesnokov EP, Schinazi RF, Götte M (2021) Molnupiravir promotes SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis via the RNA template. J Biol Chem 297(1):100770
Wang M, Wu C, Liu N, Zhang F, Dong H, Wang S, Chen M, Jiang X, Gu L (2021) SARS-CoV-2 RdRp is a versatile enzyme with proofreading activity and ability to incorporate NHC into RNA by using diphosphate form molnupiravir as a substrate. BioRxiv 2021:468737
Urakova N, Kuznetsova V, Crossman DK, Sokratian A, Guthrie DB, Kolykhalov AA, Lockwood MA, Natchus MG, Crowley MR, Painter GR (2018) β-D-N 4-hydroxycytidine is a potent anti-alphavirus compound that induces a high level of mutations in the viral genome. J Virol 92(3):e01965-17
Hashemian SMR, Pourhanifeh MH, Hamblin MR, Shahrzad MK, Mirzaei H (2022) RdRp inhibitors and COVID-19: is molnupiravir a good option? Biomed Pharmacother 146:112517
Sheahan TP, Sims AC, Zhou S, Graham RL, Pruijssers AJ, Agostini ML, Leist SR, Schäfer A, Dinnon KH III, Stevens LJ (2020) An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Sci Transl Med 12(541):eabb5883
Mestres J (2020) The target landscape of N4-hydroxycytidine based on its chemical neighborhood. BioRxiv 2020:016485
Imran M, Kumar Arora M, Asdaq SMB, Khan SA, Alaqel SI, Alshammari MK, Alshehri MM, Alshrari AS, Mateq Ali A, Al-Shammeri AM (2021) Discovery, development, and patent trends on molnupiravir: a prospective oral treatment for COVID-19. Molecules 26(19):5795
Stevaert A, Groaz E, Naesens L (2022) Nucleoside analogs for management of respiratory virus infections: mechanism of action and clinical efficacy. Curr Opin Virol 57:101279
Zarenezhad E, Marzi M (2022) Review on molnupiravir as a promising oral drug for the treatment of COVID-19. Med Chem Res 31:232–243
Gangadharan S, Ambrose JM, Rajajagadeesan A, Kullappan M, Patil S, Gandhamaneni SH, Veeraraghavan VP, Nakkella AK, Agarwal A, Jayaraman S (2022) Repurposing of potential antiviral drugs against RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 by computational approach. J Infect Public Health 15(11):1180–1191
Kabinger F, Stiller C, Schmitzová J, Dienemann C, Kokic G, Hillen HS, Höbartner C, Cramer P (2021) Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced SARS-CoV-2 mutagenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol 28(9):740–746
Fischer WA, Eron JJ Jr, Holman W, Cohen MS, Fang L, Szewczyk LJ, Sheahan TP, Baric R, Mollan KR, Wolfe CR (2021) A phase 2a clinical trial of molnupiravir in patients with COVID-19 shows accelerated SARS-CoV-2 RNA clearance and elimination of infectious virus. Sci Transl Med 14(628):eabl7430
Ju J, Kumar S, Li X, Jockusch S, Russo JJ (2020) Nucleotide analogues as inhibitors of viral polymerases. BioRxiv 2020:927574
Abuo-Rahma GE-DA, Mohamed MF, Ibrahim TS, Shoman ME, Samir E, Abd El-Baky RM (2020) Potential repurposed SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection drugs. RSC Adv 10(45):26895–26916
Jena N (2020) Role of different tautomers in the base-pairing abilities of some of the vital antiviral drugs used against COVID-19. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22(48):28115–28122
Taylor R, Bowen R, Demarest JF, DeSpirito M, Hartwig A, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Walling DM, Mathis A, Babu YS (2021) Activity of galidesivir in a hamster model of SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 14(1):8
Gandeepan P, Ackermann L (2018) Transient directing groups for transformative C–H activation by synergistic metal catalysis. Chem 4(2):199–222
Romano M, Ruggiero A, Squeglia F, Maga G, Berisio R (2020) A structural view of SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication machinery: RNA synthesis, proofreading and final capping. Cells 9(5):1267
Hasan MK, Kamruzzaman M, Manjur OHB, Mahmud A, Hussain N, Mondal MSA, Hosen MI, Bello M, Rahman A (2021) Structural analogues of existing anti-viral drugs inhibit SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase: a computational hierarchical investigation. Heliyon 7(3):e06435
Ataei M, Hosseinjani H (2020) Molecular mechanisms of galidesivir as a potential antiviral treatment for COVID-19. J Pharm Care 2020:150–151
Uzunova K, Filipova E, Pavlova V, Vekov T (2020) Insights into antiviral mechanisms of remdesivir, lopinavir/ritonavir and chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine affecting the new SARS-CoV-2. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110668
Wang M, Cao R, Zhang L, Yang X, Liu J, Xu M, Shi Z, Hu Z, Zhong W, Xiao G (2020) Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res 30(3):269–271
Pizzorno A, Padey B, Julien T, Trouillet-Assant S, Traversier A, Errazuriz-Cerda E, Fouret J, Dubois J, Gaymard A, Lescure F-X (2020) Characterization and treatment of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal and bronchial human airway epithelia. Cell Rep Med 1(4):100059
Sun G-Q, Wang S-F, Li M-T, Li L, Zhang J, Zhang W, Jin Z, Feng G-L (2020) Transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: effects of lockdown and medical resources. Nonlinear Dyn 101:1981–1993
Singh AK, Singh A, Singh R, Misra A (2020) Remdesivir in COVID-19: a critical review of pharmacology, pre-clinical and clinical studies. Diabetes Metab Syndr 14(4):641–648
Amirian ES, Levy JK (2020) Current knowledge about the antivirals remdesivir (GS-5734) and GS-441524 as therapeutic options for coronaviruses. One Health 9:100128
Li Y, Zhang D, Gao X, Wang X, Zhang L (2022) 2′-and 3′-ribose modifications of nucleotide analogues establish the structural basis to inhibit the viral replication of SARS-CoV-2. J Phys Chem Lett 13(18):4111–4118
Wakchaure PD, Ghosh S, Ganguly B (2020) Revealing the inhibition mechanism of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 by remdesivir and nucleotide analogues: a molecular dynamics simulation study. J Phys Chem B 124(47):10641–10652
Ionescu MI (2020) An overview of the crystallized structures of the SARS-CoV-2. Protein J 39(6):600–618
Padhi AK, Shukla R, Saudagar P, Tripathi T (2021) High-throughput rational design of the remdesivir binding site in the RdRp of SARS-CoV-2: implications for potential resistance. Iscience 24(1):101992
Moirangthem DS, Surbala L (2021) Remdesivir (GS-5734) in COVID-19 therapy: the fourth chance. Curr Drug Targets 22(12):1346–1356
Holshue ML, DeBolt C, Lindquist S, Lofy KH, Wiesman J, Bruce H, Spitters C, Ericson K, Wilkerson S, Tural A (2020) First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States. N Engl J Med 382:929–936
Sanchez-Codez MI, Rodriguez-Gonzalez M, Gutierrez-Rosa I (2021) Severe sinus bradycardia associated with remdesivir in a child with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur J Pediatr 180(5):1627–1627
Saqrane S, El Mhammedi M, Lahrich S, Laghrib F, El Bouabi Y, Farahi A, Bakasse M (2021) Recent knowledge in favor of remdesivir (GS-5734) as a therapeutic option for the COVID-19 infections. J Infect Public Health 14(5):655–660
Ko W-C, Rolain J-M, Lee N-Y, Chen P-L, Huang C-T, Lee P-I, Hsueh P-R (2020) Arguments in favour of remdesivir for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:105933
Belhadi D, Peiffer-Smadja N, Lescure F-X, Yazdanpanah Y, Mentré F, Laouénan C (2020) A brief review of antiviral drugs evaluated in registered clinical trials for COVID-19. MedRxiv 2020:20038190
Warren TK, Jordan R, Lo MK, Ray AS, Mackman RL, Soloveva V, Siegel D, Perron M, Bannister R, Hui HC (2016) Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 531(7594):381–385
Anastasiou IA, Eleftheriadou I, Tentolouris A, Tsilingiris D, Tentolouris N (2020) In vitro data of current therapies for SARS-CoV-2. Curr Med Chem 27(27):4542–4548
Qiao Y, Wotring JW, Zhang CJ, Jiang X, Xiao L, Watt A, Gattis D, Scandalis E, Freier S, Zheng Y (2023) Antisense oligonucleotides to therapeutically target SARS-CoV-2 infection. PLoS One 18(2):e0281281
Su X, Ma W, Feng D, Cheng B, Wang Q, Guo Z, Zhou D, Tang X (2021) Efficient inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 using chimeric antisense oligonucleotides through RNase L activation. Angew Chem 133(40):21830–21835
Sahu B, Behera SK, Das R, Dalvi T, Chowdhury A, Dewangan B, Kalia K, Shard A (2022) Design and in-silico screening of peptide nucleic acid (PNA) inspired novel pronucleotide scaffolds targeting COVID-19. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 18(1):26–40
Good SS, Westover J, Jung KH, Zhou X-J, Moussa A, La Colla P, Collu G, Canard B, Sommadossi J-P (2021) AT-527, a double prodrug of a guanosine nucleotide analog, is a potent inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and a promising oral antiviral for treatment of COVID-19. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 65(4):e02479-20
Basu D, Chavda VP, Mehta AA (2022) Therapeutics for COVID-19 and post COVID-19 complications: an update. Curr Res Pharmacol Drug Discov 2022:100086
Mungur O, Berliba E, Bourgeois S, Cardona M, Jucov A, Good S, Moussa A, Pietropaolo K, Zhou X-J, Brown N (2020) A combination of AT-527, a pan-genotypic guanosine nucleotide prodrug, and daclatasvir was well-tolerated and effective in HCV-infected subjects. J Hepatol 73:S357
Berliba E, Bogus M, Vanhoutte F, Berghmans P-J, Good SS, Moussa A, Pietropaolo K, Murphy RL, Zhou X-J, Sommadossi J-P (2019) Safety, pharmacokinetics, and antiviral activity of AT-527, a novel purine nucleotide prodrug, in hepatitis C virus-infected subjects with or without cirrhosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 63(12):e01201-19
Good SS, Moussa A, Zhou X-J, Pietropaolo K, Sommadossi J-P (2020) Preclinical evaluation of AT-527, a novel guanosine nucleotide prodrug with potent, pan-genotypic activity against hepatitis C virus. PLoS One 15(1):e0227104
Wang X, Sacramento CQ, Jockusch S, Chaves OA, Tao C, Fintelman-Rodrigues N, Chien M, Temerozo JR, Li X, Kumar S (2021) Combination of antiviral drugs to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 polymerase and exonuclease as potential COVID-19 therapeutics. bioRxiv
Eltayb WA, Abdalla M, Rabie AM (2023) Novel investigational anti-SARS-CoV-2 agent Ensitrelvir “S-217622”: a very promising potential universal broad-spectrum antiviral at the therapeutic frontline of coronavirus species. ACS Omega 8(6):5234–5246
Canard B, Shannon A, Fattorini V, Sama B, Selisko B, Feracci M, Falcou C, Gauffre P, El-Kazzi P, Decroly E (2021) A dual mechanism of action of AT-527 against SARS-CoV-2 polymerase
Shannon A, Fattorini V, Sama B, Selisko B, Feracci M, Falcou C, Gauffre P, Kazzi PE, Decroly E, Rabah N (2021) Protein-primed RNA synthesis in SARS-CoVs and structural basis for inhibition by AT-527. bioRxiv 2021:436564
Mayhoub AS (2012) Hepatitis C RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors: a review of structure–activity and resistance relationships; different scaffolds and mutations. Bioorg Med Chem 20(10):3150–3161
Elfiky AA, Elshemey WM (2016) IDX-184 is a superior HCV direct-acting antiviral drug: a QSAR study. Med Chem Res 25:1005–1008
Elfiky AA (2017) Zika virus: novel guanosine derivatives revealed strong binding and possible inhibition of the polymerase. Future Virol 12(12):721–728
Elfiky AA, Ismail AM (2018) Molecular docking revealed the binding of nucleotide/side inhibitors to Zika viral polymerase solved structures. SAR QSAR Environ Res 29(5):409–418
Noor R (2021) Antiviral drugs against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection triggering the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic. Tzu-Chi Med J 33(1):7
Elfiky AA, Ismail AM (2017) Molecular modeling and docking revealed superiority of IDX-184 as HCV polymerase inhibitor. Future Virol 12(7):339–347
Zhou X-J, Pietropaolo K, Chen J, Khan S, Sullivan-Bólyai J, Mayers D (2011) Safety and pharmacokinetics of IDX184, a liver-targeted nucleotide polymerase inhibitor of hepatitis C virus, in healthy subjects. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55(1):76–81
Elfiky AA (2022) Dual targeting of RdRps of SARS-CoV-2 and the mucormycosis-causing fungus: an in silico perspective. Future Microbiol 17(10):755–762
Murakami E, Niu C, Bao H, MicolochickSteuer HM, Whitaker T, Nachman T, Sofia MA, Wang P, Otto MJ, Furman PA (2008) The mechanism of action of β-d-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methylcytidine involves a second metabolic pathway leading to β-d-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methyluridine 5′-triphosphate, a potent inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52(2):458–464
Zhang C (2022) Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: in perspective to COVID-19. ACS Omega 7(22):18206–18212
Ma H, Jiang W-R, Robledo N, Leveque V, Ali S, Lara-Jaime T, Masjedizadeh M, Smith DB, Cammack N, Klumpp K (2007) Characterization of the metabolic activation of hepatitis C virus nucleoside inhibitor β-d-2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro-2′-C-methylcytidine (PSI-6130) and identification of a novel active 5′-triphosphate species. J Biol Chem 282(41):29812–29820
Sofia MJ, Furman PA (2019) The discovery of sofosbuvir: a liver-targeted nucleotide prodrug for the treatment and cure of HCV. HCV I:141–169
Sayad B, Sobhani M, Khodarahmi R (2020) Sofosbuvir as repurposed antiviral drug against COVID-19: why were we convinced to evaluate the drug in a registered/approved clinical trial? Arch Med Res 51(6):577–581
Murakami E, Tolstykh T, Bao H, Niu C, Steuer HMM, Bao D, Chang W, Espiritu C, Bansal S, Lam AM (2010) Mechanism of activation of PSI-7851 and its diastereoisomer PSI-7977. J Biol Chem 285(45):34337–34347
Kirby BJ, Symonds WT, Kearney BP, Mathias AA (2015) Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and drug-interaction profile of the hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitor sofosbuvir. Clin Pharmacokinet 54:677–690
Gentile I, Maraolo AE, Buonomo AR, Zappulo E, Borgia G (2015) The discovery of sofosbuvir: a revolution for therapy of chronic hepatitis C. Expert Opin Drug Discov 10(12):1363–1377
Bhatia R, Narang RK, Rawal RK (2020) Repurposing of RdRp inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 through molecular docking tools. Coronaviruses 1(1):108–116
Wang Y, Anirudhan V, Du R, Cui Q, Rong L (2021) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 as a therapeutic target. J Med Virol 93(1):300–310
Chien M, Anderson TK, Jockusch S, Tao C, Li X, Kumar S, Russo JJ, Kirchdoerfer RN, Ju J (2020) Nucleotide analogues as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase, a key drug target for COVID-19. J Proteome Res 19(11):4690–4697
Nourian A, Khalili H, Ahmadinejad Z, Kouchak HE, Jafari S, Manshadi SAD, Rasolinejad M, Kebriaeezadeh A (2020) Efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir/ledipasvir in treatment of patients with COVID-19; a randomized clinical trial. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parmensis 91(4)
Jockusch S, Tao C, Li X, Chien M, Kumar S, Morozova I, Kalachikov S, Russo JJ, Ju J (2020) Sofosbuvir terminated RNA is more resistant to SARS-CoV-2 proofreader than RNA terminated by remdesivir. Sci Rep 10(1):16577
Choudhury C, Narahari Sastry G (2019) Pharmacophore modelling and screening: concepts, recent developments and applications in rational drug design. In Structural bioinformatics: applications in preclinical drug discovery process, pp 25–53
Mosayebnia M, HajiaghaBozorgi A, Rezaeianpour M, Kobarfard F (2022) In silico prediction of SARS-CoV-2 main protease and polymerase inhibitors: 3D-pharmacophore modelling. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(14):6569–6586
Giordano D, Biancaniello C, Argenio MA, Facchiano A (2022) Drug design by pharmacophore and virtual screening approach. Pharmaceuticals 15(5):646
Schaller D, Šribar D, Noonan T, Deng L, Nguyen TN, Pach S, Machalz D, Bermudez M, Wolber G (2020) Next generation 3D pharmacophore modeling. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 10(4):e1468
Aouidate A, Ghaleb A, Chtita S, Aarjane M, Ousaa A, Maghat H, Sbai A, Choukrad MB, Bouachrine M, Lakhlifi T (2021) Identification of a novel dual-target scaffold for 3CLpro and RdRp proteins of SARS-CoV-2 using 3D-similarity search, molecular docking, molecular dynamics and ADMET evaluation. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(12):4522–4535
Singh S, Banavath HN, Godara P, Naik B, Srivastava V, Prusty D (2022) Identification of antiviral peptide inhibitors for receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 omicron and its sub-variants: an in-silico approach. 3 Biotech 12(9):198
Pundir H, Joshi T, Pant M, Bhat S, Pandey J, Chandra S, Tamta S (2022) Identification of SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase inhibitors using pharmacophore modelling, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(24):13366–13377
Aziz S, Waqas M, Mohanta TK, Halim SA, Iqbal A, Ali A, Khalid A, Abdalla AN, Khan A, Al-Harrasi A (2023) Identifying non-nucleoside inhibitors of RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 through per-residue energy decomposition-based pharmacophore modeling, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. J Infect Public Health 16(4):501–519
Brunt D, Lakernick PM, Wu C (2022) Discovering new potential inhibitors to SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) using high throughput virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations. Sci Rep 12(1):19986
Qaisar M, Muhammad S, Iqbal J, Khera RA, Al-Sehemi AG, Alarfaji SS, Khalid M, Hussain F (2022) Identification of marine fungi-based antiviral agents as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 by molecular docking, ADMET and molecular dynamic study. J Comput Biophys Chem 21(02):139–153
Velavan TP, Meyer CG (2020) The COVID-19 epidemic. Trop Med Int Health 25(3):278
Lauring AS, Tenforde MW, Chappell JD, Gaglani M, Ginde AA, McNeal T, Ghamande S, Douin DJ, Talbot HK, Casey JD (2022) Clinical severity of, and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines against, COVID-19 from Omicron, Delta, and Alpha SARS-CoV-2 variants in the United States: prospective observational study. BMJ 376
Ndwandwe D, Wiysonge CS (2021) COVID-19 vaccines. Curr Opin Immunol 71:111–116
Ng WH, Liu X, Mahalingam S (2020) Development of vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. F1000Research 9
Kremer EJ (2020) Pros and cons of adenovirus-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 2303–2304
Wang G, Dyatkina N, Prhavc M, Williams C, Serebryany V, Hu Y, Huang Y, Wan J, Wu X, Deval J (2019) Synthesis and anti-HCV activities of 4′-fluoro-2′-substituted uridine triphosphates and nucleotide prodrugs: discovery of 4′-fluoro-2′-C-methyluridine 5′-phosphoramidate prodrug (AL-335) for the treatment of hepatitis C infection. J Med Chem 62(9):4555–4570
Wang G, Dyatkina N, Prhavc M, Williams C, Serebryany V, Hu Y, Huang Y, Wu X, Chen T, Huang W (2020) Synthesis and anti-HCV activity of sugar-modified guanosine analogues: discovery of AL-611 as an HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. J Med Chem 63(18):10380–10395
Tchesnokov EP, Feng JY, Porter DP, Götte M (2019) Mechanism of inhibition of Ebola virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir. Viruses 11(4):326
Zhang L, Zhou R (2020) Structural basis of the potential binding mechanism of remdesivir to SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Phys Chem B 124(32):6955–6962
Qudsiani KS, Rahmasari R (2021) Polyamidoamine-remdesivir conjugate: physical stability and cellular uptake enhancement. Biomed Pharmacol J 14(4):2073–2084
Ning S, Yu B, Wang Y, Wang F (2021) SARS-CoV-2: origin, evolution, and targeting inhibition. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:676451
Serpi M, Pertusati F (2021) An overview of ProTide technology and its implications to drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov 16(10):1149–1161
Menéndez JC (2022) Approaches to the potential therapy of COVID-19: a general overview from the medicinal chemistry perspective. Molecules 27(3):658
Hassanipour S, Arab-Zozani M, Amani B, Heidarzad F, Fathalipour M, Martinez-de-Hoyo R (2021) The efficacy and safety of favipiravir in treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Sci Rep 11(1):11022
Malone B, Campbell EA (2021) Molnupiravir: coding for catastrophe. Nat Struct Mol Biol 28(9):706–708
Mishra A, Rathore AS (2022) Pharmacophore screening to identify natural origin compounds to target RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV2. Mol Divers 2022:1–17
Gao C, Chang L, Xu Z, Yan X-F, Ding C, Zhao F, Wu X, Feng L-S (2019) Recent advances of tetrazole derivatives as potential anti-tubercular and anti-malarial agents. Eur J Med Chem 163:404–412
Pokhodylo N, Finiuk N, Klyuchivska O, Stoika R, Matiychuk V, Obushak M (2023) Bioisosteric replacement of 1H–1, 2, 3-triazole with 1H-tetrazole ring enhances anti-leukemic activity of (5-benzylthiazol-2-yl) benzamides. Eur J Med Chem 250:115126
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201053) and the Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars (3100012222222). The image of the graphical abstract was created with tools obtained from BioRender.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shehzadi, K., Saba, A., Yu, M. et al. Structure-Based Drug Design of RdRp Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2. Top Curr Chem (Z) 381, 22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-023-00432-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-023-00432-x