Abstract
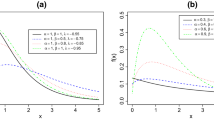
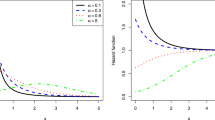
Statistical modeling data is crucial for identifying patterns, correlations, and trends that can be used to make informed decisions and put sustainable management practices into practice for the preservation of the environment and its resources. It is a useful method for assessing hazards, predicting impacts, and determining the efficacy of environmental policies and initiatives. This study introduces the Harris extended modified Lindley (HEML) distribution, a novel three-parameter lifetime distribution, to model environmental data. It is a modification of the Lindley distribution with the addition of two parameters. The paper covers its core properties, including the shapes of the related functions, tail behavior, moments, incomplete moments, inverted moments, order statistics, mean residual life function, and Rényi entropy. The adaptability of the hazard rate function for modeling increasing (and remaining constant), and decreasing data, after which it remains constant, is demonstrated. The evaluation of the developed model is conducted from a statistical perspective. The estimation of the parameters is performed using the maximum likelihood estimation method, a widely used statistical technique in the field of research. Additionally, a simulation analysis is carried out to further investigate the estimation’s behavior. This study employs two real-world datasets to exemplify the versatility of the proposed model within the context of environmental data analysis. Additionally, the model’s performance is compared to that of prominent competing models, thereby providing a comprehensive evaluation of its efficacy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chesneau, C., Tomy, L., Gillariose, J.: On the Harris extended family of distributions. J. Stat. Manag. Syst. 24(7), 1383–1403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/02331888.2014.969732
Aly, E.E.A., Benkherouf, L.: A new family of distributions based on probability generating functions. Sankhya B 73, 70–80 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13571-011-0017-9
Harris, T.E.: The Theory of Branching Processes. Springer, Berlin (1963)
Marshall, A.W., Olkin, I.: A new method for adding a parameter to a family of distributions with application to the exponential and weibull families. Biometrika 84(3), 641–652 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/84.3.641
Jose, K.K., Tomy, L., Thomas, S.P.: On a generalization of the Weibull distribution and its application in quality control. Stochastics and Quality Control 33(2), 113–124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1515/eqc-2018-0011
Jose, K.K., Varghese, J.: Harris extended log-Kumaraswamy distribution and its applications. IAPQR Trans. (2019). https://doi.org/10.32381/IAPQRT.2019.44.01.2
Ogunde, A.A., Laoye, V.E., Ezichi, O.N., Balogun, K.O.: Harris extended power Lomax distribution: properties, inference and applications. Int. J. Stat. Probab. 10(4), 1–77 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5539/ijsp.v10n4p77
Thomas, S.P., Tomy, L., Jose, K.K.: Harris extended two parameter Lindley distribution and applications in reliability. Reliability: Theory Appl. 16(3), 302–321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.24412/1932-2321-2021-363-302-321
Sivadasa, R., Jose, K.K.: Harris extended Burr XII distribution and its applications. Asia J. Stat. Sci. 2(1), 344 (2022)
Mathew, J.: Harris extended length biased exponential distribution and its applications. Int. J. Math. Comput. Res. 8(4), 2035–2041 (2020). https://doi.org/10.33826/ijmcr/v8i4.01
Maya, R., Irshad, M.R., Ahammed, M., Chesneau, C.: The Harris extended bilal distribution with applications in hydrology and quality control. Appl. Math. 3(1), 221–242 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedmath3010013
Gillariose, J., Tomy, L., Jamal, F., Chesneau, C.: The Marshall-Olkin modified lindley distribution: properties and applications. J. Reliab. Stat. Stud. (2020). https://doi.org/10.13052/jrss0974-8024.1319
Cordeiro, G.M., Mansoor, M., Provost, S.B.: The Harris extended lindley distribution for modeling hydrological data. Chilean Journal of Statistics 10(1) (2019)
Pinho, L.G.B., Cordeiro, G.M., Nobre, J.S.: The Harris extended exponential distribution. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 44(16), 3486–3502 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2013.851221
Barreto-Souza, W., Lemonte, A.J., Cordeiro, G.M.: General results for the Marshall and Olkin’s family of distributions. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 85, 3–21 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0001-37652013000100002
Gradshteyn, I.S., Ryzhik, I.M.: Table of Integrals, Series, and Products. Academic press, USA (2014)
David, H.A., Nagaraja, H.N.: Order Statistics. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey (2004)
Rényi, A.: On measures of entropy and information. In: Proceedings of the Fourth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Volume 1: Contributions to the Theory of Statistics, vol. 4, pp. 547–562. University of California Press, Berkeley (1961)
Lindley, D.V.: Fiducial distributions and Bayes theorem. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), pp 102–107 (1958)
Choulakian, V., Stephens, M.A.: Goodness-of-fit for the generalized Pareto distribution. Technometrics 43, 478–484 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1198/00401700152672573
Suleiman, A.A., Daud, H., Othman, M., Ishaq, A.I., Indawati, R., Abdullah, M.L., Husin, A.: The odd beta prime-G family of probability distributions: properties and applications to engineering and environmental data. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 7(1), 20 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/IOCMA2023-14429
Aarset, M.V.: How to identify a bathtub hazard rate. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 36(1), 106–108 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1109/TR.1987.5222310
Gill, D.R.: The total time on test plot and the cumulative total time on test statistic for a counting process. Ann. Stat. 14, 1234–1239 (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tomy, L., Veena, G. & Chesneau, C. A new three-parameter lifetime distribution for environmental data analysis: the Harris extended modified Lindley distribution. Int J Data Sci Anal (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-024-00505-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-024-00505-0