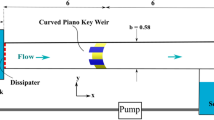
Abstract
Piano key weirs are a new type of weir designed to enhance the discharge capacity of dams. The present study is aimed at experimentally evaluating the hydraulic characteristics of a D-type triangular piano key weir. The purpose of these experiments was to study the flow regime, the stage-discharge relationship, and the effect of h/P ratio on the discharge coefficient. The results indicated that the discharge coefficient in D-type triangular piano key weirs was higher than that of rectangular ones, and it varied in the range of \(0.48 < C_{d} < 1.6\) and \(0.6 <\) (with and without a downstream ramp, respectively). Moreover, under similar laboratory conditions, the results showed that the discharge coefficient of the piano key weir is higher than that of the linear weir. The increase in the discharge coefficient of the piano key weirs, compared to linear weirs, can be up to three times in low heads. Finally, to predict the discharge coefficient of the piano key weirs, an equation was proposed for two cases, i.e., with a downstream ramp and without a downstream ramp.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Machiels O, Erpicum S, Dewals B, Archambeau P, Pirotton M (2011) Experimental observation of flow characteristics over a piano key weir. J Hydraul Res 49(3):359–366. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2011.567761
Tullis BP, Young JC, Chandler MA (2007) Head-discharge relationships for submerged labyrinth weirs. J Hydraul Eng 133(3):248–254. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2007)133:3(248)
Anderson RM, Tullis BP (2012) Comparison of piano key and rectangular labyrinth weir hydraulics. J Hydraul Eng 138(4):358–361. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000509
Blanc P, Lempérière F (2001) Labyrinth spillways have a promising future. Int J Hydropower Dams 8(4):129–131. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0001646
Machiels O (2012) Experimental study of the hydraulic behaviour of Piano Key Weirs Doctoral dissertation, Université de Liège, Belgium.
Laugier F (2007) Design and construction of the first Piano Key Weir (PKW) spillway at the Goulours dam. J Hydropower Dams 14(5):94–101
Anderson R, Tullis B (2011) Influence of piano key weir geometry on discharge. Presented at the meeting of Proceedings of International Conference Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs Liège B. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 75–80
Erpicum S, Machiels O, Archambeau P, Dewals B, Pirotton M (2011) 1D numerical modeling of the flow over a Piano Key Weir. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs-PKW. CRC Press, London, pp 151–158
Lempérière F, Vigny JP, Ouamane A (2011) General comments on Labyrinths and Piano Key Weirs: the past and present. Labyrinth and Piano Key Weirs-PKW. CRC Press, London, pp 17–24
Ribeiro M, Pfister M, Schleiss A, Boillat J (2012) Hydraulic design of A-type Piano Key Weirs. J Hydraul Res 50(4):400–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2012.695041
Lempérière F, Ouamane A (2003) The Piano Keys weir: a new cost-effective solution for spillways. Int J Hydropower Dams 10(5):144–149
Schleiss AJ (2011) From labyrinth to piano key weirs: a historical review. In: Chi M (ed) Labyrinth and Piano Key weirs (PKW). CRC Press, Leiden, pp 3–15
Anderson RM, Tullis BP (2012) Piano key weir: reservoir versus channel application. J Irrig Drain Eng 138(8):773–776. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000464
Kabiri-Samani A, Javaheri A (2012) Discharge coefficient for free and submerged flow over piano key weirs. J Hydraul Res 50(1):114–120. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2011.647888
Mehboudi A, Attari J, Hosseini A (2016) Experimental study of discharge coefficient for trapezoidal piano key weirs. J Flow Meas Instrum 50:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2016.06.005
Shahabirad N (2015) Study of flow hydraulic over Piano Key spillway, Master Thesis hydraulic structures. Sari University, pp 164 (In Persian)
Safarzadeh A, Norozi B (2013) Experimental and numerical study on hydraulics of the Piano Key weirs with modified keys. J Iran Dam Hydroelectr Powerpl 5(16):36–47 (In Persian)
Crookston BM, Anderson RM, Tullis BP (2018) Free flow discharge estimation method for Piano Key weir geometries. J Hydro-Environ Res 19:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jher.2017.10.003
Karimi M, Attari J, Saneie M, Jalili Ghazizadeh MR (2018) Side weir flow characteristics: comparison of Piano Key, Labyrinth, and linear types. J Hydraul Eng 144(12):04018075. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0001539
Karimi CM, Nazari N, Mahmoodian SM (2019) Investigating the effect of a parapet wall on the hydraulic performance of an arced piano key weir. J Hydraul Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2019.1573762
Safarrazavi Zadeh M, Esmaeili Varaki M, Biabani R (2019) Experimental study on flow over sinusoidal and semicircular labyrinth weirs. ISH J Hydraul Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/09715010.2019.1644679
Ghanbari R, Heidarnejad M (2020) Experimental and numerical analysis of flow hydraulics in triangular and rectangular Piano Key weirs. Water Sci J. https://doi.org/10.1080/11104929.2020.1724649
Bos MG (1976) Discharge measurement structures. International Institute for land Reclamation and Employment/LIRI, Wageningen, pp 107–126
Novak P, Cabelka J (1981) Models in hydraulic engineering. Pitman, London
Henderson FM (1966) Open channel flow. Macmillan, New York
French RH (1987) Open-channel hydraulics. MCGRAW-Hill International Editions, London, pp 336–339
Johnson MC (2000) Discharge coefficient analysis for flat-topped and sharp-crested weirs. J Irrig Sci 19(3):133–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002719900009
Falvey HT (2002) Hydraulics design of labyrinth weirs. ASCE, Reston
Machiels O, Erpicum S, Archambeau P, Dewals BJ, Pirotton M (2011) Influence of piano key weir height on its discharge capacity. International conference on Labyrinth and Piano Key weirs. CRC Press, London, pp 59–66
Tullis P, Amanian N, Waldron D (1995) Design of labyrinth weir spillways. J Hydrol Eng 121(3):247–255. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(1995)121:3(247)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh Sanami, F., Saneie, M. & Afshar, M.H. Experimental Study of the Hydraulic Performance of D-Type Triangular Piano Key Weirs. Int J Civ Eng 19, 1209–1220 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-021-00630-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-021-00630-y