Abstract
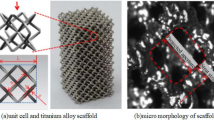
Recent advancements in additive manufacturing technology for metallic materials have paved the way for the creation of patient-specific implants with tailored mechanical properties for bone tissue reconstruction. To address the issue of stress shielding and improve osseointegration, the implants feature an architected internal structure with a unique design capable of mimicking the mechanical properties of the damaged bone. This study proposes a fast, simple, and clinically applicable approach for designing trabecular-like structures for tailored implants, specifically for the tibia component in knee joint replacement. The lattice structures with different solid fractions were designed and fabricated using the selective laser melting (SLM) technique and Ti-6Al-4V alloy. The mechanical behavior of the structures was evaluated through computational and experimental analysis, and compared with that of natural tibia bone. Moreover, the manufacturing robustness of the printed structures was assessed using X-ray computed tomography and microscopic examinations. Results show that the permeability of the fabricated structures ranges from 0.16 × 10–9 to 0.38 × 10–9 m2, comparable to that of trabecular bones. The stiffness and strength of the designed structures range from 1.08 to 4.47 GPa and 147 to 295 MPa, respectively, reasonably consistent with natural bone. Finally, the study proposes a conceptual design framework that isolates the correlation between the solid fraction of the lattices and the expected biomechanical behavior. Overall, the study highlights the potential of additive manufacturing in creating geometrically complex and mechanically tailored implants for bone tissue reconstruction.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aufa AN, Hassan MZ, Ismail Z (2022) Recent advances in Ti-6Al-4V additively manufactured by selective laser melting for biomedical implants: prospect development. J Alloys Compd 896:163072. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JALLCOM.2021.163072
Barba D, Alabort E, Reed RC (2019) Synthetic bone: Design by additive manufacturing. Acta Biomater 97:637–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2019.07.049
Benedetti M, du Plessis A, Ritchie RO, Dallago M, Razavi SMJ, Berto F (2021) Architected cellular materials: A review on their mechanical properties towards fatigue-tolerant design and fabrication. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 144:100606. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSER.2021.100606
Bertol LS, Júnior WK, da Silva FP, Aumund-Kopp C (2010) Medical design: direct metal laser sintering of Ti–6Al–4V. Mater Des 31:3982–3988. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2010.02.050
Bidan CM, Wang FM, Dunlop JWC (2013) A three-dimensional model for tissue deposition on complex surfaces. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 16:1056–1070. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2013.774384
Bobbert FSL, Lietaert K, Eftekhari AA, Pouran B, Ahmadi SM, Weinans H, Zadpoor AA (2017) Additively manufactured metallic porous biomaterials based on minimal surfaces: a unique combination of topological, mechanical, and mass transport properties. Acta Biomater 53:572–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2017.02.024
Dallago M, Fontanari V, Torresani E, Leoni M, Pederzolli C, Potrich C, Benedetti M (2018) Fatigue and biological properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI cellular structures with variously arranged cubic cells made by selective laser melting. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 78:381–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.11.044
Dhiman S, Sidhu SS, Bains PS, Bahraminasab M (2019) Mechanobiological assessment of Ti-6Al-4V fabricated via selective laser melting technique: a review. Rapid Prototyp J 25:1266–1284. https://doi.org/10.1108/RPJ-03-2019-0057/FULL/XML
Dhiman S, Joshi RS, Singh S, Gill SS, Singh H, Kumar R, Kumar V (2021) A framework for effective and clean conversion of machining waste into metal powder feedstock for additive manufacturing. Clean Eng Technol 4:100151. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLET.2021.100151
Eshawish N, Malinov S, Sha W, Walls P (2021) Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V manufactured by selective laser melting after stress relieving, hot isostatic pressing treatment, and post-heat treatment. J Mater Eng Perform 30:5290–5296. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11665-021-05753-W
Feng J, Fu J, Lin Z, Shang C, Niu X (2019) Layered infill area generation from triply periodic minimal surfaces for additive manufacturing. CAD Comput Aided Des 107:50–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2018.09.005
Fotovvati B, Namdari N, Dehghanghadikolaei A, Dai N, Zhang J, Chen Y, al Liu W, Liu Z, Simonelli M, Tse YY, Tuck C (2012) Microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V produced by selective laser melting. J Phys Conf Ser 371:012084. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/371/1/012084
Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK (2009) Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog Mater Sci 54:397–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PMATSCI.2008.06.004
Gibson LJ, Ashby MF (2014) Cellular solids: structure and properties, 2nd edition, Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–510. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139878326
Gu DD, Meiners W, Wissenbach K, Poprawe R (2013) Laser additive manufacturing of metallic components: materials, processes and mechanisms. Int Mater Rev 57:133–164. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743280411Y.0000000014
Hollister SJ (2005) Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat Mater 4(7):518–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1421
Hsieh MT, Begley MR, Valdevit L (2021) Architected implant designs for long bones: Advantages of minimal surface-based topologies. Mater Des 207:109838. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2021.109838
Jeong CG, Zhang H, Hollister SJ (2011) Three-dimensional poly(1,8-octanediol-co-citrate) scaffold pore shape and permeability effects on sub-cutaneous in vivo chondrogenesis using primary chondrocytes. Acta Biomater 7(2):505–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2010.08.027
Jinnai H, Watashiba H, Kajihara T, Nishikawa Y, Takahashi M, Ito M (2002) Surface curvatures of trabecular bone microarchitecture. Bone 30:191–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/S8756-3282(01)00672-X
Johnson GR, Cook WH (1983) A computational constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strain, high strain rates and high pressures. In: The seventh international symposium on ballistics, pp. 541–547.
Jones AC, Arns CH, Hutmacher DW, Milthorpe BK, Sheppard AP, Knackstedt MA (2009) The correlation of pore morphology, interconnectivity and physical properties of 3D ceramic scaffolds with bone ingrowth. Biomaterials 30(7):1440–1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.10.056
Katz JL (1980) Anisotropy of Young’s modulus of bone. Nature 283(5742):106–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/283106a0
Kemppainen J (2008) Mechanically stable solid freeform fabricated scaffolds with permeability optimized for cartilage tissue engineering, p. 177. http://proquest.umi.com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/pqdweb?did=1663913111&Fmt=7&clientId=17822&RQT=309&VName=PQD
Krishna BV, Bose S, Bandyopadhyay A (2007) Low stiffness porous Ti structures for load-bearing implants. Acta Biomater 3:997–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2007.03.008
Lee PD, Quested PN, McLean M (1998) Modelling of Marangoni effects in electron beam melting. Philos Trans R Soc A Math Phys Eng Sci 356:1027–1043. https://doi.org/10.1098/RSTA.1998.0207
LéonLeón YCA (1998) New perspectives in mercury porosimetry. Adv Coll Interface Sci 76–77:341–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-8686(98)00052-9
Li QM, Magkiriadis I, Harrigan JJ (2006) Compressive strain at the onset of densification of cellular solids. J Cell Plast 42(5):371–392. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021955X06063519
Li D, Liao W, Dai N, Xie YM (2019) Comparison of mechanical properties and energy absorption of sheet-based and strut-based gyroid cellular structures with graded densities. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/MA12132183
Li Y, Jahr H, Pavanram P, Bobbert FSL, Puggi U, Zhang XY, Pouran B, Leeflang MA, Weinans H, Zhou J, Zadpoor AA (2019b) Additively manufactured functionally graded biodegradable porous iron. Acta Biomater 96:646–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACTBIO.2019.07.013
Liu F, Ran Q, Zhao M, Zhang T, Zhang DZ, Su Z (2020) Additively manufactured continuous cell-size gradient porous scaffolds: pore characteristics, mechanical properties and biological responses in vitro. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/MA13112589
Ma S, Tang Q, Feng Q, Song J, Han X, Guo F (2019a) Mechanical behaviours and mass transport properties of bone-mimicking scaffolds consisted of Gyroid structures manufactured using selective laser melting. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 93:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMBBM.2019.01.023
Ma X, Zhang DZ, Zhao M, Jiang J, Luo F, Zhou H (2021) Mechanical and energy absorption properties of functionally graded lattice structures based on minimal curved surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 118:995–1008. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-021-07768-Y
Mitsak AG, Kemppainen JM, Harris MT, Hollister SJ (2011) Effect of polycaprolactone scaffold permeability on bone regeneration in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A 17(13–14):1831–1839. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2010.0560
Mullen L, Stamp RC, Brooks WK, Jones E, Sutcliffe CJ (2009) Selective Laser Melting: a regular unit cell approach for the manufacture of porous, titanium, bone in-growth constructs, suitable for orthopedic applications. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater 89:325–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/JBM.B.31219
Nauman EA, Fong KE, Keaveny TM (1999) Dependence of intertrabecular permeability on flow direction and anatomic site. Ann Biomed Eng 27(4):517–524. https://doi.org/10.1114/1.195
Pennella F, Cerino G, Massai D, Gallo D, Falvo D’Urso Labate G, Schiavi A, Deriu MA, Audenino A, Morbiducci U (2013) A survey of methods for the evaluation of tissue engineering scaffold permeability. Ann Biomed Eng 41:2027–2041. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10439-013-0815-5
Rombouts M, Kruth JP, Froyen L, Mercelis P (2006) Fundamentals of selective laser melting of alloyed steel powders. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 55:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60395-3
Sanz-Herrera JA, Garcia-Aznar JM, Doblare M (2008) A mathematical model for bone tissue regeneration inside a specific type of scaffold. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 7(5):355–366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10237-007-0089-7
Shah FA, Trobos M, Thomsen P, Palmquist A (2016) Commercially pure titanium (cp-Ti) versus titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) materials as bone anchored implants—is one truly better than the other? Mater Sci Eng C 62:960–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MSEC.2016.01.032
Singh M, Dhiman S, Singh H, Berndt CC (2020) Optimization of modulation-assisted drilling of Ti-6Al-4V aerospace alloy via response surface method. Mater Manuf Process 35:1313–1329. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2020.1772487
Singla AK, Banerjee M, Sharma A, Singh J, Bansal A, Gupta MK, Khanna N, Shahi AS, Goyal DK (2021) Selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V alloy: process parameters, defects and post-treatments. J Manuf Process 64:161–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JMAPRO.2021.01.009
The relationship between stress shielding and bone resorption around total hip stems and the effects of flexible materials - PubMed [WWW Document], n.d. URL https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1728998/. Accessed 24 Sept 2022
Titanium as the material of choice for cementless femoral components in total hip arthroplasty - PubMed [WWW Document], n.d. URL https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7634595/. Accessed 13 Nov 2022
van Blitterswijk CA, Grote JJ, Kuijpers W, Daems WT, de Groot K (1986) Macropore tissue ingrowth: a quantitative and qualitative study on hydroxyapatite ceramic. Biomaterials 7:137–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/0142-9612(86)90071-2
von Schnering HG, Nesper R (1991) Nodal surfaces of Fourier series: fundamental invariants of structured matter. Zeitschrift für Physik B Condensed Matter 83(3):407–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01313411
Wang Z, Li P (2018) Characterisation and constitutive model of tensile properties of selective laser melted Ti-6Al-4V struts for microlattice structures. Mater Sci Eng A 725:350–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.006
Wauthle R, Vrancken B, Beynaerts B, Jorissen K, Schrooten J, Kruth JP, Van Humbeeck J (2015) Effects of build orientation and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V lattice structures. Addit Manuf 5:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2014.12.008
Yadroitsev I, Bertrand P, Smurov I (2007) Parametric analysis of the selective laser melting process. Appl Surf Sci 253:8064–8069. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2007.02.088
Yan C, Hao L, Hussein A, Young P, Raymont D (2014) Advanced lightweight 316L stainless steel cellular lattice structures fabricated via selective laser melting. Mater Des 55:533–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2013.10.027
Yánez A, Cuadrado A, Martel O, Afonso H, Monopoli D (2018) Gyroid porous titanium structures: a versatile solution to be used as scaffolds in bone defect reconstruction. Mater Des 140:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.11.050
Yu G, Li Z, Li S, Zhang Q, Hua Y, Liu H, Zhao X, Dhaidhai DT, Li W, Wang X (2020) The select of internal architecture for porous Ti alloy scaffold: a compromise between mechanical properties and permeability. Mater Des 192:108754. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MATDES.2020.108754
Yuan L, Ding S, Wen C (2019) Additive manufacturing technology for porous metal implant applications and triple minimal surface structures: a review. Bioact Mater 4:56–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOACTMAT.2018.12.003
Zhang XC, Liu NN, An CC, Wu HX, Li N, Hao KM (2021) Dynamic crushing behaviors and enhanced energy absorption of bio-inspired hierarchical honeycombs with different topologies. Def Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DT.2021.11.013
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shiraz University and Mehrawin Company. The micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) test machine used in this study was funded by the preclinical laboratory of Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Funding
This work was supported by the Shiraz University and the Mehrawin Co.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, F., Shafiei-Zarghani, A. & Dehnavi, F. Manufacturability and Mechanical Assessment of Ti-6Al-4V 3D Printed Structures for Patient-Specific Implants. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 48, 397–409 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-023-00664-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-023-00664-8