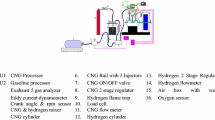
Abstract
This paper shows the effect of 0, 5, 10 and 15 % of hydrogen by energy in compressed natural gas during lean burn and stoichio. burn combustion. All trials are performed at wide open throttle position on 3-cylinder, water-cooled 796 cc S.I engine using sequential port fuel injection system at equivalence ratio of 0.7 and 1.0. Carbon-based emission decreased with increase in hydrogen addition. MBT spark timing increased with increase in speed and decreased with increase in equivalence ratio. At 12°CA spark advance and 2500 rpm, 5 % hydrogen addition shows rise in brake thermal efficiency with optimum NOx. NOx emission increased with increase in hydrogen addition and decreased with MBT spark timing. Heat release rate and maximum rate of pressure rise increased remarkably with 5 % hydrogen addition due to increase in burning velocity. Maximum brake thermal efficiency of 25 % is observed for 5 % hydrogen addition with increase in power output at stoichiometric condition.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSEC:
-
Brake specific energy consumption
- BTE:
-
Brake thermal efficiency
- CHRR:
-
Cumulative heat release rate
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide
- COVIMEP :
-
Coefficient of variation of indicated mean effective pressure
- COVPmax :
-
Coefficient of variation of maximum cylinder pressure
- CNG:
-
Compressed natural gas
- EGR:
-
Exhaust gas recirculation
- HCNG:
-
Hydrogen CNG blends
- H2 :
-
Hydrogen
- HC:
-
Hydrocarbon
- HRR:
-
Heat release rate
- IMEP:
-
Indicated mean effective pressure
- MBT:
-
Maximum brake torque
- MFB:
-
Mass fraction burn
- NOx:
-
Oxides of nitrogen
- ST:
-
Spark timing
- WOT:
-
Wide open throttle
References
Das LM, Polly M (2005) Experimental evaluation of a hydrogen added natural gas (HANG) operated SI Engine. SAE Paper. 26:29
Dimopoulos P, Rechsteinera C (2007) Increase of passenger car engine efficiency with low engine-out emissions using hydrogen–natural gas mixtures: a thermodynamic analysis. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:3073–3083
Fang Y, Liu B, Wang J, Huang Z (2007) Combustion behaviour of a direct-injection engine operating on various fractions of natural gas–hydrogen blends. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:3555–3564
Kahraman N, Ceper B (2009) Investigation of combustion characteristics and emissions in a spark-ignition engine fuelled with natural gas hydrogen blends. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:1026–1034
Ma F, Wang Y (2008) Study on the extension of lean operation limit through hydrogen enrichment in a natural gas spark-ignition engine Safety and Energy. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:1416–1424
Ma F, Wang Y, Liu H, Li Y (2007) Experimental study on thermal efficiency and emission characteristics of a lean burn hydrogen enriched natural gas engine. Int J Hydrogen Energy 32:5067–5075
Ma F, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao S (2008) Development and validation of an on-line hydrogen-natural gas mixing system for internal combustion engine testing. SAE Paper 01:1580
Mughal HU, Bhutta MA (2012) The alternative fuels for four stroke compression ignition engines: performance analysis. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 36(M2):155–164
Ortenzia F, Chiesa M, Scarcelli R (2008) Experimental tests of blends of hydrogen and natural gas in light-duty vehicles. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:3225–3229
Wang Y, Wang Y, Ma F (2008) Study on combustion behaviour and cycle-by-cycle variations in a turbocharged lean burn natural gas S.I engine with hydrogen enrichment. Int J Hydrogen Energy 33:7245–7255
Acknowledgments
I am thankful to Savitribai Phule Pune University for funding this project and also thankful to Director Col. S K Joshi (Retd.) for providing facilities to install the experimental setup in internal combustion laboratory of D Y Patil College of Engineering, Akurdi, Pune.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nitnaware, P.T., Suryawanshi, J.G. Effects of Lean Burn and Stoichio. Burn Combustion on Multi-cylinder SI Engine Using Hydrogen and CNG Blends. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Mech Eng 40, 347–357 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-016-0038-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40997-016-0038-0