Abstract
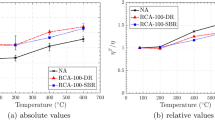
Use of recycled aggregates (RA), obtained from construction and demolition waste, to prepare concrete is very much relevant to ensure sustainable development. Although significant amount of data is available for mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) at ambient temperatures, data regarding the residual stress–strain relationship of RAC after exposure to elevated temperatures is very limited. Focus of this paper is, therefore, to experimentally investigate residual mechanical properties along with residual stress–strain relationship of concrete mixes prepared with recycled aggregates (RA) subjected to elevated temperatures. Concrete cylindrical specimens cast with 30% RA were used in the experimental program. The specimens were first exposed to various elevated temperatures ranging between 100 and 1000 °C at an interval of 100 °C, and were then tested under compression and tension after being brought to ambient temperature. Various properties including residual compressive and splitting tensile strengths, Poisson’s ratio, and modulus of elasticity along with stress–strain behavior were investigated in this study. Change in color of concrete was noticed after 300 °C; while, surface cracks were observed at 500 °C. After 600 °C, substantial loss in concrete compressive and tensile strengths, and stiffness was observed.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowicz M, Kowalski R (2007) Residual mechanical material properties for the reassessment of reinforced concrete structures after fire. In: The 9th international conference: modern building materials, structures and techniques
Arimanwa J, Iwuoha SE, Okere CE, Anyanwn TU (2016) Effect of temperature on recycled aggregate concrete. ARPN J Eng Appl Sci 11:10398–10405
ASTM (2004) ASTM annual book of standards, vol 04.01. Cement; Lime; Gypsum. American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken
Chen H-J, Yen T, Chen K-H (2003) Use of building rubbles as recycled aggregates. Cem Concr Res 33:125–132
Corinaldesi V, Moriconi G (2010) Recycling of rubble from building demolition for low-shrinkage concretes. Waste Manag 30:655–659
Freskakis GN, Burrow RC, Debbas EB (1979) Strength properties of concrete at elevated temperatures (No. CONF-790408--3). Burns and Roe
Gales J, Parker T, Cree D, Green M (2016) Fire performance of sustainable recycled concrete aggregates: mechanical properties at elevated temperatures and current research needs. Fire Technol 52:817–845
Ghanchibhai SF, Rasoolbhai IU, Pandya TH (2019) A review paper on use of recycled concrete aggregate in concrete. http://ir.paruluniversity.ac.in:8080/xmlui/handle/123456789/7840
Ingham JP (2009) Application of petrographic examination techniques to the assessment of fire-damaged concrete and masonry structures. Mater Charact 60:700–709
Khan A-U-R, Aziz T, Fareed S, Xiao J (2020) Behaviour and residual strength prediction of recycled aggregates concrete exposed to elevated temperatures. Arab J Sci Eng 45:8241–8253
Khan A-U-R, Nasir R, Fareed S (2022) Simulation of reinforced concrete columns strengthened with cfrp wraps. Int J Civ Eng 21(2):299–313
Khoury G (1992) Design of concrete for better performance in fire. In: Institution of mechanical engineers conference publications. Medical Engineering Publications Ltd, 121–121
Laneyrie C, Beaucour A-L, Green MF, Hebert RL, Ledesert B, Noumowe A (2016) Influence of recycled coarse aggregates on normal and high performance concrete subjected to elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater 111:368–378
Levy SM, Helene P (2004) Durability of recycled aggregates concrete: a safe way to sustainable development. Cem Concr Res 34:1975–1980
Liu C, Chen J (2022) High temperature degradation mechanism of concrete with plastering layer. Materials 15:398
Malešev M, Radonjanin V, Marinković S (2010) Recycled concrete as aggregate for structural concrete production. Sustainability 2:1204–1225
Najm HM, Nanayakkara O, Ahmad M, Sabri Sabri MM (2022) Colour change of sustainable concrete containing waste ceramic and hybrid fibre: effect of temperature. Materials 15:2174
Rafi MM, Aziz T, Lodi SH (2019) Residual properties of concrete exposed to elevated temperatures. In: Proceedings of the institution of civil engineers-structures and buildings, pp 1–17
Sarhat SR, Sherwood EG (2013) Residual mechanical response of recycled aggregate concrete after exposure to elevated temperatures. J Mater Civ Eng 25:1721–1730
Short N, Purkiss J, Guise S (2001) Assessment of fire damaged concrete using colour image analysis. Constr Build Mater 15:9–15
Tabsh SW, Abdelfatah AS (2009) Influence of recycled concrete aggregates on strength properties of concrete. Constr Build Mater 23:1163–1167
Tam VW, Gao X, Tam CM (2005) Microstructural analysis of recycled aggregate concrete produced from two-stage mixing approach. Cem Concr Res 35:1195–1203
Tam VW, Tam CM, Wang Y (2007) Optimization on proportion for recycled aggregate in concrete using two-stage mixing approach. Constr Build Mater 21:1928–1939
Teranishi K, Dosho Y, Narikawa M, Kikuchi M (1998) Application of Recycled Aggregate Concrete for Structural Concrete. Part 3-Production of Recycled Aggregate by Real-Scale Plant And Quality Of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Sustainable Construction: Use of Recycled Concrete Aggregate: Proceedings of the International Symposium Organised by the Concrete Technology Unit, University of Dundee and Held at the Department of Trade and Industry Conference Centre, London, UK on 11–12 November 1998. Thomas Telford Publishing, pp 143–156
Toumi B, Resheidat M, Guemmadi Z, Chabil H (2009) Coupled effect of high temperature and heating time on the residual strength of normal and high-strength concretes. Jordan J Civ Eng 3:322–330
Vieira J, Correia J, De Brito J (2011) Post-fire residual mechanical properties of concrete made with recycled concrete coarse aggregates. Cem Concr Res 41:533–541
Xiao J, Li W, Poon C (2012) Recent studies on mechanical properties of recycled aggregate concrete in China—a review. Sci China Technol Sci 55:1463–1480
Yang Y, Hou R (2012) Experimental behaviour of racfst stub columns after exposed to high temperatures. Thin-Walled Struct 59:1–10
Yang J, Peng G-F, Zhao J, Shui G-S (2019) On the explosive spalling behavior of ultra-high performance concrete with and without coarse aggregate exposed to high temperature. Constr Build Mater 226:932–944
Yazıcı Ş, Sezer Gİ, Şengül H (2012) The effect of high temperature on the compressive strength of mortars. Constr Build Mater 35:97–100
Zaharieva R, Buyle-Bodin F, Skoczylas F, Wirquin E (2003) Assessment of the surface permeation properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Cem Concr Compos 25:223–232
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the, NED University of Engineering and Technology, Karachi, Pakistan, and Pakistan Science Foundation (PSF) through Joint Research Project between NSFC and PSF (PSF/NSFC-Eng/S-NED (05)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, AuR., Fareed, S. & Aziz, T. Residual Mechanical Properties of Concrete with 30% Recycled Concrete Aggregates Exposed to Elevated Temperatures. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 48, 315–327 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01253-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-023-01253-0