Abstract
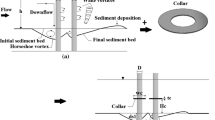
A detailed investigation has been conducted to study the shift location of the point of the maximum scour depth for both bridge abutment-collar and pier-collar arrangements. In the present study, an experimental program has been conducted for abutment-collar arrangements and additionally, the data obtained from the literature for the pier-collar arrangements have been revisited and analyzed to complement the framework of this study. For the abutment-collar arrangements, a series of experiments under clear-water conditions were carried out for different abutment lengths with fixed values of collar location and collar width. For pier-collar arrangements, data used from the literature have been involved constant pier diameter with various collar sizes at various elevations. To describe the locations of these maximum scour depths, their coordinates with respect to the location of the abutment or the pier were obtained. Results from this investigation showed that when a collar placed on or below the bed level was used as a countermeasure against scouring, either on an abutment or on a pier, it was observed that the maximum scour depth was routed downstream of the bridge structure.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- B :
-
Width of the channel
- B a :
-
Width of the abutment
- B c :
-
Width of the collar
- d 50 :
-
Median grain size of the sediment
- d 84 :
-
Sediment sizes for which 84% of the sediments are finer
- d 16 :
-
Sediment sizes for which 16% of the sediments are finer
- Fr :
-
Froude number
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration
- L :
-
Shift distance of the maximum scour depth location around bridge abutment or pier with a collar
- L a :
-
The length of the abutment perpendicular to the flow direction
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- S :
-
Slope of the channel
- t :
-
Time of scour
- T c :
-
Thickness of the collar
- U :
-
Mean velocity of the approach flow
- U c :
-
Critical velocity for initiation of sediment particle motion
- x :
-
Coordinate system axis
- y :
-
Depth of the approach flow
- Z c :
-
Elevation of the collar with respect to the bed level
- Ź:
-
Coordinate system axis
- \(\sigma\) g :
-
Geometric standard deviation of sediment size distribution, (d84,d16)0.5
- θ :
-
Angle of maximum scour depth deviation (in degree)
- \(\rho\) s :
-
Density of the sediment
- \(\rho\) :
-
Density of the fluid
- µ :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid
References
Chiew YM (1992) Scour protection at bridge pier. J Hydraulic Eng 18(9):1260–1269
Ettema RM, Bergendahl BS, Yorozuya A, Idil-Bektur P (2016) Breaching of bridge abutments and scour at exposed abutment columns. J. Hydraul. Eng. 142(10):06016010
Garcia MH (ed) (2007) Sedimentation engineering. ASCE Manuals and reports on engineering practice No: 110, Reston, Virginia
Hong SH, Abid I (2019) Scour around an erodible abutment with riprap apron over time. J Hydraulic Eng 145(6):060190071–060190076
Karami H, Hosseinjanzadeh H, Hosseini K, Ardeshir A (2018) Scour and three-dimensional flow field measurement around short vertical-wall abutment protected by collar. KSCE J Civil Eng 22(1):141–152
Kas I (2005). Effects of collars on local scour around bridge piers. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Gazi Univ., Ankara, Turkey (in Turkish)
Kayaturk S Y, Kokpinar, M A , Gogus, M (2004a). Reduction of local scour around bridge abutments with collars. In: Proc., 2nd Int. Conf. on Fluvial Hydraulics, Balkema, Napoli, Italy (pp. 609–614)
Kayaturk S Y, Kokpinar M A, Gogus, M (2004b). Effect of collar on temporal development of scour around bridge abutments. In: Proc., 2nd Int. Conf. on Scour and Erosion, Surbana, Meritus Mandarin, Singapore (pp. 180–186)
Kayaturk S Y (2005). Scour and scour protection at bridge abutments. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Middle East Technical Univ., Ankara, Turkey
Khosravinia P, Malekpour A, Hosseinzadehdalir A, Farsadizadeh D (2018) Effect of trapezoidal collars as a scour countermeasure around wing-wall abutments. Water Science and Engineering 11(1):53–60
Kuhnle RA, Alonso CV, Shields FD Jr (1999) Geometry of scour holes associated with 90° spur dikes. J Hydraulic Eng 125(9):972–978
Kumar V, Raju KGR, Vittal N (1999) Reduction of local scour around bridge piers using slots and collars. J Hydraulic Eng 125(12):1302–1305
Kumcu SY, Gogus M, Kokpinar MA (2007) Temporal scour development at bridge abutments with a collar. Can j Civ Eng 34(4):549–556
Kumcu SY, Gogus M, Kokpinar MA (2013). Effect of abutment-collar arrangement on the location of the maximum scour depth. In: Proceedings of 2013 IAHR Congress, Tsinghua University Press, Beijing.
Kumcu SY, Kokpinar MA, Gogus M (2014) Scour protection around vertical-wall bridge abutments with collars. KSCE J Civil Eng Korean Soc Civil Eng 18(6):1884–1895
Lim SY (1997) Equilibrium clear-water scour around an abutment. J Hydraulic Eng 123(3):237–243
Melville BW (1992) Local scour at bridge abutments. J Hydraulic Eng 118(4):615–631
Melville BW, Coleman SE (2000) Bridge scour. Water Resources Publications, LLC, Colorado, USA
Mohamed YA, Nasr-Allah TH, Abdel-Aal GM, Awad AS (2015) Investigating the effect of curved shape of bridge abutment provided with collar on local scour, experimentally and numerically. Ain Shams Eng J 6(2):403–411
Nasr-Allah TH, Moussa YAM, Abdel-Aal G, M, Awad, A S, (2016) Experimental and numerical simulation of scour at bridge abutment provided with different arrangements of collars. Alex Eng J 55(2):1455–1463
Osroush M, Hosseini SA, Kamanbedast AA, Khosrojerdi A (2019) The effects of height and vertical position of slot on the reduction of scour hole depth around bridge abutments. Ain Shams Eng J 10(3):651–659
Osroush M, Hosseini SA, Kamabedast AA (2021) Countermeasures against local scouring around bridge abutments: combined system of collar and slot. Iranian J Sci Technol Transac Civil Eng 45:11–25
Singh, C P, Setia, B, and Verma, D V S (2001). Collar-sleeve combination as a scour protection device around a circular pier. In: Proc. of 29th IAHR Congress, IAHR (pp. 202–210)
Sturm TW (2006) Scour around bankline and setback abutments in compound channels. J Hydraulic Eng 132(1):21–32
Sadat, S H and Tominaga, A (2013). Mitigation of local scour hazard at the foot of single spur dike by using optimum footin. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Symposium On River Sedimentation, Advances in River Sediment Research, Taylor & Francis Group (pp. 869–878)
Zarrati AR, Gholami H, Mashahir MB (2004) Application of collar to control scouring around rectangular bridge piers. J Hydraulic Res 42(1):97–103
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumcu, S.Y., Kokpinar, M.A. & Gogus, M. Effect of Collars on the Downstream Movement of the Maximum Scour Depth Location Around Bridge Abutments and Piers. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 46, 1421–1432 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00654-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-021-00654-3