Abstract
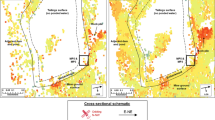
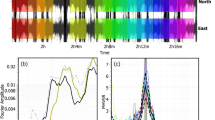
Seismic ambient noise is nowadays widely used in geophysics to characterize the subsoil structure. They are convenient, practical, and low-cost tool to provide reliable information about the underground structure especially in urbanized area. In this paper, seismic ambient noise measurements are used to study the subsoil properties at a site in the south of Tehran. Single station RayDec (Random Decrement method) and three-component F–K (frequency–wavenumber) array methods are considered. RayDec is scrutinized more precisely through applying different signal processing parameters. In this regard, a set of synthetic seismic ambient noise is produced for a 1-D earth structure very similar to what already is known in the south of Tehran, near to the place of seismic ambient noise measurements in an array of stations. The effects of applying different filters and triggering conditions on ellipticity curves are studied. Then, resultant ellipticity curves are compared to the theoretical curve obtained from known earth model to find the suitable parameters. The resultant ellipticity curve plus the dispersion curve obtained from F–K are used as targets in the inversion process. The shear wave velocity and the depth of bedrock at the site in the south of Tehran are estimated about 2200 ± 200 m/s and 700 ± 70 m, respectively. They show agreement with geological evidences and also the previous studies in this site.












Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
The Geopsy software package is available at http://www.geopsy.org (last accessed April 2019). The RayDec code (Hobiger et al. 2009) is available upon request. The revised RayDec code is accessible from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References:
Asmussen JC (1997) Modal analysis based on the random decrement technique: application to civil engineering structures. PhD thesis, Univ. Aalborg, Denmark
Asmussen JC, Ibrahim SR, Brincker R (1998) Random decrement: Identification of structures subjected to ambient excitation. In: Proceedings of the 16th international modal analysis conference, Santa Barbara, California, USA, vol 2, pp 914–921
Asten MW, Henstridge JD (1984) Array estimators and the use of microseisms for reconnaissance of sedimentary basins. Geophysics 49(11):1828–1837. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1441596
Bettig B, Bard PY, Scherbaum F, Riepl J, Cotton F, Cornou C, Hatzfeld D (2001) Analysis of dense array noise measurements using the modified spatial auto-correlation method (SPAC): application to the Grenoble area. Boll Geof Teor Appl 42:281–304
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Cotton F, Bard PY (2006) The nature of noise wavefield and its applications for site effects studies. A literature review. Earth-Sci Rev 79:205–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2006.07.004
Bonnefoy-Claudet S, Köhler A, Cornou C, Wathelet M, Bard PY (2008) Effects of love waves on microtremor H/V ratio. Bull Seismol Soc Am 98(1):288–300. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120070063
Capon J (1969) High-resolution frequency-wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proc IEEE 57:1408–1418. https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1969.7278
Cole HA (1973) On-line failure detection and damping measuremnet of aerospace structures by Random Decremnet signatures. NASA CR-2205.
Endrun B (2011) Love wave contribution to the ambient vibration H/V amplitude peak observed with array measurements. J Seismol 15:443–472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-010-9191-x
Fäh D, Kind F, Giardini D (2001) A theoretical investigation of average H/V ratios. Geophys J Int 145:535–549. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0956-540x.2001.01406.x
Fäh D, Wathelet M, Kristekova M, Havenith H, Endrun B, Stamm G, Poggi V, Burjanek J, Cornou C (2009) Using ellipticity information for site characterisation. NERIES deliverable JRA4D4, Final Report. http://www.neries-jra4.geopsy.org
Haghshenas E (2005) Condition Géotechniques et Aléa Sismique Local à Téhéran. Ph.D Thesis, Fourier University, France, Grenoble
Hisada Y (1994) An efficient method for computing Green’s functions for a layered half-space with sources and receivers at close depths. Bull Seismol Soc Am 84(5):1456–1472
Hisada Y (1995) An efficient method for computing Green’s functions for a layered half-space with sources and receivers at close depths (Part 2). Bull Seismol Soc Am 85(4):1080–1093
Hobiger M (2011) Polarization of surface waves: characterization, inversion and application to seismic hazard assessment. PhD thesis, Univ. Joseph Fourier, Grenoble, Fr.
Hobiger M, Bard PY, Cornou C, Le Bihan N (2009) Single station determination of Rayleigh wave ellipticity by using the random decrement technique (RayDec). Geophys Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL038863
Hobiger M, Cornou C, Wathelet M, Di Giulio G, Knapmeyer-Endrun B, Renalier F, Bard PY, Savvaidis A, Hailemikael S, Le Bihan N, Ohrnberger M, Theodoulidis N (2013) Ground structure imaging by inversions of Rayleigh wave ellipticity: sensitivity analysis and application to European strong-motion sites. Geophys J Int 192:207–229. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggs005
Jafari MK, Razmkhah A, Keshavarz-bakhshayesh M, Sohrabi A, Pourazian Kh (2001) Etude Complementaire de Microzonage Sismique au Sud de Téhéran. Pub, IIEES, Spec
JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency) & CEST (Centre for Earthquake & Environmental Studies of Tehran, Tehran Municipality) (2000) The Study on Seismic Microzoning of the Greater Tehran Area in The Islamic Republic of Iran, Final report.
Köhler A, Ohrnberger M, Scherbaum F, Wathelet M, Cornou C (2007) Assessing the reliability of the modified three-component spatial autocorrelation technique. Geophys J Int 168:779–796. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2006.03253.x
Konno K, Ohmachi T (1998) Ground-motion characteristics estimated from spectral ratio between horizontal and vertical components of microtremor. Bull Seismol Soc Am 88(1):228–241
Lacoss RT, Kelly EJ, Toksöz MN (1969) Estimation of seismic noise structure using arrays. Geophysics 34:21–38. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1439995
Michel C, Guéguen P, Bard PY (2008) Dynamic parameters of structures extracted from ambient vibration measurements: An aid for the seismic vulnerability assessment of existing buildings in moderate seismic hazard regions. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2007.10.002
Moczo P, Kristek J (2002) FD Code to generate noise synthetics, SESAME Rep. D02.09, IGSAS, Bratislava. http://SESAME-FP5.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr
Nakamura Y (1989) A method for dynamic characteristics estimation of subsurface using microtremor on the ground surface. Q Report of RTRI 30(1):25–33
Nogoshi M, Igarashi T (1971) On the Amplitude characteristics of microtremor (Part 2) (in Japanese with English Abstract). J Seismol Soc Jpn 24:26–40. https://doi.org/10.4294/zisin1948.24.1_26
Parolai S, Picozzi M, Richwalski SM, Milkereit C (2005) Joint inversion of phase velocity dispersion and H/V ratio curves from seismic noise recordings using a genetic algorithm, considering higher modes. Res. Lett, Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL021115
Poggi V, Fäh D, Burjanek J, Giardini D (2012) The use of Rayleigh-wave ellipticity for site-specific hazard assessment and microzonation: Application to the city of Lucerne, Switzerland. Geophys J Int 188(3):1154–1172. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.05305.x
Scherbaum F, Hinzen KG, Ohrnberger M (2003) Determination of shallow shear wave velocity profiles in the cologne, Germany area using ambient vibrations. Geophys J Int 152(3):597–612. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-246X.2003.01856.x
SESAME group (2004) Report of the WP04 – H/V technique: Empirical evaluation comparison of experimentally and theoretically estimated transfer functions with the (H/V) spectral ratio and evaluation of the applicability of the latter in cases of linear or/and non-linear soil behaviour, SESAME deliverable D16.04. http://sesame-fp5.obs.ujf-grenoble.fr/Deliverables/D16-04.pdf
Shabani E, Cornou C, Haghshenas E, Wathelet M, Bard PY, Mirzaei N, Eskandari-Ghadi M (2008) Estimating shear-waves velocity structure by using array methods (FK and SPAC) and inversion of ellipticity curves at a site in south of Tehran. In: Proceedings of the 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Beijing, China
Smith SW (1999) The scientist and engineer’s guide to digital signal processing, California Technical Publishing. http://www.dspguide.com
Wathelet M (2005) Array recordings of ambient vibrations : surface-wave inversion. PhD thesis, Univ. Liège, Belgium
Wathelet M (2008) An improved neighborhood algorithm: parameter conditions and dynamic scaling. Geophys Res Lett 35:L09301. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008GL033256
Wathelet M, Jongmans D, Bonnefoy-Claudet OM, S, (2008) Array performances for ambient vibrations on a shallow structure and consequences over Vs inversion. J Seismol 12:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-007-9067-x
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES), for giving permission to use of the data of project no. 6506 done in 2008. Also, we are thankful to the anonymous reviewer and Dr. Shomali for their constructive comments which helped improve this manuscript.
Funding
No funding is dedicated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and material
The synthetic data produced for this study could be accessed via request. The seismic ambient noise recorded in Tehran used in this study can be accessed by permit, and it is borrowed from the International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IIEES).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moghadasi, N.S., Shabani, E., Fotouhimehr, M. et al. Analysis of RayDec Parameters in Extracting Ellipticity Curve to Retrieve Shear Wave Velocity Profile: A Case Study in the South of Tehran. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Civ Eng 45, 2413–2424 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00557-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-020-00557-9