Abstract
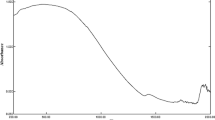
This study explores the fabrication of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles utilizing aqueous extracts of Plectranthus amboinicus, which act as reducing and stabilizing agents. The prepared hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles have been characterized by TGA, PXRD, FT-IR, Raman, DRS UV–visible, Photoluminescence, SEM, Particle size distribution, and zeta potential measurements (DLS), respectively. According to the XRD reports, hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles are rhombohedral with a crystallite size of 7.0 nm. As of the FT-IR spectrum, the peaks attained at 544 and 447 cm−1 are attributes of Fe–O stretching in α-Fe2O3. As a result of Raman analysis, the existence of vibration modes of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles was confirmed. Through the DRS UV–visible reflectance, the bandgap energy of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles was detected to be 2.0 eV. The photoluminescence spectrum shows band edge emission at 552 nm. The morphology of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles was aggregated with dense irregular shape and highly porous. Particle size distribution and zeta potential value of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles were reported at 40 nm and − 35 mV, respectively. These nanoparticles exhibit strong antibacterial activity at a concentration of 30 μg/mL and also exhibit substantial minimum inhibition concentration value for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The proposed strategy is therefore rapid, simple, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly which can be employed for the fabrication of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles and can be used as a potent antibacterial agent.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bashir AKH, Furqan CM, Bharuth-Ramc K, Kaviyarasu K, Tchokontée MBT, Maazaa M (2019) Structural, optical and Mössbauer investigation on the biosynthesized α-Fe2O3: study on different precursors. Physica E 111:152–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2019.03.010
Darezereshki E, Bakhtiari F, Alizadeh M, Vakylabad AB, Ranjbar M (2012) Direct thermal decomposition synthesis and characterization of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process 1:91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2011.09.009
Fu L, Fu Z (2014) Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract–assisted biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.10.069
Fu L, Zheng Y, Ren Q, Wang A, Deng B (2015) Green biosynthesis of Sno2 nanoparticles by Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract their photocatalytic activity toward rhodamine B degradation. J Ovonic Res 11:21–26
James Jeyaseelan S, Parasuraman K, Johnson Jeyakumar S, Jothibas M (2019) Structural, optical and magnetic properties of (Fe2O3 synthesis via Sol-Gel technique. Int J Anal Exper Modal Anal. 9(7), ISSN NO: 0886-9367
Jha R, Dhagar R, Sharma N (2016) Aloe vera mediated synthesis of ε-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Int J Innov Eng Technol 1:663–667
Kareem ZH, Shareef HK, Alkaim AF (2018) Evaluation of antibacterial activity of Fe2O3 nanoparticles against Shigella dysenteriae. J Pharm Sci Res 10:1980–1982
Khalil AT, Ovais M, Ullah I, Ali M, Shinwari ZK, Maaza M (2017) Biosynthesis of iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles via aqueous extracts of Sageretia thea (Osbeck.) and their pharmacognostic properties. Green Chem Lett Rev 4:186–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2017.1339831
Kumar P, Sangam, Kumar N (2020) Plectranthus amboinicus: a review on its pharmacological and pharmacognostical studies. Am J Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 10:55–62. https://doi.org/10.5455/ajpbp.20190928091007
Lassoued A, Dkhil B, Gadri A, Ammar S (2017) Control of the shape and size of iron oxide (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles synthesized through the chemical precipitation method. Results Phys 7:3007–3015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.07.066
Maji SK, Mukherjee N, Mondal A, Adhikary B (2012) Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Polyhedron 1:145–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poly.2011.11.017
Naz S, Islam M, Tabassum S, Fernandes NF, Esperanza J, de Blanco C, Zia M (2019) Green synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles using Rhus punjabensis extract and their biomedical prospect in pathogenic diseases and cancer. J Mol Struct 1185:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.02.088
Pallelaa PNVK, Ummeyb S, Ruddarajuc LK, Gadia S, Cherukuria CS, Barlaa S, Pammid SVN (2019) Antibacterial efficacy of green synthesized α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using Sida cordifolia plant extract. Heliyon 5:e02765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02765
Parthasarathy S, Jayacumar S, Chakraborty S, Soundararajan P, Joshi D, Gangwar K, Bhattacharjee A, Pandima Devi Venkatesh M (2020) Fabrication and characterization of copper nanoparticles by green synthesis approach using Plectranthus amboinicus leaves extract. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-55984/v1
Qi K, Cheng B, Jiaguo Yu, Ho W (2017) Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. J Alloy Compd 727:792–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.142
Raja K, Mary Jaculine M, Jose M, Sunil V, Prince AAM, Ilangovan K, Sethusankar K, Jerome Das S (2015) Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Superlattices Microstruct 86:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.07.044
Ramalingam V, Harshavardhan M, Kumar SD, Malathi Devi S (2020) Wet chemical mediated hematite α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesis: preparation, characterization and anticancer activity against human metastatic ovarian cancer. J Alloy Compd 834:155118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155118
Ramesh R, Yamini V, Rajkumar D, John Sundaram S, Lakshmia D, Liakath Ali Khan F (2020) Biogenic synthesis of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles using Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.095
Rufus A, Sreeju R, Philip D (2016) Synthesis of biogenic hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticles for antibacterial and nanofluid applications. RSC Adv 96:94206–94217. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA20240C
Rufus A, Sreeju N, Philip D (2018) Size tunable biosynthesis and luminescence quenching of nanostructured hematite (α- α-Fe2O3) for catalytic degradation of organic pollutants. J Phys Chem Solids 124:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.09.026
Satyajit SD, Nahar L, Kumarasamy Y (2007) Microtitre plate-based antibacterial assay incorporating resazurin as an indicator of cell growth, and its application in the in vitro antibacterial screening of phytochemicals. Methods 4:321–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.01.006
Sheik Fareed S, Mythili N, Vijayaprasath G, Chandramohan R, Ravi G (2018) α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as a by-product from the thin film (SILAR) deposition process: a study on the product. Mater Today Proc 10:20955–20965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.485
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kasu NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett 7:219–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-015-0040-x
Tadic M, Trpkov D, Kopanja L, Vojnovic S, Panjan M (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanoparticle forms: synthesis conditions, structure, particle shape analysis, cytotoxicity and magnetic properties. J Alloy Compd 792:599e609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.414
Tawfik EK, Eisa WH, Okasha N, Ashry HA (2020) Influence of annealing temperature of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles on structure and optical properties. J Sci Res Sci 37:1–20
Valgas C, Machado de Souza S, de Smânia EFA, Smânia A (2007) Screening methods to determine antibacterial activity of natural products. Braz J Microbiol 38:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822007000200034
Velasankar K, Vinothini V, Sudhahar S, Krishna Kumar M, Mohandoss S (2020) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles via Plectranthus amboinicus leaves extract with its characterization on structural, morphological, and biological properties. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01504-w
Zheng Y, Wang Z, Peng F, Fu L (2017) Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Plectranthus amboinicus leaf extract and their catalytic activity towards methylene blue degradation. Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química. 16:41–45
Funding
The author, Dr. K. Venkatachalam gratefully acknowledges the financial assistance from the Department of Science and Technology, India for the DST-SERB Project (Ref. No. EEQ/2016/000559, date.: 06.02.2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Credit Authorship Statement
Prashanna Suvaitha Sundara Selvam – Conceptualization; Methodology; Formal analysis; Investigation; Resources; Data Curation; Writing original draft preparation; Writing-review and editing. Sangeetha Govindan – Methodology. Bhavani Perumal – Visualization. Venkatachalam Kandan – Writing-review, Funding acquisition; Visualization; Supervision; Project administration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sundara Selvam, P.S., Govindan, S., Perumal, B. et al. Screening of In Vitro Antibacterial Property of Hematite (α-Fe2O3) Nanoparticles: A Green Approach. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 45, 177–187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00995-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-020-00995-0