Abstract
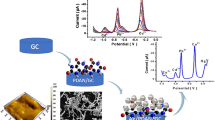
A novel sensor was fabricated for simultaneous quantification of tin and lead. The sensor is based on the adsorptive accumulation of tin and lead onto an amino-functionalized superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (spion)/glassy carbon electrode. Main parameters affecting the stripping performance mainly, accumulation potential, pH, accumulation time and interference by other ions were studied. The detection limits were found to be 0.12 and 0.10 ng/mL at an accumulation time of 100 s for lead and tin, respectively. The proposed procedure was validated using a standard procedure. The sensor is applied to analysis of tin and lead in water samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Farmany A, Mortazavi SS (2010) Ultrasensitive simultaneous quantification of nanomolar level of Cd and Zn by cathodic adsorptive stripping voltammetry in some real samples. Electroanalysis 22:2884–2888
Abbasi S, Daneshfar A, Hamdghadareh S, Farmany A (2011) Quantification of sub-nanomolar levels of gallic acid by adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:4843–4852
Adeloju SBO, Pablo F (1995) Simultaneous determination of lead and tin in biological and environmental materials by differential pulse cathodic voltammetry on a glassy carbon mercury film electrode. Electroanalysis 7:750–755
Cutress IJ, Compton RG (2009) Stripping voltammetry at microdisk electrode arrays: theory. Electroanalysis 21:2617–2625
Delshab H, Farshchi P, Mohammadi M (2016) Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci. doi:10.1007/s40995-016-0031-x
Diasa LF, Saintpierre TD, Maia SM, Dasilva MAM, Frescura VLA, Welzb B, Curtius AJ (2002) Determination of arsenic, lead, selenium and tin in sediments by slurry sampling electrothermal vaporization inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry using Ru as permanent modifier and NaCl as a carrier. Spectrochim Acta Part B 57:2003–2015
Dirilgen N, Dogan F (2004) Anodic stripping voltammetry: sn and pb analysis in archaeometallurgical samples. Int J Environ Anal Chem 84(11):855–864
Farmany A, Mortazavi SS, Mahdavi H (2016) Ultrasond-assisted synthesis of Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell with enhanced adsorption capacity for diazinon removal. J Magn Magn Mater 416:75–80
Heidarimoghaddam R, Mortazavi SS, Farmany A (2015) New electrochemical sensor for sensitive quantification of copper in river, city, bottled and drinking water samples. J Water Suppl Res Technol Aqua 64(6):749–754
Hu Q, Yang G, Li H, Tai X, Yin J (2004) Determination of Seven transition metal ions in water and food by. microcolumn. Bull Korean Chem Soc 25:694
Izadkhah V, Farmany A, Mortazavi SS (2015) Voltammetric determination of copper in water samples using a Schiff base/carbon nanotube-modified carbon paste electrode. J Ind Eng Chem 21:994–996
Liao M, Guo J, Chen W (2006) disposable amperometric ethanol biosensor based on screen-printed carbon electrodes mediated with ferricyanide-magnetic nanoparticle mixture. J Magn Magn Mater 304:e421–e423
March G, Nguyen TD, Piro B (2015) Modified electrodes used for electrochemical detection of metal ions in environmental analysis. Biosensors 5:241–275
Melgar MJ, Miguez B, Perez M, Garcia MA, Fernandez MI, Vidal M (1997) Heavy metals (Cd, Pb, Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu) in drinking water as toxicological indicators. J Environ Sci Health 32:687–697
Melucci D, Torsi G, Locatelli C (2007) Analytical procedure for the simultaneous voltammetric determination of trace metals in food and environmental matrices. Critical comparison with atomic absorption spectroscopic measurements. Ann Chim 97(3–4):141–151
Ni Y, Wang L (1999) Simultaneous polarographic determination of Lead (II) and Tin (II) by multivariate calibration. Anal Lett 32:2081–2089
Niazi A, Sharifi S, Amjadi E (2008) Least-squares support vector machines for simultaneous voltammetric determination of lead and tin: A comparison between LSSVM and PLS in voltammetric data. J Electroanal Chem 623:86–92
Penkova A, Martínez Blanes JM, Cruz SA, Centeno MA, Hadjiivanov K, Odriozola JA (2009) Gold nanoparticles on silica monospheres modified by amino groups. Microporous Mesoporous Materials 117:530–534
Sabry SM, Wahbi A-AM (1999) Application of orthogonal functions to differential pulse voltammetric analysis. Anal Chim Acta 401:173–183
Shams E, Abdollahi H, Yekehtaz M, Hajian R (2004) H-point standard addition determination of lead and tin. Talanta 63:359–364
Sobhanardakani S, Farmany A, Abbasi S (2014) A new modified multiwalled carbon nanotube paste electrode for quantification of tin in fruit juice and bottled water samples. J Ind Eng Chem 20:3214–3216
Wang J, Kawde A-N (2002) Magnetic-field stimulated DNA oxidation. Electrochem Commun 4:349–352
Yamaura M, Camilo RL, Sampaio LC, Macedo MA, Nakamura M, Toma HE (2004) Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 279:210–216
Yang TZ, Shen CM, Gao HJ (2005) Highly ordered self-assembly with large area of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the magnetic properties. J Phys Chem B 109:23233
Zacharia A, Gucer S, Izgl B, Chebotarev A, Karaaslan H (2007) Direct atomic absorption spectrometry determination of tin, lead, cadmium and zinc in high-purity graphite with flame furnace atomizer. Talanta 72:825–830
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mortazavi, S.S., Farmany, A. 3-Aminopropyl-triethoxysilane/spion/GC Electrode for Simultaneous Quantification of Tin and Lead. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 42, 539–545 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0231-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-017-0231-z