Abstract
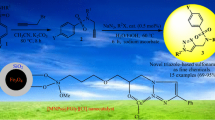
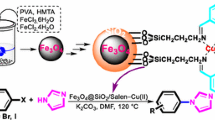
We report a recyclable ligand complex of copper(II) supported on superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticle catalytic system for efficiently synthesis of 1-aryl-1,2,3-triazole derivatives in excellent yields. The desired triazoles were obtained from the reaction of the corresponding aryl bronic acid derivatives, alkyne, NaN3, and 2.0 mol % of the catalyst in H2O as the green solvent at 60 °C without the additional use of external reducing agent. The mechanism revealed that sodium azide, which is used as azidonating reagent in one-pot protocol reduces Cu(II) to click-active Cu(I). The suggested method offers several advantages such as excellent yields, short reaction time, operational simplicity, a cleaner reaction, and absence of any tedious workup or purification. In addition, the excellent catalytic performance in a water medium and the thermal stability, easy preparation and separation of the catalyst make it a good heterogeneous system and a useful alternative to other heterogeneous catalysts. Also, the aforementioned catalyst can be easily recovered by an external magnetic field and reused for subsequent reactions at least eight times without noticeable deterioration in catalytic activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson S, Safraou W, Malezieux B, Dupuis V, Borensztajn S, Briot E, Bée A (2011) An eco-friendly route to magnetic silica microspheres and nanospheres. J Colloid Interface Sci 364:324–332
Amantini D, Fringuelli F, Piermatti O, Pizzo F, Zunino E, Vaccaro L (2005) Synthesis of 4-Aryl-1H-1,2,3-triazoles through TBAF-catalyzed [3 + 2] cycloaddition of 2-Aryl-1-nitroethenes with TMSN3 under solvent-free conditions. J Org Chem 70:6526–6529
Chassaing S, Sido ASS, Alix A, Kumarraja M, Pale P, Sommer J (2008) Click Chemistry in zeolites: copper(I) zeolites as new heterogeneous and ligand-free catalysts for the Huisgen [3 + 2] cycloaddition. Chem Eur J 14:6713–6721
Chen FH, Gao Q, Ni JZ (2008) The grafting and release behavior of doxorubincin from Fe3O4@SiO2 core-shell structure nanoparticles via an acid cleaving amide bond: the potential for magnetic targeting drug delivery. Nanotechnology. 2008(19):165103
Deng Y, Qi D, Deng C, Zhang X, Zhao D (2008) Superparamagnetic high-magnetization microspheres with an Fe3O4@SiO2 core and perpendicularly aligned mesoporous SiO2 shell for removal of microcystins. J Am Chem Soc 130:28–29
Deng Y, Cai Y, Sun Z, Liu J, Liu C, Wei J, Li W, Liu C, Wang Y, Zhao D (2010) Multifunctional mesoporous composite microspheres with well-designed nanostructure: a highly integrated catalyst system. J Am Chem Soc 132:8466–8473
Esmaeilpour M, Javidi J, Nowroozi Dodeji F, Abarghoui MM (2014) M(II) Schiff base complexes (M 5 zinc, manganese, cadmium, cobalt, copper, nickel, iron, and palladium) supported on superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and catalytic activity for Sonogashira-Hagihara coupling reactions. Transit Met Chem 39:797–809
Esmaeilpour M, Javidi J, Zandi M (2015) One-pot synthesis of multisubstituted imidazoles under solvent-free conditions and microwave irradiation using Fe3O4@SiO2-imid-PMAn magnetic porous nanospheres as a recyclable catalyst. New J Chem 39:3388–3398
Frank E, Molnár J, Zupkó I, Kádár Z, Wölfling J (2011) Synthesis of novel steroidal 17α-triazolyl derivatives via Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition, and an evaluation of their cytotoxic activity in vitro. Steroids 76:1141–1148
Girard C, Önen E, Aufort M, Beauvière S, Samson E, Herscovici J (2006) Reusable polymer-supported catalyst for the [3 + 2] Huisgen cycloaddition in automation protocols. Org Lett 8:1689–1692
Himo F, Lovell T, Hilgraf R, Rostovtsev VV, Noodleman L, Sharpless KB, Fokin VV (2005) Copper(I)-catalyzed synthesis of azoles. DFT study predicts unprecedented reactivity and intermediates. J Am Chem Soc 127:210–216
Jacob K, Stolle A, Ondruschka B, Jandt KD, Keller TF (2013) Cu on porous glass: an easily recyclable catalyst for the microwave-assisted azide–alkyne cycloaddition in water. Appl Catal A Gen 451:94–100
Javidi J, Esmaeilpour M (2013) Synthesis of Fe3O4@silica/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) as a novel thermo-responsive system for controlled release of H3PMo12O40 nano drug in AC magnetic field. Colloid Surf B. 102:265–272
Javidi J, Esmaeilpour M, Nowroozi Dodeji F (2015) Immobilization of phosphomolybdic acid nanoparticles on imidazole functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2: a novel and reusable nanocatalyst for one-pot synthesis of Biginelli-type 3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2-(1H)-ones/thiones under solvent-free conditions. RSC Adv. 5:308–315
Jiang Y, Kuang C, Yang Q (2009) The use of calcium carbide in the synthesis of 1-monosubstituted aryl 1,2,3-triazole via click chemistry. Synlett 3163–3166
Jlalia I, Gallier F, Brodie-Linder N, Uziel J, Augé J, Lubin-Germain N (2014) Copper(II) SBA-15: a reusable catalyst for azide-alkyne cycloaddition. J Mol Catal A Chem 393:56–61
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: the influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J Phys Chem B. 107:668–677
Lipshutz BH, Taft BR (2006) Heterogeneous copper-in-charcoal-catalyzed click chemistry. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:8235–8238
Lu W, Lieber CM (2007) Nanoelectronics from the bottom up. Nat Mater 6:841–850
Masuyama Y, Yoshikawa K, Suzuki N, Hara K, Fukuoka A (2011) Hydroxyapatite-supported copper(II)-catalyzed azide–alkyne [3 + 2] cycloaddition with neither reducing agents nor bases in water. Tetrahedron Lett 52:6916–6918
Meldal M, Tomøe CW (2008) Cu-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition. Chem Rev 108:2952–3015
Miao T, Wang L (2008) Regioselective synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles by use of a silica-supported copper(I) catalyst. Synthesis 363–368
Mohammed S, Padala AK, Dar BA, Singh B, Sreedhar B, Vishwakarma RA, Bharate SB (2012) Recyclable clay supported Cu (II) catalyzed tandem one-pot synthesis of 1-aryl-1,2,3-triazoles. Tetrahedron 68:8156–8162
Namitharan K, Kumarraja M, Pitchumani K (2009) CuII–Hydrotalcite as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for Huisgen [3 + 2] cycloaddition. Chem Eur J 15:2755–2758
Reiss G, Hütten A (2005) Magnetic nanoparticles: applications beyond data storage. Nat Mater 4:725–726
Rostovtsev VV, Green LG, Fokin VV, Sharpless KB (2002) A stepwise huisgen cycloaddition process: copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “Ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew Chem Int Ed 41:2596–2599
Schweinfurth D, Strobel S, Sarkar B (2011) Expanding the scope of ‘Click’ derived 1,2,3-triazole ligands: new palladium and platinum complexes. Inorg Chim Acta 374:253–260
Shao M, Ning F, Zhao J, Wei M, Evans DG, Duan X (2012) Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2@layered double hydroxide core-shell microspheres for magnetic separation of proteins. J Am Chem Soc 134:1071–1077
Wu H, Tang L, An L, Wang X, Zhang H, Shi J, Yang S (2012) pH- responsive magnetic mesoporous silica nanospheres for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. React Funct Polym 72:329–336
Xia Y, Fan Z, Yao J, Liao Q, Li W, Qu F, Peng L (2006) Discovery of bitriazolyl compounds as novel antiviral candidates for combating the tobacco mosaic virus. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:2693–2698
Young Kim J, Chan Park J, Kang H, Song H, Hyun Park K (2010) CuO hollow nanostructures catalyze [3 + 2] cycloaddition of azides with terminal alkynes. Chem Commun 46:439–441
Zhang J, Sun W, Bergman L, Rosenholm JM, Lindén M, Wu G, Xu H, Gu HC (2012) Magnetic mesoporous silica nanospheres as DNA/drug carrier. Mater Lett 67:379–382
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to the council of Iran National Science Foundation and University of Shiraz for their unending effort to provide financial support to undertake this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esmaeilpour, M., Javidi, J. & Davan, E.E. Click Synthesis of 1-Aryl-1,2,3-Triazole Derivatives Catalyzed by Recyclable Ligand Complex of Copper(II) Supported on Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanoparticles. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 42, 487–496 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0125-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0125-5