Abstract
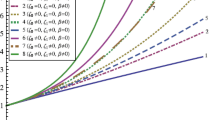
In this paper, we constructed Kaluza–Klein FRW model with modified cosmic Chaplygin gas in presence of bulk viscosity. We used exponential function method (Ganji and Hasheni Kachapi 2011) to solve non-linear differential equation and obtained time dependent dark energy density. We explained the nature of the energy density for different values of parameters through graphical representation briefly. Also, we investigated the nature of the energy density with and without bulk viscosity. Finally we discussed stability of this theory and obtained that, the model does not have any singularity in presence and absence of bulk viscosity.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afshordi N, Chung DJH, Geshnizjani G (2007) Causal field theory with an infinite speed of sound. Phys Rev D 75:083513
Amani AR, Pourhassan B (2013) Viscous generalized Chaplygin gas with arbitrary α. Int J Theor Phys 52:1309
Appelquist T, Chodos A, Freund PGO (1987) Modern Kaluza–Klein theories. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Benaoum HB (2012) Modified Chaplygin gas cosmology. Adv High Energy Phys 2012:357802. doi:10.1155/2012/357802
Bali R, Jain DR (1988) Some expanding and shearing viscous fluid cosmological models in general relativity. Astrophys Space Sci 141:207
Bali R, Jain DR (1991) Viscous fluid universe filled with stiff fluid in general relativity. Astrophys Space Sci 185:211
Bali R, Kumawat P (2008) Bulk viscous LRS Bianchi type V tilted stiff fluid cosmological model in general relativity. Phys Lett B 665:332
Bali R, Pradhan A (2007) Bianchi type-III string cosmological models with time dependent bulk viscosity. Chin Phys Lett 24:585
Banerjee A, Santos NO (1986) Homogeneous anisotropic cosmological models with viscous fluid and magnetic field. Gen Relativ Gravit 18:1251
Banerjee A, Duttachoudhury SB, Sanyal AK (1986) Bianchi type-II cosmological model with viscous fluid. Gen Relativ Gravit 18:461
Bazeia D (1999) Galileo invariant system and the motion of relativistic d-branes. Phys Rev D 59:085007
Bento MC, Bertolami O, Sen AA (2002) Generalized Chaplygin gas, accelerated expansion, and dark-energy-matter unification. Phys Rev D 66:43507
Bento MC, Bertolami D, Sen AA (2003) WMAP constraints on the generalized Chaplygin gas model. Phys Lett B 575:172
Bilic N, Tupper GB, Viollier RD (2002) Unification of dark matter and dark energy: the inhomogeneous Chaplygin gas. Phys Lett B 535:17
Bordemann M, Hoppe J (1993) The dynamics of relativistic membranes. Reduction to 2-dimensional fluid dynamics. Phys Lett B 317:315
Caldwell RR (2002) A phantom menace? Cosmological consequences of a dark energy component with super-negative equation of state. Phys Lett B 545:23
Capozziello S, Cardone VF, Farajollahi H, Ravanpak A (2011) Cosmography in f (T) gravity. Phys Rev D 84:043527
Chao LJ, Li-Xin X, Jian-Bo L, Rong CB, Hong-Ya L (2008) Constraints on deceleration parameter of a 5D bounce cosmological model from recent cosmic observations. Chin Phys Lett 25:802
Chaplygin S (2004) On gas jets. Sci Mem Moscow Univ Math Phys 21:1
Cline JM, Jeon S, Moore GD (2004) The phantom menaced: constraints on low-energy effective ghosts. Phys Rev D 70:043543
Collins PDB, Martin AD, Squires EJ (1989) Particle physics and cosmology. Wiley, London
Debnath U, Banerjee A, Chakraborty S (2004a) Role of modified Chaplygin gas in accelerated universe. Class Quantum Gravity 21:5609
Debnath U, Banerjee A, Chakraborty S (2004b) Role of modified Chaplygin gas in accelerated universe. Class Quantum Gravity 21:5609
Fabris JC, Goncalves SVB, De Souza PE (2002) Letter: density perturbations in a universe dominated by the Chaplygin gas. Gen Relativ Gravit 34:53
Feng B, Wang XL, Zhang XM (2005) Dark energy constraints from the cosmic age and supernova. Phys Lett B 607:35
Ganji DD, Hasheni Kachapi SH (2011) Analytical and numerical methods in engineering and applied sciences. Prog Non Linear Sci 3:1
Gonzalez-Diez PF (2003) You need not be afraid of phantom energy. Phys Rev D 68:021303
Gorini V, Kamenshchik A, Moschella U (2003) Can the Chaplygin gas be a plausible model for dark energy? Phys Rev D 67:063509
Heller M, Klimek Z (1975) Viscous universes without initial singularity. Astrophys Space Sci 33:L37
Jackiw R, Polychronakos AP (2000) Supersymmetric fluid mechanics. Phys Rev D 62:085019
Johri VB, Sudarshan R (1988) Friedmann universes with bulk viscosity. Phys Lett A 132:316
Kaluza T (1921) Zum unitätsproblem der physik. Zum Unitatsproblem der Physik Sitz Press Akad Wiss Phys Math K 1:966
Kamenshchik A, Moschella U, Pasquier V (2001) An alternative to quintessence. Phys Lett B 511:265
Klein O (1926) Quantum theory and five dimensional theory of relativity (In German and English). Zeits Phys 37:895
Lee HC (1984) An introduction to Kaluza–Klein theories. World Scientific, Singapore
Lu J, Xu L, Li J, Chang B, Gui Y, Liu H (2008) Constraints on modified Chaplygin gas from recent observations and a comparison of its status with other models. Phys Lett B 662:87
Lu J, Xu L, Liu M (2011) Constraints on kinematic models from the latest observational data. Phys Lett B 699:246
Mahanta KL (2014) Bulk viscous cosmological models in f (R,T) theory of gravity. Astrophys Space Sci 353:683
Makler M, de Oliveira SQ, Waga I (2003) Constraints on the generalized Chaplygin gas from supernovae observations. Phys Lett B 555:1
Mazumdar N, Biswas R, Chakraborty S (2012) FRW cosmological model with modified Chaplygin gas and dynamical system. Int J Theor Phys 51:2754
Misner CW (1967) Transport processes in the primordial fireball. Nature 214:40
Misner CW (1968) The isotropy of the universe. Astrophys J 151:431
Mohanty G, Pattanaik RR (1991) Anisotropic, spatially homogeneous, bulk viscous cosmological model. Int J Theor Phys 30:239
Mohanty G, Samanta GC (2009) Five dimensional axially symmetric string cosmological models with bulk viscous fluid. Int J Theor Phys 48:2311
Overduin JM, Wesson PS (1997) Kaluza–klein gravity. Phys Rep 283:303
Padmanabhan T (2003) Cosmological constant—the weight of the vacuum. Phys Rep 380:235
Padmanabhan T, Chitre SM (1987) Viscous universes. Phys Lett A 120:433
Perlmutter S et al (1999) Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys J 517:565
Pradhan A, Pandey P (2004) Some Bianchi type-I viscous fluid cosmological models with a variable cosmological constant. Astrophys Space Sci 30:127
Riess AG, Filippenko AV, Challis P, Clocchiatti A, Diercks A, Garnavich PM, Gilliland Ron L et al (1998) Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 116:1009
Ross GG (1984) Grand unified theories. Benjamin-Cummings, Massachusetts
Roy SR, Prakash S (1976) Some viscous fluid cosmological models of plane symmetry. J Phys A Math Gen 9:261
Roy SR, Prakash S (1977) A gravitationally non-degenerate viscous fluid cosmological model in general relativity. Indian J Pure Appl Math 8:723
Saadat H, Farahani H (2013) Viscous Chaplygin gas in non-flat universe. Int J Theor Phys 52:1160
Saadat H, Pourhassan B (2013) FRW bulk viscous cosmology with modified Chaplygin gas in flat space. Astrophys Space Sci 343:783
Sadeghi J, Setare MR, Amani AR, Noorbakhsh SM (2010) Bouncing universe and reconstructing vector field. Phys Lett B 685:229
Saha B (2005) Bianchi type I universe with viscous fluid. Mod Phys Lett A 20:2127
Sahni V, Starobinsky AA (2000) The case for a positive cosmological Λ-term. Int J Mod Phys D 9:373
Samanta GC, Biswal SK, Sahoo PK (2013a) Five dimensional bulk viscous String cosmological models in Saez and Ballester theory of gravitation. Int J Theor Phys 52:1504
Samanta GC, Dhal S, Mishra B (2013b) Five dimensional bulk viscous cosmological model with wet dark fluid in general relativity. Astrophys Space Sci 346:233
Sandvik HB, Tegmark M, Zaldarriage M, Waga L (2004) The end of unified dark matter? Phys Rev D 69:123524
Setare MR (2007) Interacting holographic generalized Chaplygin gas model. Phys Lett B 654:1
Setare MR (2009) Holographic Chaplygin DGP cosmologies. Int J Modif Phys D 18:419
Setrae MR (2007) Holographic Chaplygin gas model. Phys Lett B 648:329
Spergel DN et al (2003) First year Wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP) observations: determination of cosmological parameters. Astrophys J Supp 148:175
Tsien HS (1939) Two-dimensional subsonic flow of compressible fluids. J Aeronaut Sci 6:399
Visser M (2004) Jerk, snap and the cosmological equation of state. Class Quantum Gravity 21:113
Wetterich C (1988) Cosmology and the fate of dilatation symmetry. Nucl Phys B 302:668
Xu YD, Huang ZG, Zhai XH (2012) Generalized Chaplygin gas model with or without viscosity in the w–w′ plane. Astrophys Space Sci 337:493
Zhai XH, Xu YD, Li XZ (2006) Viscous generalized Chaplygin gas. Int J Mod Phys D 15:1115
Zhu ZH (2004) Generalized Chaplygin gas as a unified scenario of dark matter/energy: observational constraints. Astron Astrophys 423:421
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous referee for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samanta, G.C., Bishi, B.K. Universe Described by Kaluza–Klein Space Time with Viscous Modified Cosmic Chaplygin Gas in General Relativity. Iran J Sci Technol Trans Sci 40, 245–254 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0089-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-016-0089-5