Abstract
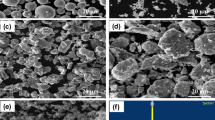
Additively manufactured titanium metal matrix composites (TMCs) reinforced with TiB2 ceramic particles and prepared using selective laser melting (SLM) were subjected to annealing at 850 °C for 2 h. The effect of annealing on the microstructures was characterized through a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD). The martensitic structure of plain Ti–6Al–4 V changed to a lamellar structure after annealing. An increase in the weight percentage of a TiB2 powder induced a drastic change in the overall morphology. A considerable refinement of both α and β grains enabled β grains to obtain a globular shape. The change in the microstructure can be attributed to the pinning effect caused by the formation of TiB precipitates and the β phase. Wear performance is enhanced with an increase in the weight percentage of TiB. The tribological performance confirmed that the growth of β grains acts as an obstacle to plastic deformations, and delamination improved with the help of TiB in the matrix.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
Medvedev AE, Lui EW, Edwards D, Leary M, Qian M, Brandt M (2021) Improved ballistic performance of additively manufactured Ti6Al4V with α-β lamellar microstructures. Mater Sci Eng A 825:141888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141888
Oyesola M, Mathe N, Mpofu K, Fatoba S (2018) Sustainability of Additive Manufacturing for the South African aerospace industry: a business model for laser technology production, commercialization and market prospects. Procedia CIRP. Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam, pp 1530–1535
Dutta B, Froes FHS (2017) The additive manufacturing (AM) of titanium alloys. Met Powder Rep 00:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mprp.2016.12.062
Murr LE, Quinones SA, Gaytan SM, Lopez MI, Rodela A, Martinez EY, Hernandez DH, Martinez E, Medina F, Wicker RB (2009) Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti–6Al–4V produced by rapid-layer manufacturing, for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2:20–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmbbm.2008.05.004
Zhang L-C, Attar H (2016) Selective laser melting of titanium alloys and titanium matrix composites for biomedical applications: a review. Adv Eng Mater 18:463–475. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201500419
Kruth JP, Leu MC, Nakagawa T (1998) Progress in additive manufacturing and rapid prototyping. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63240-5
Yap CY, Chua CK, Dong ZL, Liu ZH, Zhang DQ, Loh LE, Sing SL (2015) Review of selective laser melting: materials and applications. Appl Phys Rev 2:041101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4935926
Liu S, Shin YC (2019) Additive manufacturing of Ti6Al4V alloy: a review. Mater Des 164:107552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2018.107552
Molinari A, Straffelini G, Tesi B, Bacci T (1997) Dry sliding wear mechanisms of the Ti6Al4V alloy. Wear 208:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(96)07454-6
Kermanpur A, Sepehri Amin H, Ziaei-Rad S, Nourbakhshnia N, Mosaddeghfar M (2008) Failure analysis of Ti6Al4V gas turbine compressor blades. Eng Fail Anal 15:1052–1064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2007.11.018
Kumar S, Kruth J-P (2008) Wear performance of SLS/SLM materials. Adv Eng Mater 10:750–753. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.200800075
Javaid M, Haleem A (2017) Additive manufacturing applications in medical cases: a literature based review. Alexandria J Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2017.09.003
Hussein MA, Mohammed AS, Al-aqeeli N, Arabia S (2015) Wear characteristics of metallic biomaterials: a review. Materials 8:2749–2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8052749
Bell T, Morton PH, Bloyce A (1994) Towards the design of dynamically loaded titanium engineering components. Mater Sci Eng A 184:73–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-5093(94)91022-7
Dong H, Bell T (2000) Enhanced wear resistance of titanium surfaces by a new thermal oxidation treatment. Wear 238:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00359-2
Buchanan RA, Rigney ED, Williams JM (1987) Ion implantation of surgical Ti-6Al-4V for improved resistance to wear-accelerated corrosion. J Biomed Mater Res 21:355–366. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.820210308
Yetim AF, Celik A, Alsaran A (2010) Surface & coatings technology improving tribological properties of Ti6Al4V alloy with duplex surface treatment. Surf Coat Technol 205:320–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2010.06.048
Fu Y, Loh NL, Batchelor AW, Liu D, Xiaodong Zhu J, He KXu (1998) Improvement in fretting wear and fatigue resistance of Ti–6Al–4V by application of several surface treatments and coatings. Surf Coat Technol 106:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0257-8972(98)00528-3
Heer B, Bandyopadhyay A (2018) Silica coated titanium using laser engineered net shaping for enhanced wear resistance. Addit Manuf 23:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2018.08.022
Attar H, Bönisch M, Calin M, Zhang L-C, Scudino S, Eckert J (2014) Selective laser melting of in situ titanium–titanium boride composites: processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. Acta Mater 76:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2014.05.022
Kühnle T, Partes K (2012) In-situ formation of titanium boride and titanium carbide by selective laser melting. Phys Proc 39:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.10.058
Koo MY, Park JS, Park MK, Kim KT, Hong SH (2012) Effect of aspect ratios of in situ formed TiB whiskers on the mechanical properties of TiBw/Ti–6Al–4V composites. Scr Mater 66:487–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.12.024
An Q, Huang LJ, Bao Y, Zhang R, Jiang S, Geng L, Xiao M (2018) Dry sliding wear characteristics of in-situ TiBw/Ti6Al4V composites with different network parameters. Tribol Int 121:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.01.053
Patil AS, Hiwarkar VD, Verma PK, Khatirkar RK (2019) Effect of TiB2 addition on the microstructure and wear resistance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy fabricated through direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). J Alloys Compd 777:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.10.308
Galarraga H, Warren RJ, Lados DA, Dehoff RR, Kirka MM, Nandwana P (2017) Effects of heat treatments on microstructure and properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy fabricated by electron beam melting (EBM). Mater Sci Eng A 685:417–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.01.019
Wauthle R, Vrancken B, Beynaerts B, Jorissen K, Schrooten J, Kruth J-P, Van Humbeeck J (2015) Effects of build orientation and heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V lattice structures. Addit Manuf 5:77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2014.12.008
Welsch G, Boyer R, Collings EW (1998) Materials properties handbook: titanium alloys, 2nd edn. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0045782504000313
Semiatin SL, Fagin PN, Glavicic MG, Sukonnik IM, Ivasishin OM (2001) Influence on texture on beta grain growth during continuous annealing of Ti-6Al-4V. Mater Sci Eng A 299:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(00)01371-X
Zhu Y, Chen X, Zou J, Yang H (2016) Sliding wear of selective laser melting processed Ti6Al4V under boundary lubrication conditions. Wear 368–369:485–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2016.09.020
Azarniya A, Colera XG, Mirzaali MJ, Sovizi S, Bartolomeu F, St Weglowski Mare K, Wits WW, Yap CY, Ahn J, Miranda G, Silva FS, Madaah Hosseini HR, Ramakrishna S, Zadpoor AA (2019) Additive manufacturing of Ti–6Al–4V parts through laser metal deposition (LMD): process, microstructure, and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd 804:163–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.255
McEldowney DJ, Tamirisakandala S, Miracle DB (2010) Heat-treatment effects on the microstructure and tensile properties of powder metallurgy Ti-6Al-4V alloys modified with boron. Metall Mater Trans A 41:1003–1015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0157-y
Vrancken B, Thijs L, Kruth J-P, Van Humbeeck J (2012) Heat treatment of Ti6Al4V produced by selective laser melting: microstructure and mechanical properties. J Alloys Compd 541:177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.07.022
Yan X, Yin S, Chen C, Huang C, Bolot R, Lupoi R, Kuang M, Ma W, Coddet C, Liao H, Liu M (2018) Effect of heat treatment on the phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V fabricated by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd 764:1056–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.06.076
Brandl E, Schoberth A, Leyens C (2012) Morphology, microstructure, and hardness of titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) blocks deposited by wire-feed additive layer manufacturing (ALM). Mater Sci Eng A 532:295–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2011.10.095
Huang LJ, Xu HY, Wang B, Zhang YZ, Geng L (2012) Effects of heat treatment parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ TiBw/Ti6Al4V composite with a network architecture. Mater Des 36:694–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.12.021
Gil Mur FX, Rodríguez D, Planell JA (1996) Influence of tempering temperature and time on the α′-Ti-6Al-4V martensite. J Alloys Compd 234:287–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-8388(95)02057-8
Zhang X, Lü W, Zhang D, Wu R, Bian Y, Fang P (1999) In situ technique for synthesizing (TiB+TiC)/Ti composites. Scr Mater 41:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(99)00087-1
Yang YF, Yan M, Luo SD, Schaffer GB, Qian M (2013) Modification of the α-Ti laths to near equiaxed α-Ti grains in as-sintered titanium and titanium alloys by a small addition of boron. J Alloys Compd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.097
Li J, Wang L, Qin J, Chen Y, Lu W, Zhang D (2011) The effect of heat treatment on thermal stability of Ti matrix composite. J Alloys Compd 509:52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.09.005
Hill D, Banerjee R, Huber D, Tiley J, Fraser HL (2005) Formation of equiaxed alpha in TiB reinforced Ti alloy composites. Scr Mater 52:387–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2004.10.019
Tamirisakandala S, Bhat RB, Miracle DB, Boddapati S, Bordia R, Vanover R, Vasudevan VK (2005) Effect of boron on the beta transus of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Scr Mater 53:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.03.038
Murray JL (1987) Phase diagrams of binary titanium alloys. ASM Int., Metals Park, p 354
Fujii H, Takahashi K, Yamashita Y (2003) Application of titanium and its alloys for automobile parts. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep
Zhu J, Kamiya A, Yamada T, Shi W, Naganuma K (2003) Influence of boron addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of dental cast titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng A 339:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(02)00102-8
Wang F, Mei J, Wu X (2008) Direct laser fabrication of Ti6Al4V/TiB. J Mater Process Technol 195:321–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.05.024
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Facility of Texture and OIM (A DST-IRPHA), IIT Bombay, for their assistance in performing the EBSD and XRD measurements. The corresponding author acknowledges the SERB-DST, India for providing the required equipment and testing support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nichul, U., Warghane, S., Kumar, P. et al. Evolution of equiaxed α/β microstructure of annealed SLM-built Ti64: role of TiB2. Prog Addit Manuf 8, 907–918 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-022-00364-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40964-022-00364-w