Abstract
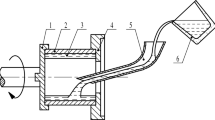
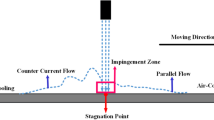
This paper investigates the performance of a water sprinkler cooling system for a centrifugal Babbitt lining machine, used to renovate industrial bearings. A three-dimensional and transient numerical simulation was conducted to study the effects of various parameters on the solidification rate, including mold rotational speed, sprinkler flow rate and angle, and initial temperatures of the mold and Babbitt alloy. Results demonstrate that the temperature drop in the Babbitt layer and mold is directly proportional to the rotational speed, with a 15% change in rotational speed from the reference case resulting in a 5 °C change in the average temperature of the Babbitt alloy, while clockwise (CW) rotation of the mold leads to greater temperature reduction. An optimal rotational speed of 550 rpm CW was determined. The study also identified an optimal total water flow rate of 8.7e−5 m3/s, with minimal additional cooling benefits beyond that point. Furthermore, vertical water sprinkler angles were found to provide superior cooling performance. The initial mold temperature was found to have a more significant influence on the final average Babbitt temperature than the initial Babbitt temperature, due to the mold’s larger mass and thermal inertia. The qualitative and quantitative results of this research offer valuable insights for enhancing the design of water sprinkler cooling systems in centrifugal Babbitt lining machines, providing a pathway for transitioning from manual to automated cooling processes. This innovative approach has the potential to transform industries in underdeveloped countries, improving their efficiency, quality, and safety.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, I. Tudela, M. Pal, I. Kerr, High strength tin-based overlay for medium and high speed diesel engine bearing tribological applications. Tribol. Int. 93, 687–695 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2015.03.010
H. Wu, Q. Bi, S. Zhu, J. Yang, W. Liu, Friction and wear properties of Babbitt alloy 16-16-2 under sea water environment. Tribol. Int. 44(10), 1161–1167 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.05.007
M. Moazami Goudarzi, S.A. Jenabali Jahromi, A. Nazarboland, Investigation of characteristics of tin-based white metals as a bearing material. Mater. Des. 30(6), 2283–2288 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2008.07.056
H. Wu, S. Zhu, J. Cheng, Z. Qiao, J. Yang, Tribological behavior of tin-based babbitt alloy lubricated by seawater. Tribol. Trans. 59(5), 838–844 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10402004.2015.1110863
S. Ishihara, K. Tamura, T. Goshima, Effect of amount of antimony on sliding wear resistance of white metal. Tribol. Int. 43(5), 935–938 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.12.047
Y.S. Korobov, S.V. Nevezhin, M.A. Filippov, V.V. Ilyushin, B.A. Potekhin, L.V. Gogolev, Effect of production methods on tribological characteristics of Babbitt coatings. J. Frict. Wear 33(3), 190–194 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1068366612030063
P. Diouf, A. Jones, Investigation of bond strength in centrifugal lining of Babbitt on cast iron. Met. Mater. Trans. A. 41, 603–609 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0112-y
M. Wei et al., Microstructure and bonding strength of tin-based Babbitt alloy on ASTM 1045 steel by MIG arc brazing. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 32(19), 2150–2161 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2018.1464239
T.P.D. Rajan, B.C. Pai, Formation of solidification microstructures in centrifugal cast functionally graded aluminium composites. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 62(4), 383–389 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-009-0067-0
V. Malhotra, Y. Kumar, Casting defects: an literature review. Int. J. Des.Manuf. Technol. 7(1), 60–62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.34218/IJDMT.7.1.2016.006
S. Pandey, S. K. Jha, Casting defects and its optimization method in centrifugal casting process: a review. in International Conference on Advances in Materials and Manufacturing (2017)
C.G. Kang, P.K. Rohatgi, C.S. Narendranath, G.S. Cole, A solidification analysis on centrifugal casting of metal matrix composites containing graphite particles. ISIJ Int. 34(3), 247–254 (1994). https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.34.247
R. Zagorski, J. Sleziona, Pouring mould during centrifugal casting process. Arch. Mater. Sci. Eng. 28(7), 441–444 (2007)
M. Raudenský, A.A. Tseng, J. Horský, J. Komínek, Recent developments of water and mist spray cooling in continuous casting of steels. Met. Res. Technol. 113(5), 509 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/metal/2016029
N.S. Madhusudhan, G.M. Kumar, Experimental study on cooling rate of centrifugal casting based on grain size. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 3(1), 1–3 (2012)
M. Yousefi, H. Doostmohammadi, Microstructural evolution and solidification behavior of functionally graded in situ Al–Cr composites during centrifugal casting. Int. J. Met. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00499-y
Z. Xu, N. Song, R.V. Tol, Y. Luan, D. Li, Modelling of horizontal centrifugal casting of work roll. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 33(1), 012030 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/33/1/012030
J. Bohacek, A. Kharicha, A. Ludwig, M. Wu, Simulation of horizontal centrifugal casting: mold filling and solidification. ISIJ Int. 54(2), 266–274 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.54.266
J.-W. Park, H.-J. Kim, Melt filling behaviors and primary si particle distribution on horizontal centrifugal casting in B390 aluminum alloy. Int. J. Met. 11, 802–811 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0127-2
S.-L. Lu, F.-R. Xiao, S.-J. Zhang, Y.-W. Mao, B. Liao, Simulation study on the centrifugal casting wet-type cylinder liner based on ProCAST. Appl. Therm. Eng. 73(1), 512–521 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.07.073
Q. Dong, Z. Yin, H. Li, G. Gao, Y. Mao, Simulation study on filling and solidification of horizontal centrifugal casting babbitt lining of bimetallic bearing. Int. J. Met. 15(1), 119–129 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00429-y
P. Shailesh, S. Sundarrajan, M. Komaraiah, Optimization of process parameters of Al–Si alloy by centrifugal casting technique using taguchi design of experiments. Procedia Mater. Sci. 6, 812–820 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.098
P.G. Mukunda, R.A. Shailesh, S.S. Rao, Influence of rotational speed of centrifugal casting process on appearance, microstructure, and sliding wear behaviour of Al–2Si cast alloy. Met. Mater. Int. 16(1), 137–143 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-010-0137-1
M. El-Sayed, Effect of the mould rotational speed on the quality of centrifugal castings. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 9(21), 11575–11582 (2014)
M. Arabi-Nour, F. Fereshteh-Saniee, Effects of mold rotation speed and cast thickness on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ80 prepared by centrifugal casting. Int. J. Met. 16, 894–908 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00651-2
A. Vajd, A. Samadi, Optimization of centrifugal casting parameters to produce the functionally graded Al–15wt%Mg2Si composites with higher tensile properties. Int. J. Met. 14, 937–948 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00394-1
A. Kheirabi, M. Pourgharibshahi, S.M.A. Boutorabi et al., tensile properties enhancement response of A413 and A356 aluminum casting alloys to direct water spray processing. Int. J. Met. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01045-2
N. Zhang, C. Lei, T. Liu et al., Parameter optimization of Al-5Mg-3Zn-1Cu basin-shaped centrifugal casting: simulation and experimental verification. Int. J. Met. 17, 900–909 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00822-9
X. Wang, R. Chen, Q. Wang et al., Influence of rotation speed and filling time on centrifugal casting through numerical simulation. Int. J. Met. 17, 1326–1339 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-022-00841-6
P. Lan, J. Zhang, Study on the mechanical behaviors of grey iron mould by simulation and experiment. Mater. Des. 53, 822–829 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.077
M. Alizadeh, H. Edris, A. Shafyei, Mathematical modeling of heat transfer for steel continuous casting process. Int. J. Iron Steel Soc. Iran 3(2), 7–16 (2006)
SolidWorks, Flow simulation technical reference (2023). https://files.solidworks.com/Supportfiles/Flow_Simulation_2023/English/Techref/index.html. Accessed June 14 (2023)
R. Lopez-Ruiz (ed.), Numerical Simulation: From Brain Imaging to Turbulent Flows (BoD-Books on Demand, 2016)
A.A. Zainulabdeen, F.A. Hashim, S.H. Assi, Mechanical properties of tin-based babbitt alloy using the direct extrusion technique. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 518(3), 032031 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/518/3/032031
N. Habibi et al., The effect of shot peening on fatigue life of welded tubular joint in offshore structure. Mater. Des. 1980–2015 36, 250–257 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.11.024
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions. The authors would like to thank TABA Engineering and Services Company for providing the necessary equipment to perform the research and Safat Energy Yazd Company for providing experimental data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasanpour, E., Fesharakifard, R. Numerical Analysis of Water Sprinkler Cooling System for a Centrifugal Babbitt Lining Machine. Inter Metalcast (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01172-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01172-w