Abstract
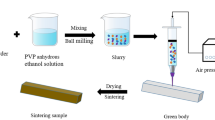
In this study, the effects of different ZnO, SiO2, and MgO ceramic powder addition on the mechanical properties of NaCl–Na2SO4 water-soluble salt core (WSSC) were compared, and the comparison results were analyzed. First, the results of molecular dynamics simulations indicated that the interface structure of ZnO–NaCl–Na2SO4 was more stable than SiO2–NaCl–Na2SO4 and MgO–NaCl–Na2SO4. Subsequently, the experimental comparison suggested that the strength of WSSC first increased and then decreased with the addition of ZnO ceramic powder. The bending strength of the WSSC reached 27.4 MPa with the addition of 15 wt% ZnO. At the water temperature of 85 °C, the water solubility rate was 142.22 kg/min m2. Lastly, the microscopic morphology and phase composition of the WSSC were characterized through SEM and X-ray diffraction. The results of this study revealed that the mechanical properties of WSSC can be enhanced by refining WSSC particles and ZnO dispersion strengthening.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Gong, W. Jiang, F. Liu, et al., Effects of glass fiber size and content on microstructures and properties of KNO3-based water-soluble salt core for high pressure die casting. Int. J. Metalcast. 15, 520–529 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00480-9
X.Y. Liu, W.H. Liu, X.T. Wang, et al., Composition optimization and strengthening mechanism of high-strength composite water-soluble salt core for foundry. Int. J. Metalcast. 16, 1809–1816 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00725-1
R. Huang, B. Zhang, Study on the composition and properties of salt cores for zinc alloy die casting. Int. J. Metalcast. 11(3), 440–447 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-016-0086-7
F.C. Liu, S. Tu, X.L. Gong et al., Comparative study on performance and microstructure of composite water-soluble salt core material for manufacturing hollow zinc alloy castings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 252, 123257 (2020)
H. Sun, COMPASS: an ab Initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 102(38), 7338–7364 (1998)
Y. Lan, D. Li, R. Yang et al., Computer simulation study on the compatibility of cyclotriphosphazene containing aminopropylsilicone functional group in flame retarded polypropylene/a mmonium polyphosphate composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 88(1), 9–15 (2013)
L.I. Shuo, Formation of in-situ dispersion strengthening particles in cast FeCrAl alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17, 74–78 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Xt., Song, L., Liu, Wh. et al. Effect of Ceramic Powder on the Performance of Composite Water-Soluble Salt Cores: Comparison of Experimental Data and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Inter Metalcast 18, 494–504 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01039-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-023-01039-0