Abstract
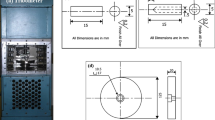
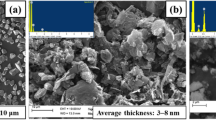
The paper reports wear and friction performance of Al-12Si aluminum alloy reinforced with 1.5 wt% submicron boron carbide (B4C) particles. Composite material is fabricated by ultrasonic stir casting process. Microstructural examination is carried out using optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). Incorporation and agglomeration-free dispersion of B4C particles is detected in the aluminum matrix. Pin-on-disc tribotester is used to evaluate tribological performance of fabricated composite and base alloy under room temperature dry conditions. Nominal contact pressure of 0.707 MPa is applied against EN31 steel counterface, and sliding speeds are varied between 0.25 and 1.25 m/s. Influence of sliding distance is investigated by varying sliding durations from 10 to 40 min at two fixed load-speed (PV) factors of 10 and 25 Nm/s. Worn pin surfaces and collected wear debris are analyzed using FESEM and energy-dispersive spectroscopy to reveal undergoing wear mechanisms. After initial decrease, wear rate increased almost linearly with speed and became twofold at the top speed. Wear rate transition is seen at 0.5 m/s with sliding distance for the applied pressure. Friction coefficient is not influenced significantly with sliding distance for the fixed PV condition. Adhesion and delamination governed the wear mechanism of base alloy while mechanically mixed layer played key role in the wear performance of composite matrix. Improved wear resistance of aluminum matrix is observed due to incorporation of small amount of B4C particulates making the composite better suited for wear-resistant applications than base alloy.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Rambabu, N.P. Eswara, V.V. Kutumbarao, R.J.H. Wanhill, Aluminum alloys for aerospace applications, in Aerospace materials and material technologies, Indian institute of metals series. ed. by N.P. Eswara, R.J.H. Wanhill (Springer, India, 2017), pp. 29–52
S.V. Prasada, R. Asthana, Aluminum metal-matrix composites for automotive applications: tribological considerations. Tribol. Lett. 17(3), 445–453 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TRIL.0000044492.91991.f3
P.A. Kumar, P. Rohatgi, D. Weiss, 50 years of foundry-produced metal matrix composites and future opportunities. Int J Metalcast. 14, 291–317 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-019-00375-4
X. Zhang, Y. Chen, J. Hu, Recent advances in the development of aerospace materials. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 97, 22–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paerosci.2018.01.001
D.M. Shinde, P. Sahoo, Fabrication of aluminium metal matrix nanocomposites: an overview, in Recent advances in layered materials and structures, material horizons: from nature to nanomaterials. ed. by S. Sahoo (Springer, Singapore, 2021), pp. 107–132
X. Li, Y. Yang, X. Cheng, Ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of metal matrix nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 3211–3212 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000025862.23609.6f
L. Poovazhagan, K. Kalaichelvan, A. Rajadurai, Preparation of SiC nano-particulates reinforced aluminum matrix nanocomposites by high intensity ultrasonic cavitation process. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 67(2), 229–237 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-013-0340-0
H.M. Vishwanathaa, J. Eravellya, C.S. Kumarb, S. Ghosha, Dispersion of ceramic nano- particles in the Al-Cu alloy matrix using two step ultrasonic casting and resultant strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 708, 222–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.09.117
X. Liu, S. Jia, L. Nastac, Ultrasonic cavitation-assisted molten metal processing of cast A356-nanocomposites. Int J Metalcast. 8, 51–58 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355591
U. Aybarc, O. Ertugrul, M.O. Seydibeyoglu, Effect of Al2O3 particle size on mechanical properties of ultrasonic-assisted stir-casted Al A356 matrix composites. Int. J. Metalcast. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00490-7
F. He, E. Forthofer, Microstructure of high-performance pure Al/Nano-Si3N4 composites. Int. J. Metalcast. 5, 71–72 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03355512
G.P. Chaudhari, N. Srivastava, Microstructural evolution and mechanical behavior of ultrasonically synthesized Al6061-nano alumina composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 724, 199–207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.06.023
H. Demirtaş, R. Yildiz, E. Çevik, Mechanical and wear properties of high rate NiAl particle-reinforced Al composites produced by pressure infiltration method. Int. J. Metalcast. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-020-00564-6
M. Moazami-Goudarzi, F. Akhlaghi, Wear behavior of Al 5252 alloy reinforced with micrometric and nanometric SiC particles. Tribol. Int. 102, 28–37 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.05.013
A. Nieto, H. Yang, L. Jiang, J.M. Schoenung, Reinforcement size effects on the abrasive wear of boron carbide reinforced aluminum composites. Wear 390–391, 228–235 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2017.08.002
A.P. Reddy, P.V. Krishna, R.N. Rao, Dry sliding wear behaviour of ultrasonically-processed AA6061/SiCp nanocomposites. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 14, 4747–4568 (2017). https://doi.org/10.15282/ijame.14.4.2017.12.0373
D.M. Shinde, P. Sahoo, J.P. Davim, Tribological characterization of particulate-reinforced aluminum metal matrix nanocomposites: a review. Adv. Compos. Lett. 29, 1–28 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1177/2633366X20921403
R. Ambigai, S. Prabhu, Optimization of friction and wear behaviour of Al-Si3N4 nano composite and Al-Gr-Si3N4 hybrid composite under dry sliding conditions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 27, 986–997 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60116-X
Y. Liu, Z. Han, H. Cong, Effects of sliding velocity and normal load on the tribological behavior of a nanocrystalline Al based composite. Wear 268, 976–983 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2009.12.027
N.G.S. Kumar, T.R. Prabhu, G.S.S. Shankar, S. Basavarajappa, Dry sliding wear properties of unhybrid and hybrid Al alloy based nanocomposites. Tribol. Mater. Surf. Interface 10, 138–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/17515831.2016.1247132
A. Baradeswaran, A.E. Perumal, Influence of B4C on the tribological and mechanical properties of Al 7075- B4C composites. Comp. Part B 54, 146–152 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.05.012
I. Baker, Y. Sun, F.E. Kennedy, P.R. Munroe, Dry sliding wear of eutectic Al-Si. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 969–978 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-4027-1
M.J.N. Isfahani, F. Payami, M.A. Asadabad, A.A. Shokri, Investigation of the effect of boron carbide nanoparticles on the structural, electrical and mechanical properties of Al-B4C nanocomposites. J. Alloy. Comp. 797, 1348–1358 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.188
F. Ubaid, P.R. Matli, R.A. Shakoor, G. Parande, V. Manakari, A.M.A. Mohamed, M. Gupta, Using B4C nanoparticles to enhance thermal and mechanical response of aluminum. Materials 10, 621 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma10060621
F. Thevenot, Boron carbide- a comprehensive review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 6, 205–225 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0955-2219(90)90048-K
A.J. Fyzik, D.R. Beaman, Al-B-C phase development and effects on mechanical properties of B4C/Al-derived composites. J Am. Cerum. Soc. 78(2), 305–312 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1995.tb08801.x
J.C. Viala, J. Bouix, G. Gonzalez, C. Esnouf, Chemical reactivity of aluminium with boron carbide. J. Mater. Res. 32, 4559–4573 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018625402103
S. Poria, G. Sutradhar, P. Sahoo, Corrosion and lubricated sliding tribological behavior of Al-TiB2-nano Gr hybrid composites. Mater. Res. Express. 5, 076519 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aad07b
A. Pal, S. Poria, G. Sutradhar, P. Sahoo, Tribological behavior of Al-WC nano-composites fabricated by ultrasonic cavitation assisted stir-cast method. Mater. Res. Express 5, 036521 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/aab577
J. Li, S. Lü, S. Wu, Q. Gao, Effects of ultrasonic vibration on microstructure and mechanical properties of nano-sized SiC particles reinforced Al-5Cu composites. Ultrason. Sonochem. 42, 814–822 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.12.038
N. Srivastava, G.P. Choudhari, Strengthening in Al alloy nano composites fabricated by ultrasound assisted solidification technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 651, 241–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2015.10.118
R. Raj, D.G. Thakur, Qualitative and quantitative assessment of microstructure in Al-B4C metal matrix composite processed by modified stir casting technique. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 16, 949–960 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acme.2016.07.004
F. Toptan, A. Kilicarslan, I. Kerti, The effect of Ti addition on the properties of Al-B4C interface: a microstructural study. Mater. Sci. Forum 637, 192–197 (2010). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.636-637.192
W.H. Tarn, P. Walker, Handbook of Metal Etchants (CRC Press LLC, New York, 1991)
J. Hemanth, Tribological behavior of cryogenically treated B4C/Al-12%Si composites. Wear 258, 1732–1744 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2004.12.009
J. Zhang, A.T. Alpas, Transition between mild and severe wear in aluminium alloys. Acta. Mater. 45(2), 513–528 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6454(96)00191-7
S. Wilson, A.T. Alpas, Wear mechanism maps for metal matrix composites. Wear 212, 41–49 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(97)00142-7
M.R. Dehnavi, B. Niroumand, F. Ashrafizadeh, P.K. Rohatgi, Effects of continuous and discontinuous ultrasonic treatments on mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics of cast A413-SiCnp nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 617, 73–83 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.08.042
S. Kandemir, H.V. Atkinson, D.P. Weston, S.V. Hainsworth, Thixoforming of A356/SiC and A356/TiB2 nanocomposites fabricated by a combination of green compact nanoparticle iincorporation and ultrasonic treatment of the melted compact. Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 45A, 5785–5798 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2501-0
S. Jia, D. Zhang, Y. Xuan, L. Nastac, An experimental and modeling investigation of aluminum-based alloys and nanocomposites processed by ultrasonic cavitation processing. Appl. Acoust. 103, 226–231 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2015.07.016
M.K. Akbari, H.R. Baharvandi, K. Shirvanimoghaddam, Tensile and fracture behavior of nano/micro TiB2 particle reinforced casting A356 aluminum alloy composites. Mater. Des. 66, 150–161 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.048
D.M. Shinde, S. Poria, P. Sahoo, Synthesis and characterization of Al-B4C nano composites. Mater Today-Proc. 19, 170–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.641
Y. Xuan, L. Nastac, The role of ultrasonic cavitation in refining the microstructure of aluminum based nanocomposites during the solidification process. Ultrasonics 83, 94–102 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultras.2017.06.023
H.M. Vishwanatha, J. Eravelly, C.S. Kumar, S. Ghosh, Dispersion of ceramic nano-particles in the Al-Cu alloy matrix using two-step ultrasonic casting and resultant strengthening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 708, 222–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2017.09.117
C. Subramanian, Effects of sliding speed on the unlubricated wear behaviour of Al-12.3wt.% Si alloy. Wear 151, 97–110 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1648(91)90349-Y
A. Daouda, M.T. Abou-Elkhair, P. Rohatgi, Wear and friction behavior of near eutectic Al–Si+ZrO2 or WC particle composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64, 1029–1040 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2003.09.020
H.R. Lashgari, A.R. Sufizadeh, M. Emamy, The effect of strontium on the microstructure and wear properties of A356–10%B4C cast composites. Mater. Des. 31, 2187–2195 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.10.049
V.V. Monikandan, M.A. Joseph, P.K. Rajendrakumar, M. Sreejith, Tribological behavior of liquid metallurgy-processed AA6061-B4C composites. Mater. Res. Express 2, 016507 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/2/1/016507
A. Ravikiran, M.K. Surappa, Oscillations in coefficient of friction during dry sliding of A356-30% wt SiCp MMC against steel. Scripta Mataialia 36(1), 95–98 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-6462(96)00337-5
S.A. Alidokht, A. Abdollah, H. Assadi, Effect of applied load on the dry sliding wear behavior and the subsurface deformation on hybrid metal matrix composite. Wear 305, 291–298 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2012.11.043
A. Abdollahi, A. Alizadeh, H.R. Baharvandi, Dry sliding tribological behavior and mechanical properties of Al2024–5 wt.%B4C nanocomposite produced by mechanical milling and hot extrusion. Mater. Des. 55, 471–481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.09.024
M.R. Rosenberger, C.E. Schvezov, E. Forlerer, Wear of different aluminum matrix composites under conditions that generate a mechanically mixed layer. Wear 259, 590–601 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2005.02.003
X.Y. Li, K.N. Tandon, Mechanical mixing induced by sliding wear of an Al-Si alloy against M2 steel. Wear 225–229, 640–648 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(99)00021-6
D. Lu, M. Gu, Z. Shi, Material transfer and formation of mechanically mixed layer in dry sliding wear of metal matrix composites against steel. Tribol. Lett. 6, 57–61 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1019182817316
L. Poovazhagan, K. Kalaichelvan, T. Sornakumar, Processing and performance characteristics of aluminum-nano boron carbide metal matrix nanocomposites. Mater. Manuf. Process 31, 1275–1285 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2015.1026354
D.K. Dwivedi, A. Sharma, T.V. Rajan, Interface temperature under dry sliding conditions. Mater. Trans. 43(9), 2256–2261 (2002). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.43.2256
S.T. Kumaran, M. Uthayakumar, Investigation on the dry sliding friction and wear behavior of AA6361-SiC-B4C hybrid metal matrix composites. Proc. IMechE Part J: J. Eng. Tribol. 228(3), 332–338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/1350650113508103
N. Yuvaraj, S. Aravindan, Vipin, Fabrication of Al5083/B4C surface composite by friction stir processing and its tribological characterization. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 4(4), 398–410 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2015.02.006
Acknowledgment
We gratefully acknowledge material characterization (FESEM-EDS) facilities provided at Mechanical engineering department, Indian Institute of Technology, Mumbai.
Funding
This research study has not received financial support from any organization in public or private sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shinde, D.M., Sahoo, P. Influence of Speed and Sliding Distance on the Tribological Performance of Submicron Particulate Reinforced Al-12Si /1.5 Wt% B4C Composite. Inter Metalcast 16, 739–758 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00636-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40962-021-00636-1