Abstract
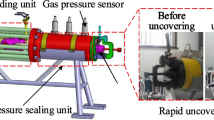
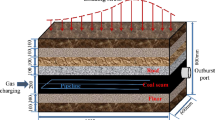
With a self-designed physical simulation test system for coal and gas outburst and instantaneous gas desorption of coal, orthogonal tests were designed and conducted to investigate the influences of initial gas pressure, coal particle size and outburst mouth diameter on coal and gas outburst firstly, then gas pressure variation tests were conducted under different initial gas pressures and coal quantities to investigate the variation characteristics of gas pressure. The results show that the influence of outburst mouth diameter on the intensity and duration time of coal and gas outburst was biggest followed by coal particle size and initial gas pressure. The total outburst time was shorter when outburst mouth diameter was bigger, meanwhile the outburst intensity and outburst distance were larger when initial gas pressure was higher, coal particle size was smaller or outburst mouth diameter was larger. In some gas pressure variation tests, the maximum instantaneous gas pressure exceeded the initial gas pressure when the latter was larger, which means the initial gas pressure play a crucial role in coal and gas outburst initiation. Finally, the critical initial gas pressure and gas content were calculated as a reference to predict coal and gas outburst danger.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado MBD, Nicieza CG (2007) Control and prevention of gas outbursts in coal mines Riosa–Olloniego coalfield, Spain. Int J Coal Geol 69:253–266
An FH, Cheng YP, Wang L, Li W (2013) A numerical model for outburst including the effect of adsorbed gas on coal deformation and mechanical properties. Comput Geotech 54(10):222–231
Beamish BB, Crosdale PJ (1998) Instantaneous outbursts in underground coal mines: an overview and association with coal type. Int J Coal Geol 35:27–55
Fisne A, Esen O (2014) Coal and gas outburst hazard in Zonguldak Coal Basin of Turkey and association with geological parameters. Nat Hazards 74:1363–1390
Geng J, Xu J, Wen N, Peng S, Zhang C, Luo X (2017) Regression analysis of major parameters affecting the intensity of coal and gas outbursts in laboratory. Int J Min Sci Technol 27(02):327–332
Jin K, Cheng YP, Ren T, Zhao W, Tu QY, Dong J, Wang ZY, Biao H (2018) Experimental investigation on the formation and transport mechanism of outburst coal–gas flow: implications for the role of gas desorption in the development stage of outburst. Int J Coal Geol 194:45–58
Lama R, Bodziony J (1998) Management of outburst in underground coal mines. Int J Coal Geol 35:83–115
Lama R, Saghafi A (2002) Overview of gas outbursts and unusual emissions. In: 3rd coal operators’ conference, Wollongong, University of Wollongong and the Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, pp 74–88
Peng S, Xu J, Yang H, Liu D (2012) Experimental study on the influence mechanism of gas seepage on coal and gas outburst disaster. Saf Sci 50(4):816–821
Shi X, Song D, Qian Z (2017) Classification of coal seam outburst hazards and evaluation of the importance of influencing factors. Open Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1515/geo-2017-0024
Skoczylas N (2012) Laboratory study of the phenomenon of methane and coal outburst. Int J Rock Mech Min 55(10):102–107
Sobczyk J (2011) The influence of sorption processes on gas stresses leading to the coal and gas outburst in the laboratory conditions. Fuel 90(3):1018–1023
Sobczyk J (2014) A comparison of the influence of adsorbed gases on gas stresses leading to coal and gas outburst. Fuel 115(2):288–294
State Administration of Work Safety (2016) Coal mine safety regulation. Coal Industry Press, Beijing
Vishal V, Ranjith PG, Singh TN (2015) An experimental investigation on behaviour of coal under fluid saturation, using acoustic emission. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 22:428–436
Wang L, Cheng Y, Liu H (2014) An analysis of fatal gas accidents in Chinese coal mines. Saf Sci 62:107–113
Xue S, Yuan L, Xie J, Wang Y (2014) Advances in gas content based on outburst control technology in Huainan, China. Int J Min Sci Technol 24:385–389
Zhi S, Elsworth D (2016) The role of gas desorption on gas outbursts in underground mining of coal. Geomech Geophys Geo Energy Geo Resour 2:151–171
Acknowledgements
The research described in this paper was financially supported by the China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 51109076) and the key scientific and technological project of Henan Province (Grant No. 152102210316).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, B., Li, Y., Jiao, F. et al. Experimental study on coal and gas outburst and the variation characteristics of gas pressure. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-energ. Geo-resour. 4, 355–368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0092-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-018-0092-8