Abstract
Introduction
Endometrial cancer usually has a good prognosis. The recurrence and survival in endometrial cancer are based on multiple prognostic factors like patient age, histological grade, myometrial invasion, and lymphovascular space invasion. We investigated various clinicopathological features determining tumor recurrence in stage I endometrial cancer with endometrioid histology.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed stage I endometrial cancer patients who underwent surgery at the Basavatarakam Indo American Cancer Hospital between 2010 and 2015. Patients who had tumor recurrence were documented. Various risk factors like size, grade, depth, lymphovascular involvement, etc., were studied, their relation with recurrence was noted, and statistical analysis was done.
Results
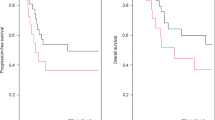
Twenty-three patients exhibited tumor recurrence in stage I EEC (13.3%). When considering the depth of myometrial invasion, the 5-year RFS of stage IA EEC is 90.4% in comparison with 66.6% when the depth of invasion is more than half of myometrial invasion. The 5-year RFS of the patients with stage I EEC is 100% in tumors with size less than 2 cms, 92.15% in tumor size 2–4 cms, and 70.45% when the tumor size is greater than 4 cms. The 5-year RFS of the patients is 94.7% in grade 1, 87.3% in grade 2, and 54.2% in grade 3.
Conclusion
Depth of myometrial invasion, grade, and size of the primary tumor are shown to affect recurrence. LUS involvement, intracervical glandular involvement, and the lymphovascular space invasion did not affect recurrence in endometrioid endometrial cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
www.icmr.nic.in (Consensus document for the management of uterine cancer).
Chan JK, Sherman AE, Kapp DS, et al. Influence of gynecologic oncologists on the survival of patients with endometrial cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:832–8.
Benedetti Panici P, Basile S, Salerno MG, et al. Secondary analyses from a randomized clinical trial: age as the key prognostic factor in endometrial carcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014;210(363):e361–3.
Doll KM, Tseng J, Denslow SA, et al. High-grade endometrial cancer: revisiting the impact of tumor size and location on outcomes. Gynecol Oncol. 2014;132:44.
Pecorelli S. Revised FIGO staging for carcinoma of the vulva, cervix, and endometrium. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2009;105:103–4.
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C, et al. Endometrial cancer. Lancet. 2016;387:1094–108.
Creutzberg CL, van Putten WL, Koper PC, et al. Surgery and postoperative radiotherapy versus surgery alone for patients with stage-1 endometrial carcinoma: multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355(9213):1404–11.
Zusterzeel PL, Bekkers RL, Hendriks JC, et al. Prognostic factors for recurrence in patients with FIGO stage I and II, intermediate or high risk endometrial cancer. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2008;87(2):240–6.
Canlorbe G, Bendifallah S, Laas E, et al. Tumor size, an additional prognostic factor to include in low-risk endometrial cancer: results of a French multicenter study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23:1717.
Mariani A, Webb MJ, Keeney GL, Haddock MG, Calori G, Podratz KC. Low-risk corpus cancer: is lymphadenectomy or radiotherapy necessary? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;182:1506–19.
Milam MR, Java J, Walker JL, Metzinger DS, Parker LP, Coleman RL, Gynecologic Oncology Group. Nodal metastasis risk in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;119:286–92.
Colombo N, Creutzberg C, Amant F, et al. ESMO-ESGO-ESTRO consensus conference on endometrial cancer: diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2016;26:2–30.
Zeimet AG, Reimer D, Huszar M, et al. L1CAM in early-stage type I endometrial cancer: results of a large multicenter evaluation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105(15):1142–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, V., Ramani, K., Raju, K. et al. Various Clinicopathological Factors Impacting Recurrence in Stage I Endometrial Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Indian J Gynecol Oncolog 17, 56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40944-019-0300-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40944-019-0300-7