Abstract
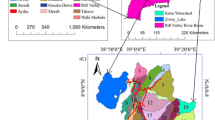
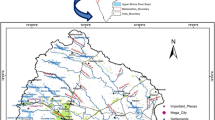
This study estimated the runoff potential of Manchar Lake (Pakistan) as having enormous economic, environmental, and strategic value. In the recent floods, the lake overflowed, inundating surrounding villages. Had the timings and quantum of the expected flows known, the government could have minimized the damages by diverting the water to the sea. A hydrologic model can provide such information, but Manchar is ungauged, and model calibration/validation is challenging without observed data. An upstream Gaj basin had daily stream flow records only for four months. However, these data were insufficient in an ideal condition and were the only model calibration/validation option. For runoff simulation, Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) was used. Land use/cover (Sentinel-2), soils (Food and Agriculture Organization), Digital Elevation Model (Advanced Land Observing Satellite), and hydro-meteorological information were model inputs. The Gaj basin model simulated well with coefficients of determination (R2 = 0.92/96), Nash–Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE = 0.82/0.85), root mean square error (RMSE = 159.4/98.9 ft3/s), RMSE-observation standard deviation ratio (RSR = 0.42/0.39), and percent bias (PBIAS = 8.01/31.75%) during calibration/validation periods. The calibrated parameters were then applied to the entire watershed using the regionalization concept of spatial proximity. The simulated runoff (mean annual volume) entering the lake from 2004 to 2020 was 1.662 ± 0.871 MAF per year and during the 2022 floods (June–September) was 4.28 MAF. This approach is helpful in water and land resource planning and managing ungauged catchments during dry periods and will significantly reduce flood damages through early warnings and timely flood management.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed/generated for the current research are available in the manuscript.
References
Acuña-Alonso C, Novo A, Rodríguez JL, Varandas S, Álvarez X (2022) Modelling and evaluation of land use changes through satellite images in a multifunctional catchment: social, economic and environmental implications. Ecol Inform 71:101777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2022.101777
Ahmad I, Wajid SA, Ahmad A, Cheema MJM, Judge J (2019) Optimizing irrigation and nitrogen requirements for maize through empirical modeling in semiarid environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:1227–1237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2772-x
Ahmed I, Ur Rahman MH, Ahmed S, Hussain J, Ullah A, Judge J (2018) Assessing the impact of climate variability on maize using simulation modeling under semiarid environment of Punjab. Pakistan Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:28413–28430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2884-3
Ali Z (2022) Sindh on its toes as Manchar Lake surges. The Express Tribune, 03 September, 2022. https://tribune.com.pk/story/2374633/sindh-on-its-toes-as-manchar-lake-surges.
Al-Mukhtar M, Al-Yaseen F (2019) Modeling water quality parameters using data-driven models, a case study Abu-Ziriq Marsh in South of Iraq. Hydrology. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology6010024
Ammari A, Bahmanpouri F, Khelfi MEA, Moramarco T (2022) The regionalizing of the entropy parameter over the north Algerian watersheds: a discharge measurement approach for ungauged river sites. Hydrol Sci J 67:1640–1655. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2022.2099744
Arain MB, Kazi TG, Jamali MK, Jalbani N, Afridi HI, Shah A (2008) Total dissolved and bioavailable elements in water and sediment samples and their accumulation in Oreochromis mossambicus of polluted Manchar Lake. Chemosphere 70:1845–1856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.08.005
ASCE (2017) Report of Task Group on Curve Number Hydrology. USA: SERVICE), A. A. S. O. A. A. B. E.-N. N. R. C. Accessed 2017.
Ayangbenro AS, Babalola OO (2021) Reclamation of arid and semiarid soils: the role of plant growth-promoting archaea and bacteria. Curr Plant Biol 25:100173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpb.2020.100173
Bitew GT, Mulugeta AB, Miegel K (2019) Application of HEC-HMS Model for Flow Simulation in the Lake Tana Basin: the Case of Gilgel Abay Catchment, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Hydrology
Borel K, Swaminathan V, Vance C, Roberts G, Srinivasan R, Karthikeyan R (2017) Modeling the dispersion of E. coli in waterbodies due to urban sources: a spatial approach. Water 9:665. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090665
Bunganaen W, Frans JH, Seran YA, Legono D, Krisnayanti DS (2021) Rainfall-runoff simulation using HEC-HMS model in the Benanain Watershed, Timor Island. J Civ Eng Forum 7:359
Chaaban F, El Khattabi J, Darwishe H (2022) Accuracy assessment of ESA WorldCover 2020 and ESRI 2020 land cover maps for a Region in Syria. J Geovisualiz Spatial Anal 6:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41651-022-00126-w
Chakraborty S, Biswas S (2021) Simulation of flow at an ungauged river site based on HEC-HMS model for a mountainous river basin. Arab J Geosci 14:2080. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-08385-5
Cheng X, Ma X, Wang W, Xiao Y, Wang Q, Liu X (2021) Application of HEC-HMS parameter regionalization in small watershed of hilly area. Water Resour Manage 35:1961–1976
Cydzik K, Hogue TS (2009) Modeling postfire response and recovery using the hydrologic engineering center hydrologic modeling system (HEC-HMS) 1. JAWRA J Am Water Resour Assoc 45:702–714
Drisya J, Sathish Kumar D (2023) Evaluation of the drought management measures in a semiarid agricultural watershed. Environ Dev Sustain 25:811–833. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02079-4
Fanta SS, Sime CH (2021) Performance assessment of SWAT and HEC-HMS model for runoff simulation of Toba watershed, Ethiopia. Sustain Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-021-00596-8
Fanta SS, Sime CH (2022) Performance assessment of SWAT and HEC-HMS model for runoff simulation of Toba watershed, Ethiopia. Sustain Water Resour Manag 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-021-00596-8
FAO (1977) Guidelines for soil profile description. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome
FAO/UNESCO (1974) Soil Map of the World [Online]. Paris. Available: http://www.fao.org/soils-portal/data-hub/soil-maps-and-databases/faounesco-soil-map-of-the-world/en/. Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Ford D, Pingel N, DeVries J (2002) Hydrologic modeling system HEC-HMS: applications guide, US Army Corps of Engineers, Hydrologic Engineering Center
Fragoso-Campón L, Durán-Barroso P, Quirós E (2022) Analysing the capability of a catchment’s spectral signature to regionalize hydrological parameters. Hydrol Process 36:e14673. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.14673
Giraldez JV (2010) Sergio E. Serrano: hydrology for engineers, geologists, and environmental professionals. HydroScience Ambler, Pennsylvania
Gonzalez A, Temimi M, Khanbilvardi R (2015) Adjustment to the curve number (NRCS-CN) to account for the vegetation effect on hydrological processes. Hydrol Sci J 60:591–605. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2014.898119
Grimaldi S, Volpi E, Langousis A, Papalexiou SM, De Luca DL, Piscopia R, Nerantzaki SD, Papacharalampous G, Petroselli A (2022) Continuous hydrologic modelling for small and ungauged basins: a comparison of eight rainfall models for sub-daily runoff simulations. J Hydrol 610:127866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127866
Guduru JU, Jilo NB, Rabba ZA, Namara WG (2023) Rainfall-runoff modeling using HEC-HMS model for Meki River watershed, rift valley basin, Ethiopia. J Afr Earth Sci 197:104743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2022.104743
Gumindoga W, Rwasoka DT, Nhapi I, Dube T (2017) Ungauged runoff simulation in Upper Manyame Catchment, Zimbabwe: application of the HEC-HMS model. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 100:371–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2016.05.002
Harlow J, Hagedorn B (2019) SWB modeling of groundwater recharge on Catalina Island, California, during a period of severe drought. Water 11:58. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11010058
Hasan MA, Pradhanang SM (2017) Estimation of flow regime for a spatially varied Himalayan watershed using improved multi-site calibration of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) model. Environ Earth Sci 76:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7134-3
Ibrahim-Bathis K, Ahmed SA (2016) Rainfall-runoff modelling of Doddahalla watershed—an application of HEC-HMS and SCN-CN in ungauged agricultural watershed. Arab J Geosci 9:170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2228-2
Imran U, Mahar RB, Ullah A, Shaikh K (2021) Seasonal variability of heavy metals in manchar lake of arid southern pakistan and its consequential human health risk. Polish J Environ Stud 30:163. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/120363
Imran U, Ullah A, Mahar RB, Shaikh K (2022) Distribution, Source Identification, and Ecological Risk Assessment of Selected Trace Elements in Sediments from Manchar Lake, Pakistan. Soil Sediment Contaminat Int J. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2022.2122929
Jahangir TM, Khuhawar MY, Leghari SM, Mahar MT, Mahar KP (2015) Water quality and sediment assessment of Manchar Lake, Sindh, Pakistan: after effects of the super flood of 2010. Arab J Geosci 8:3259–3283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1395-x
Jaiswal R, Ali S, Bharti B (2020) Comparative evaluation of conceptual and physical rainfall–runoff models. Appl Water Sci 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-1122-6
Jiang R (2001) Investigation of Runoff Curve Number Initial Abstraction Ratio
Kabiri R, Ramani Bai V, Chan A (2014) Assessment of hydrologic impacts of climate change on the runoff trend in Klang Watershed, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 73:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3392-5
Kazi TG, Arain MB, Jamali MK, Jalbani N, Afridi HI, Sarfraz RA, Baig JA, Shah AQ (2009) Assessment of water quality of polluted lake using multivariate statistical techniques: a case study. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:301–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.02.024
Kokab RU, Nawaz A (2013) Indus water treaty: need for review. Asian Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities 2: 210–218, http://www.ajssh.leena-luna.co.jp/AJSSHPDFs/Vol.2(2)/AJSSH2013(2.2-23).pdf
Kumar A, Kanga S, Taloor AK, Singh SK, Đurin B (2021) Surface runoff estimation of Sind river basin using integrated SCS-CN and GIS techniques. HydroResearch 4:61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2021.08.001
Li C-Z, Wang H, Liu J, Yan D-H, Yu F-L, Zhang L (2010) Effect of calibration data series length on performance and optimal parameters of hydrological model. Water Science and Engineering 3:378–393. https://doi.org/10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.04.002
Liu W, Feng Q, Wang R, Chen W (2021) Effects of initial abstraction ratios in SCS-CN method on runoff prediction of green roofs in a semiarid region. Urban for Urban Green 65:127331
Liu T, Wang Y, Yu H, Chen Y (2022) Using statistical functions and hydro-hydraulic models to develop human vulnerability curves for flash floods: the flash flood of the Taitou catchment (China) in 2016. Int J Disaster Risk Reduction. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.102876
Mahmood R, Jia S (2019) Assessment of hydro-climatic trends and causes of dramatically declining stream flow to Lake Chad, Africa, using a hydrological approach. Sci Total Environ 675:122–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.219
Meresa H (2018) Modelling of river flow in ungauged catchment using remote sensing data: application of the empirical (SCS-CN), Artificial Neural Network (ANN) and Hydrological Model (HEC-HMS). Model Earth Syst Environ 5:257–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0532-z
Moghaddasi M, Anvari S, Akhondi NJT, Climatology A (2022) A Trade-off Analysis of Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Future Optimized Rule Curves Based on Simulation Algorithm and Hedging Rules 148:65–78
Mohammadinezhad S, Ahmadvand M (2020) Modeling the internal processes of farmers’ water conflicts in arid and semiarid regions: extending the theory of planned behavior. J Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124241
Monheit AC (2011) Running on empty. INQUIRY J Health Care Organization Provision Financ 48:177–182
Nagaveni C, Kumar KP, Ravibabu MV (2019) Evaluation of TanDEMx and SRTM DEM on watershed simulated runoff estimation. J Earth Syst Sci 128:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-018-1035-z
Naheed G, Mahmood A (2009) Water requirement of wheat crop in Pakistan. Pakistan J Meteorol 6:89–97
Natarajan S, Radhakrishnan N (2020) An integrated hydrologic and hydraulic flood modeling study for a medium-sized ungauged urban catchment area: a case study of Tiruchirappalli City using HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS. J Inst Eng (india) Ser A 101:381–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00427-2
Ndeketeya A, Dundu M (2021) Application of HEC-HMS Model for Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting Potential in a Semiarid City. Water Resour Manage 35:4217–4232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-02941-0
Niyazi BA, Masoud MH, Ahmed M, Basahi JM, Rashed MA (2020) Runoff assessment and modeling in arid regions by integration of watershed and hydrologic models with GIS techniques. J African Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103966
NRCS A-A (2017) Published. Report of Task Group on Curve Number Hydrology, Chapters 8 (Land Use and Land Treatment Classes), 9 (Hydrologic Soil Cover Complexes), 10 (Estimation of Direct Runoff from Storm Rainfall), 12 (Hydrologic Effects of Land Use and Treatment). ASCE Reston, VA, USA
Odusanya AE, Schulz K, Mehdi-Schulz B (2022) Using a regionalisation approach to evaluate streamflow simulated by an ecohydrological model calibrated with global land surface evaporation from remote sensing. J Hydrol Region Stud 40:101042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101042
Palacios-Cabrera T, Valdes-Abellan J, Jodar-Abellan A, Rodrigo-Comino J (2022) Land-use changes and precipitation cycles to understand hydrodynamic responses in semiarid Mediterranean karstic watersheds. Sci Total Environ 819:153182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153182
Pandey A, Sahu A (2009) Generation of Curve Number Using Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System [Online]. Geospatial World. https://www.geospatialworld.net/article/generation-of-curve-number-using-remote-sensing-and-geographic-information-system/. Accessed 09 Jan 2009.
Ramly S, Tahir W (2016) Published. Application of HEC-GeoHMS and HEC-HMS as rainfall–runoff model for flood simulation. In: ISFRAM 2015: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Flood Research and Management 2015. Singapore. Springer, 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0500-8_15
Reig E, Boucher M-A, Tremblay É (2020) Ensemble hydrological forecasts for reservoir management of the Shipshaw River catchment using limited data. Can Water Resour J Revue Canadienne Des Ressources Hydriques 45:372–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/07011784.2020.1834880
Sahu MK, Shwetha HR, Dwarakish GS (2023) State-of-the-art hydrological models and application of the HEC-HMS model: a review. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-023-01704-7
Sime CH, Demissie TA, Tufa FG (2020) Surface runoff modeling in Ketar watershed, Ethiopia. J Sedimentary Environ 5:151–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43217-020-00009-4
Yoo C, Na W, Cho E, Chang K-H, Yum SS, Jung W (2022) Evaluation of cloud seeding on the securement of additional water resources in the Boryeong Dam Basin, Korea. J Hydrol 613:128480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128480
Zhu Y, Liu L, Qin F, Zhou L, Zhang X, Chen T, Li X, Ao T (2021) Application of the regression-augmented regionalization approach for BTOP model in Ungauged basins. Water 13:2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13162294
Acknowledgements
The US–Pakistan Center for Advanced Studies in Water (USPCAS-W), Mehran University of Engineering and Technology (MUET) Jamshoro, Sindh, Pakistan, is acknowledged for providing laboratory facilities (licensed software) for conducting this study. Dr. Rick Bereit, the English Writing Centre instructor at the United States Air Force Academy, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, contributed editing and language verification while preparing the final version of this article.
Funding
This research was funded by USPCAS-W, supported by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
UI contributed to conceptualization, methodology, GIS and HEC-HMS modeling, and writing—original draft. AU helped in writing and supervision. AZ contributed to writing and supervision. RBM helped in supervision. WAK contributed to writing, GIS and HEC-HMS modeling. BN contributed to GIS and remote sensing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent to publish
Authors allow publication if the research is accepted.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, U., Zaidi, A.Z., Ullah, A. et al. Surface runoff water potential in the ungauged multi-basin Manchar Lake of Pakistan. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 9, 180 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00959-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00959-3