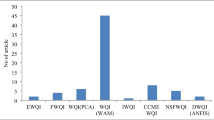
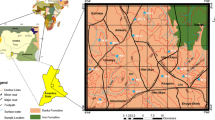
Abstract
Uncontrolled development and industrial progression exacerbate surface water quality, posing a risk of water-borne diseases. To assess the suitability of the water for potable use, the water quality index (WQI) has proven an effective approach. Numerous WQIs are being applied in practice; however, there is no universally accepted method that is flexible enough to assess drinking water quality for all regions around the world. To assess the water quality and validate the applicability of the proposed method, an extensive water quality survey was conducted across the Jaipur municipality, Rajasthan, India, and multiple physico-chemical parameters were analysed. The current study proposes a novel ‘Weight Integrated Health-Hazard Index’ approach to classifying water samples based on their potential risks to human health. Simultaneously, the study employs a ‘fuzzy derived index’ WQI to classify water samples based on their contaminant levels. Finally, both WQIs are utilized to classify the collected samples, and the results are integrated using a Geographical Information System (GIS) environment providing citywide visualizations. The findings reveal that more than half of the city receives ‘poor’ quality water directly associated with ‘medium’ or ‘high’ health risk levels. The proposed methodology is highly adaptable and useful for identifying priority areas within any region. It can also serve as a benchmark for similar studies in the future.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
References
Abtahi M, Golchinpour N, Yaghmaeian K, Rafiee M, Jahangiri-Rad M, Keyani A, Saeedi R (2015) A modified drinking water quality index (DWQI) for assessing drinking source water quality in rural communities of Khuzestan Province Iran. Ecol Indic 53:283–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLIND.2015.02.009
Achary MS, Panigrahi S, Satpathy KK, Prabhu RK, Panigrahy RC (2016) Health risk assessment and seasonal distribution of dissolved trace metals in surface waters of Kalpakkam, southwest coast of Bay of Bengal. Reg Stud Marine Sci 6:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSMA.2016.03.017
Adimalla N, Qian H (2019) Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, south India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 176:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2019.03.066
Asgari G, Komijani E, Seid-Mohammadi A, Khazaei M (2021) Assessment the quality of bottled drinking water through mamdani fuzzy water quality index. Water Resour Manag 35(15):5431–5452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-021-03013-z
Avvannavar SM, Shrihari S (2007) Evaluation of water quality index for drinking purposes for river Netravathi Mangalore South India. Environ Monit Assess 143(1):279–290. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-007-9977-7
Balasopoulou A, Κokkinos P, Pagoulatos D, Plotas P, Makri OE, Georgakopoulos CD, Vantarakis A, Li Y, Liu JJ, Qi P, Rapoport Y, Wayman LL, Chomsky AS, Joshi RS, Press D, Rung L, Ademola-popoola D, Africa S, Article O, Loukovaara S (2017) Symposium Recent advances and challenges in the management of retinoblastoma Globe - saving treatments. BMC Ophthalmol 17(1):1. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijo.IJO
Banerjee T, Srivastava RK (2009) Application of water quality index for assessment of surface water quality surrounding integrated industrial estate-Pantnagar. Water Sci Technol 60(8):2041–2053. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2009.537
Bertinato J, Xiao CW, Ratnayake WMN, Fernandez L, Lavergne C, Wood C, Swist E (2015) Lower serum magnesium concentration is associated with diabetes, insulin resistance, and obesity in South Asian and white Canadian women but not men. SNF Swed Nutr Found. https://doi.org/10.3402/FNR.V59.25974
Cabral Pinto MMS, Ordens CM, Condesso de Melo MT, Inácio M, Almeida A, Pinto E, Ferreira da Silva EA (2020) An inter-disciplinary approach to evaluate human health risks due to long-term exposure to contaminated groundwater near a chemical complex. Exposure Health 12(2):199–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12403-019-00305-Z/FIGURES/6
Campisano A, Butler D, Ward S, Burns MJ, Friedler E, DeBusk K, Fisher-Jeffes LN, Ghisi E, Rahman A, Furumai H, Han M (2017) Urban rainwater harvesting systems: Research, implementation and future perspectives. Water Res 115:195–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2017.02.056
Chau KW (2006) A review on integration of artificial intelligence into water quality modelling. Mar Pollut Bull 52(7):726–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARPOLBUL.2006.04.003
Dadhich PN, Hanaoka S (2011) Spatio-temporal Urban Growth Modeling of Jaipur, India. J Urabn Technol 18(3):45–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10630732.2011.615567
Dietrich AM, Glindemann D, Pizarro F, Gidi V, Olivares M, Araya M, Camper A, Duncan S, Dwyer S, Whelton AJ, Younos T, Subramanian S, Burlingame GA, Khiari D, Edwards M (2004) Health and aesthetic impacts of copper corrosion on drinking water. Water Sci Technol 49(2):55–62. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2004.0087
Eggers MJ, Doyle JT, Lefthand MJ, Young SL, Moore-Nall AL, Kindness L, Medicine RO, Ford TE, Dietrich E, Parker AE, Hoover JH, Camper AK (2018) Community engaged cumulative risk assessment of exposure to inorganic well water contaminants crow reservation Montana. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(1):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH15010076
Environmental Protection Agency 40 CFR Parts 141 and 142 National Primary Drinking Water Regulations for Lead and Copper: Short-Term Regulatory Revisions and Clarifications (2022) www.regulations.gov. Retrieved July 20, 2022
FAO Map Catalog (2022) https://data.apps.fao.org/map/catalog/srv/eng/catalog.search?id=14116#/metadata/446ed430-8383-11db-b9b2-000d939bc5d8. Retrieved 04 May 2022
Fazal-ur-Rehman SA (2018) Hardness in drinking-water, its sources, its effects on humans and its household treatment. J Chem Appl 4(1):01–04. https://doi.org/10.13188/2380-5021.1000009
Gharibi H, Sowlat MH, Mahvi AH, Mahmoudzadeh H, Arabalibeik H, Keshavarz M, Karimzadeh N, Hassani G (2012a) Development of a dairy cattle drinking water quality index (DCWQI) based on fuzzy inference systems. Ecol Ind 20:228–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLIND.2012.02.015
Gharibi H, Mahvi AH, Nabizadeh R, Arabalibeik H, Yunesian M, Sowlat MH (2012b) A novel approach in water quality assessment based on fuzzy logic. J Environ Manag 112:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2012.07.007
Ghosh D, Medhi CR, Purkait MK (2010) Treatment of drinking water containing iron using electrocoagulation. Int J Environ Eng 2(1/2/3):212. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEE.2010.029829
Haiyan W (2002) Assessment and prediction of overall environmental quality of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province China. J Environ Manag 66(3):329–340. https://doi.org/10.1006/JEMA.2002.0590
Handbook of Water Analysis (2000) Taylor & Francis, USA
Hoque A, Panda BK, Ali H (2018) Study of chloride level in drinking water at Malda district of West Bengal and its impact on human health. Asian J Res Chem 11(2):329. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-4150.2018.00060.3
Hu G, Kaur M, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2019) Fuzzy clustering analysis of hydraulic fracturing additives for environmental and human health risk mitigation. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21(1):39–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10098-018-1614-3/FIGURES/8
Hu G, Mian HR, Abedin Z, Li J, Hewage K, Sadiq R (2022) Integrated probabilistic-fuzzy synthetic evaluation of drinking water quality in rural and remote communities. J Environ Manag 301:113937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113937
Human Health Evaluation Manual (1989) Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: pt. A. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, USA
Icaga Y (2007) Fuzzy evaluation of water quality classification. Ecol Ind 7(3):710–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLIND.2006.08.002
Jandu A, Malik A, Dhull SB (2021) Fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of rural habitations of semiarid region of northern Rajasthan, India: a hydrogeochemical, multivariate statistical, and human health risk assessment perspective. Environ Geochem Health 43(10):3997–4026. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10653-021-00882-6/FIGURES/10
Jang JSR, Sun CT (1995) Neuro-Fuzzy Modeling and Control. Proc IEEE 83(3):378–406. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.364486
Javed M, Usmani N (2016) Accumulation of heavy metals and human health risk assessment via the consumption of freshwater fish Mastacembelus armatus inhabiting, thermal power plant effluent loaded canal. Springerplus 5(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2471-3
Jinturkar AM, Deshmukh SS, Agarkar SV, Chavhan GR (2010) Determination of water quality index by fuzzy logic approach: a case of ground water in an Indian town. Water Sci Technol 61(8):1987–1994. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2010.095
Kar S, Gupta R (2022) Fluoride toxicity in Rajasthan, India: water filter distribution, monitoring and user perception. Water Conserv Sci Eng 7(4): 561–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-022-00163-y
Kar S, Gupta R (2023) Fluoride toxicity in Rajasthan, India: human health risk assessment, low-cost water filter preparation, and contaminant remediation. Water Conserv Sci Eng 8(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41101-023-00175-2
Karmakar S, Mujumdar PP (2006) Grey fuzzy optimization model for water quality management of a river system. Adv Water Resour 29(7):1088–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ADVWATRES.2006.04.003
Karr CL, Gentry EJ (1993) Fuzzy Control of Ph Using Genetic Algorithms. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 1(1):46–53. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.1993.390283
Keesari T, Goyal MK, Gupta B, Kumar N, Roy A, Sinha UK, Surampalli RY, Zhang TC, Goyal RK (2021) Big data and environmental sustainability based integrated framework for isotope hydrology applications in India. Environ Technol Innov 24:101889. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ETI.2021.101889
Khandare AL, Validandi V, Rajendran A, Singh TG, Thingnganing L, Kurella S, Nagaraju R, Dheeravath S, Vaddi N, Kommu S, Maddela Y (2020) Health risk assessment of heavy metals and strontium in groundwater used for drinking and cooking in 58 villages of Prakasam district, Andhra Pradesh India. Environ Geochem Health 42(11):3675–3701. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10653-020-00596-1/TABLES/10
Kumar Tatawat R, Singh Chandel CP (2007) A hydrochemical profile for assessing the groundwater quality of Jaipur city. Environ Monit Asses. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9936-3
Kumari M, Tripathi S, Pathak V, Tripathi BD (2013) Chemometric characterization of river water quality. Environ Monit Assess 185(4):3081–3092. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10661-012-2774-Y/FIGURES/4
Le T, Hassan F, Le C, Jeong HD (2019) Understanding dynamic data interaction between civil integrated management technologies: a review of use cases and enabling techniques. Int J Constr Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/15623599.2019.1678863
Li P, Tian R, Xue C, Wu J (2017) Progress, opportunities, and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13224–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-017-8753-7/FIGURES/1
Matinpoor B (2018) Development and application of a potentiometric hg2+- imprinted polymer/graphitic carbon nitride/carbon paste electrode. J Nuts 9(2):92–100
Meenakshi C, Maheshwari RC (2006) Fluoride in drinking water and its removal. J Hazard Mater 137(1):456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2006.02.024
Nabizadeh R, Mahvi AH, Khazaei M, Zamanzadeh M, Yari AR, Jafari A (2018) A fuzzy multi-criteria decision making approach for evaluating the health-care waste treatment alternatives. Environ Eng Manag J 17(12):2795–2805. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2018.279
Nayak JG, Patil LG, Patki VK (2020) Development of water quality index for Godavari River (India) based on fuzzy inference system. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100350. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GSD.2020.100350
Nelson C, Lurie N, Wasserman J, Zakowski S (2007) Conceptualizing and defining public health emergency preparedness. Am J Public Health 97(Suppl):1. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.114496
Ocampo-Duque W, Osorio C, Piamba C, Schuhmacher M, Domingo JL (2013) Water quality analysis in rivers with non-parametric probability distributions and fuzzy inference systems: application to the Cauca River, Colombia. Environ Int 52:17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVINT.2012.11.007
Onkal-Engin G, Demir I, Hiz H (2004) Assessment of urban air quality in Istanbul using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. Atmos Environ 38(23):3809–3815. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ATMOSENV.2004.03.058
Patil D, Kumar G, Kumar A, Gupta R (2022) A systematic basin-wide approach for locating and assessing volumetric potential of rainwater harvesting sites in the urban area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23039-z
Patki VK, Shrihari S, Manu B, Deka PC (2015) Fuzzy system modeling for forecasting water quality index in municipal distribution system. Urban Water J 12(2):89–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2013.820333
Rahman MA, Hashem MA (2019) Arsenic, Iron and chloride in drinking water at primary school, Satkhira, Bangladesh. Phys Chem Earth Parts a/b/c 109:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PCE.2018.09.008
Rapant S, Cvečková V, Hiller E, Jurkovičová D, Kožíšek F, Stehlíková B (2020) Proposal of new health risk assessment method for deficient essential elements in drinking water—case study of the Slovak Republic. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(16):5915. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH17165915
Razmkhah H, Abrishamchi A, Torkian A (2010) Evaluation of spatial and temporal variation in water quality by pattern recognition techniques: a case study on Jajrood River (Tehran, Iran). J Environ Manag 91(4):852–860. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2009.11.001
Rezaei A, Hassani H, Hayati M, Jabbari N, Barzegar R (2018) Risk assessment and ranking of heavy metals concentration in Iran’s Rayen groundwater basin using linear assignment method. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 32(5):1317–1336. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00477-017-1477-X/TABLES/13
Rezaei A, Hassani H, Hassani S, Jabbari N, Fard Mousavi SB, Rezaei S (2019) Evaluation of groundwater quality and heavy metal pollution indices in Bazman basin southeastern Iran. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100245. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GSD.2019.100245
Rezaei A, Hassani H, Tziritis E, Fard Mousavi SB, Jabbari N (2020) Hydrochemical characterization and evaluation of groundwater quality in Dalgan basin SE Iran. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100353. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GSD.2020.100353
Robinson DT, Schertenleib A, Kunwar BM, Shrestha R, Bhatta M, Marks SJ (2018) Assessing the impact of a risk-based intervention on piped water quality in rural communities: the case of mid-western Nepal. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:1616. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH15081616
Ross TJ (2005) Fuzzy logic with engineering applications. Wiley
Sachdev V, Tillotson GHR, Sachdev G, Tillotson V (2002) Building Jaipur: the Making of an Indian City. Reaktion, UK
Sharma S, Chhipa RC (2013) Interpretation of ground water quality parameter for selected area of Jaipur using regression and correlation analysis. J Sci Ind Res 72:781–783
Shen G, Lu Y, Wang M, Sun Y (2005) Status and fuzzy comprehensive assessment of combined heavy metal and organo-chlorine pesticide pollution in the Taihu Lake region of China. J Environ Manag 76(4):355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2005.02.011
Soleimani H, Nasri O, Ojaghi B, Pasalari H, Hosseini M, Hashemzadeh B, Kavosi A, Masoumi S, Radfard M, Adibzadeh A, Feizabadi GK (2018) Data on drinking water quality using water quality index (WQI) and assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes in Qorveh & Dehgolan, Kurdistan. Iran Data Brief 20:375–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DIB.2018.08.022
Tsakiris V, Alexakis D, Tsihrintzis VA (2017) Assessing the quality of bottled water brands using a new water quality index. Eur Water 58:331–335
Turksen IB (1991) Measurement of membership functions and their acquisition. Fuzzy Sets Syst 40(1):5–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(91)90045-R
Tyagi S, Rawtani D, Khatri N, Tharmavaram M (2018) Strategies for nitrate removal from aqueous environment using nanotechnology: a review. J Water Process Eng 21:84–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JWPE.2017.12.005
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency) (1997) Exposure factors handbook. EPA/600/P-95/002Fa-c. USEPA, Cham
Vyas V, Singh AP, Srivastava A (2019) A decision making framework for condition evaluation of airfield pavements using non-destructive testing. Airfield Highw Pavements. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784482476.034
Wilkinson CF, Christoph GR, Julien E, Kelley JM, Kronenberg J, McCarthy J, Reiss R (2000) Assessing the risks of exposures to multiple chemicals with a common mechanism of toxicity: how to cumulate? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 31(1):30–43. https://doi.org/10.1006/rtph.1999.1361
Zadeh LA (1996) Fuzzy sets. World Scientific, pp 394–432. https://doi.org/10.1142/9789814261302_0021
Zadeh LA, Klir GJ, Yuan B (1996) Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy systems. World Sci. https://doi.org/10.1142/2895
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for providing the financial assistance under the project vide grant.
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Department of Science & Technology, New Delhi, for providing financial assistance under the project vide under Grant No. DST/TMD/EWO/WTI/2K19/UWS-04(C1) titled Structured Dialogues for Sustainable Urban Water Management (SDSUWM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DP: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing original draft, and Paper administration; SK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Article writing, Review and editing; VS: Review and editing; RG: Conceptualization, Guidance, Supervision, and Motivation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, D., Kar, S., Shastri, V. et al. Qualitative and health risk assessment of water using a novel weight-integrated health hazard and fuzzy-derived indices. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 9, 55 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00832-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-023-00832-3